How Many Countries Are There In The Middle East Today: Facts, Figures and Population
 How Many Countries Are There In Oceania: Facts, Figures and Population How Many Countries Are There In Oceania: Facts, Figures and Population |
 How Many Countries Are There in Africa Today: Facts, Figures and Population How Many Countries Are There in Africa Today: Facts, Figures and Population |
 |
| The Middle East Map. Photo: Pinterest |
| Contents |
The Middle East, which stretches from the Israeli coasts to Saudi Arabia's vast deserts, is full of fascinating topographies and cutting-edge urban centers. In this region, one can see incredible cultural legacies from various nations that date back to the dawn of time.
Middle East: Quick Facts
♦ Middle East consists of 18 nations. These include Yemen, Bahrain, Cyprus, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the Syrian Arab Republic, the United Arab Emirates, and the Persian Gulf state of Syria.
♦ The term "Greater Middle East"—which includes Afghanistan, the Comoros, Djibouti, the Maghreb, Pakistan, Sudan, and Somalia—is occasionally added to the definition of the Middle East.
♦ The Middle East is made up of nations that are similar in terms of ethnic groups, geographical characteristics, religious convictions, and political history.
Why Is It Called The Middle East?
The term "Middle East" was coined by Europeans who also referred to Eastern Asia as "the Far East." The transcontinental region between Western Asia and Egypt is referred to as the Middle East. It has 17 member countries and an estimated 371 million people. The biggest cities in the region include Cairo, Istanbul, and Riyadh.
Background Middle East
The British India Office is credited with coining the term "Middle East" in the 1850s. In 1902, American naval strategist Alfred Thayer Mahan used the phrase to describe the area between Arabia and India. The region surrounding the Persian Gulf was considered to be the Middle East by Mahan. This definition was expanded by Sir Ignatius Valentine Chirol to include the Asian nations whose borders reached into India.
The eastern Mediterranean shores as well as the regions centered around Turkey were included in the "Near East" prior to World War II. The British used the term "Middle East" when naming its command in Egypt in the late 1930s. The phrase started to be used frequently in the West after this instance. The Middle East Institute opened its doors in Washington, D.C., the nation's capital, in 1946.
Geographic Location of Middle East
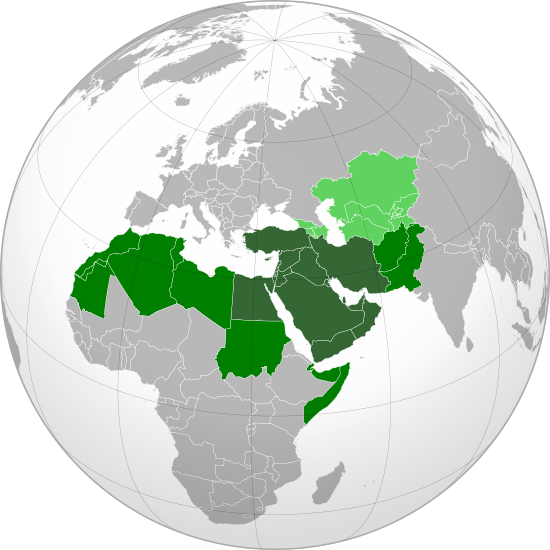 |
| Photo: Wikipedia |
Geographically, the Middle East includes parts of Western Asia and North Africa. This region has a very rich history, culture, and religious traditions. If the Greater Middle East is not included in the definition of the Middle East, there are 18 nations that make up this region: Yemen, Israel, Egypt, Iran, West Bank, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Iraq, the Gaza Strip (technically a territory), Cyprus, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
The first section of this article will examine capitals, and the second section will apply the same pattern to nations.
This overview of the Middle East includes basic information about the countries' populations, areas, and other stats. It is perfect for basic fact-finding for a research project or to use for stats when studying for an exam.
What Makes Middle East?The region's nations have a number of characteristics in common, as was already mentioned. For instance, Arabs are the dominant ethnic group in the Middle East. The next two common ethnic groups are those who speak Iranian and Turkic. The predominant religion in the area is Islam. In actuality, the region is where Christianity, Judaism, and Islam all originated. Arabic is the most common language used here, as one might expect. Persian, Kurdish, Hebrew, and Turkish are some additional widely-spoken languages. |
History Of The Region
In the Middle Ages, the region now referred to as the Middle East was referred to as the Near East. As the location of some of the oldest human developments, it is often referred to as the birthplace of civilization. Mesopotamia, ancient Egypt, the Hittite, Greek, Levant, Persia, and the Arabian Peninsula are a few examples of such civilizations. The Neo-Assyrian, Achaemenid, Macedonian, Iranian, Roman, and Byzantine empires were followed by others that ruled the ancient Near East.
In the seventh century, the Islamic Caliphate began the Arab conquest of the region. After the First World War, the British overthrew the Ottoman Empire, which had gained control of the area. After implementing their partition, the French and the British divided power in the Middle East, establishing some of the modern-day geographic boundaries in the process. Middle Eastern countries had achieved independence by the late 1960s and were looking for a place in the world. The presence of oil reserves has helped the area grow economically.
Why was the Middle East Important to the British?Because it served as a buffer zone in the defense of British interests in India during this time in history, the Middle Eastern region was particularly significant to the British. When the terms were first introduced, they made sense and were useful for identifying places in relation to Europe. After being used in an article by American naval officer and historian Alfred Thayer Mahan to describe the region between Arabia and India in 1902, the term "Middle East" eventually gained widespread usage. The term "Middle East" became well-established after the Ottoman Empire fell as a result of World War I and other geopolitical events, and it is now frequently used by people both inside and outside the region. Many contend that the term should be replaced with one that is more appropriate because it is Eurocentric and only applies from a Western perspective. For instance, Jerwaharlal Nehru, the first Prime Minister of India, argued that the phrase ought to be changed to "West Asia." His idea is still backed by many academics and is widely accepted. Because it is unavoidably a Western term that reflects a Western viewpoint, "Middle East" is problematic. |
Ethnicity, Language, And Religion
Arabs make up the majority of the region's population, with Turkic, Arameans, Persians, Kurds, Berbers, Shabaks, Zazas, Assyrians, and Samaritans making up the remainder.
The Middle East is home to many Arabic-speaking people who speak a variety of dialects. The majority of the states in the region have literary Arabic as their official language. Persian, Turkish, Hebrew, Kurdish, Armenian, Greek, and English are additional languages that are spoken. The Middle East is the origin of many of the major world religions, such as Islam, Christianity, and Judaism. Even today, there are still many followers of these religions in the Middle East. Yazidism, the Bahá' Faith, Shabakism, and Mandaeism are among the other religions practiced in the region.
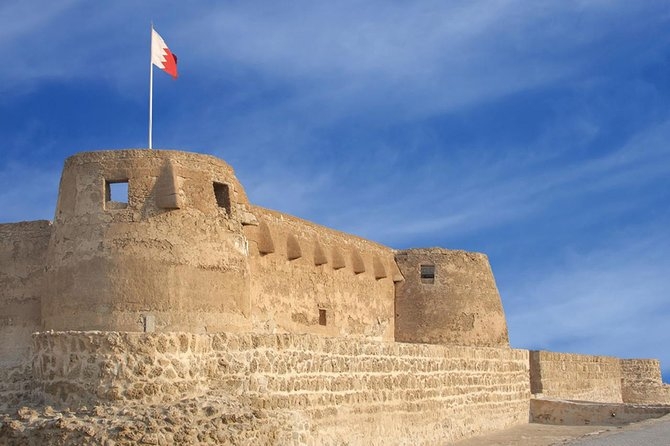
What are the safest countries in the Middle East?
 |
| Photo: Viator |
The media and tourism industries in the West frequently sloppily label travel to the Middle East as "dangerous." This is primarily a result of the conditions present in Yemen, Afghanistan, and Iraq. The majority of the Middle East is safe for travel, though.
Particularly, Oman and Jordan are extremely safe. As are the UAE, Egypt, Lebanon, Qatar, Bahrain, and Israel.
Despite this, travel for single women or members of the LGBTQ community is difficult outside of the more developed Israel and Jordan due to the staunch outdated religious beliefs of much of the region.
What makes Bahrain safe?
Bahrain has a low overall crime rate, and violent crime is incredibly uncommon. However, it's crucial to maintain some level of caution because petty crimes like theft and burglary are more frequent.
Politically motivated protests and demonstrations are known to take place here, but they typically concentrate in a small number of locations and are usually accompanied by a visible security presence.
30 Interesting Facts about Middle EastStudents in HIST 3354 Modern Middle East created a list of information about the Middle East that was disseminated throughout campus in an effort to raise awareness of Middle Eastern history and culture and to create a more welcoming environment for ISU's international students from the region. The Idaho State Journal published an early article about the project. Here are a few of the statistics they gathered. In addition to showcasing student knowledge, the project demonstrated how students applied that knowledge to participate in community-wide debates about Middle Eastern students enrolled at the university. * A variety of countries make up the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), including Algeria, Bahrain, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Tunisia, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. * Widely spoken languages in the Middle East and North Africa include Arabic, Persian, Turkish, Berber, Kurdish, French, and English. * The Middle East has been referred to as ?the crossroads of the world? because it connects the three continents of Asia, Africa, and Europe. * The majority of Muslims do not live in the Middle East. More Muslims live in South Asia than in the Middle East and North Africa combined. * The country with the world?s largest Muslim population is Indonesia, which is in South Asia, not the Middle East. * Roughly 60% of the population in the Middle East is under 25 years old. * The term “Arab” generally refers to people who speak Arabic as their first language. * The majority of Arabs are Muslims, but the majority of Muslims are not Arabs. * The words Islam and Muslim are derived from the Arabic word salam, which means peace. * Judaism, Christianity, and Islam are the three largest monotheistic and Abrahamic religions in the world, each of which originates in the Middle East. * The Islamic calendar is based on lunar cycles, unlike the Gregorian and other calendars that are based on the Earth?s rotation around the sun. * The Arabic language uses the same punctuation marks as English, but some of them are inverted or reversed. * Arabic is the most commonly spoken language in the Middle East. It is the official language of more than 20 countries and is spoken by approximately 300 million people worldwide. * Sunni Muslims make up roughly 85% - 90% of the global Muslim population and 60% of the population in the Middle East. * The global population of Muslims is approximately 1.6 billion people, roughly 23% of the world’s population. * The term “mocha” is derived from the city of Mocha in Yemen, where coffee production was commercialized by the year 1400. * In 1997, three men from Yemen tried to sue NASA for trespassing on Mars, claiming they had inherited it from their ancestors 3,000 years ago. * Arabic is the world’s 5th most widely spoken language after Chinese, Spanish, English, and Hindi. * Some of the world’s oldest civilizations were connected with parts of today’s Middle East. These include the Egyptian, Sumerian, Assyrian, and Babylonian civilizations. * Three of the seven wonders of the ancient world are in the Middle East: the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, and the Lighthouse of Alexandria. * Cairo, Egypt is the largest city in the Middle East with a population of roughly 16 million. * The world’s tallest building, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, is 2,717 feet tall and the second tallest building is the Royal Clock Tower Hotel in Mecca, which is 1,972 feet tall. * The five pillars of Islam are prayer, pilgrimage to Mecca, the profession of faith, fasting, and almsgiving. * The Prophet Muhammed had four daughters and three sons. Each of these children died before Muhammad, except Fatimah. * There are no permanent rivers in Saudi Arabia, but the country does have permanently or intermittently dry riverbeds, which are called wadis. * Ibn al-Haytham, the eleventh-century Middle Eastern scientist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher, wrote a seven-volume book on optics and is widely considered to be one of the world?s first theoretical physicists. * Abu Rayhan al-Biruni, the eleventh-century Middle Eastern scholar, explained the lunar eclipse six centuries prior to Galileo. * Ibn Bajjah, the twelfth-century Middle Eastern scholar, proposed an early version of Newton’s third law of motion, which states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. * Psychiatric hospitals were first constructed in Baghdad and Cairo in the 8th and 9th centuries CE. * Tulips were cultivated by the Ottomans and exported to Europe in the early modern period, resulting in “tulip mania” in which tulip bulbs were bought and sold at exorbitant prices, especially in the Netherlands. |
 |
Arabian Peninsula
With the Red Sea in the southwest, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman in the west, and the Arabian Sea in the southeast, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. It is located in Southwest Asia.
According to political definition, the nations that make up the peninsula are Qatar, the UAE, Oman, and Yemen. Most of the center is occupied by Saudi Arabia. The King Fahd Causeway connects Saudi Arabia and Bahrain, an island nation.
The Syrian Desert, which is located in the northern portion of the peninsula and includes northeastern Jordan, southeast Syria, and western Iraq.
Israel and the Palestinian territories are located along the Mediterranean Sea's coast to the northwest.
Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula connects Asia with Africa, while the Dardanelles, the Sea of Marmara and the Bosporus form a narrow separation from Europe. The Sinai Peninsula is the only part of Egypt's territory that lies in Asia.
Which Middle Eastern countries protect Christian minorities?
Since Christians make up the majority in Lebanon's government, they are undoubtedly protected.
In Morocco, Syria, Jordan, and Tunisia, hate speech directed at Christians is prohibited, and they are free to practice their religion in its entirety. Even though the king of Morocco is a Muslim, the country is accused of encouraging Muslim citizens to convert to Christianity. This incident reminds me of one I had in Syria, where it is dangerous to refer to "Christians" without also identifying them as your brothers because hate speech is so strictly forbidden. Once, I was in a mosque in Latakia where the imam was praising his "brothers" who were Christians. When I went to him to express my appreciation for his openness after the sermon, he nervously glanced around to make sure I was the only person there before declaring all Christians to be dogs and claiming that he only did so because government officials ordered him to.
Iraq also makes an effort to safeguard Christians, but it appears that they are failing miserably. In the time of Saddam, laws were much more strictly enforced, but this government is a complete failure.
Since the inception of ISIS, Kuwait and the United Arab Emirates have surrounded their churches with police who will frisk anyone who even walks by, protecting the Christians there from hate crimes. However, hate speech is openly used there. However, they are not permitted to openly sell religious symbols there or to practice outside of the church due to severe restrictions on their freedom.
Saudi Arabia is the only Middle Eastern nation, in my opinion, without any churches. Although the Armenians have churches and seats in parliament, Iran also targets non-Armenian Christians and Muslims who become Christians.
The only nations where Christians are consistently in danger are Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Iraq, along with Syria because of the revolution.
Top 3 Most Beautiful Places In The Middle East
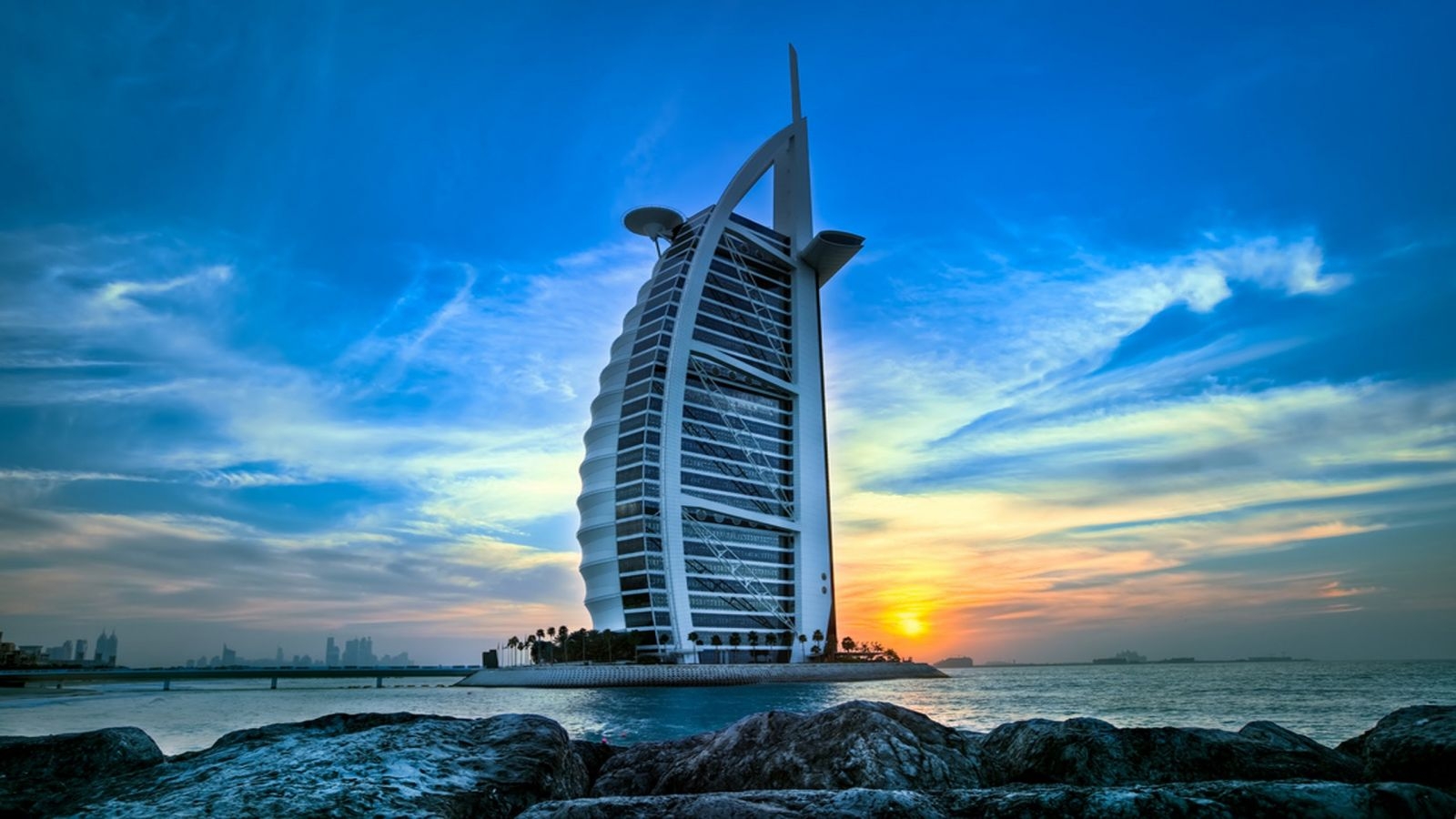
1. Dubai
 |
| Photo: J Travel |
Perhaps the first one on the list, Dubai is a vacation paradise. With timeless deserts and exquisite shopping malls, beaches and with the world’s tallest buildings, Dubai is a great place to have in your passport.
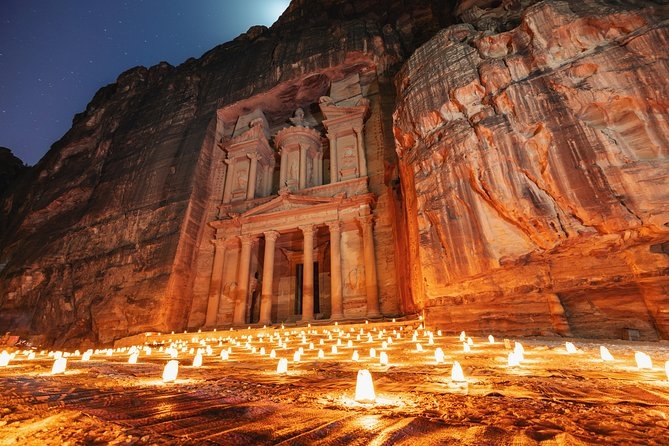
2. Petra
 |
| Photo: Viator |
Situated in Jordan, Petra is a great destination for visitors looking for prehistoric times and ancient beauty. The peace surrounds throughout the city and definitely provides a lifetime experience with all the red colored rock carvings throughout the city and magnificent primeval structures. Petra, because of these reasons is declared as World heritage site by UNESCO
3. Beirut
 |
| Photo: TripAdvisor |
Beirut, the capital of Lebanon, has experienced wartime conditions, but despite this, it has overcome the worst and grown to be one of the most popular tourist destinations in the Middle East. Beirut has been described as the fusion of the past and the present. It is a small isthmus that stretches from the Mediterranean Sea into hills. The city is dotted with medieval-era monuments, and since its revitalization, it has also benefited from stunning beaches, tall buildings, and opulent hotels.
What are the countries of the Middle East?
1.Bahrain
- Area: 760 km2
- Population: 1,641,170
- Capital: Manama
Between Saudi Arabia and the peninsula of Qatar, in the Persian Gulf, is the archipelago nation of Bahrain. It has a population of just over 1.64 million and a land area of 760 km2. Foreigners make up nearly half of Bahrain's population. The Middle East's most independent economy, according to the 2011 Index of Economic Freedom, is in this nation. Prior to that, Bahrain was renowned for having the fastest-growing banking and financial services industries worldwide.
2.Cyprus
- Area: 9,251 km2
- Population: 1,198,580
- Capital: Nicosia
Between Turkey and Egypt in the Mediterranean Sea is another island country called Cyprus. The population of the nation, which has a total area of 9,251 km2, is roughly 1.19 million. After gaining its independence from Great Britain in 1961, Cyprus joined the Commonwealth of Nations, and in 2004 it was admitted as a member of the European Union. Because its tax rates are lower than the average for the European Union, Cyprus serves as a hub for foreign businesses. The economy of the nation is based on tourism, shipping, banking, and financial services.
3.Egypt
- Area: 1,010,40 km2
- Population: 100,388,070
- Capital: Cairo
Egypt is a country in northeastern Africa, bordered by the Red Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Gulf of Aqaba. The Sinai Peninsula, which has borders with both Israel and Palestine, is also included in its territory. Egypt is a transcontinental nation thanks to this peninsula, which links it to the Middle East. Egypt has a population of more than 100 million people and a total area of 1,010,40 km2. Nearly 25% of its exports are crude petroleum oil. Agriculture, tourism, and natural gas are the mainstays of the rest of the economy.
4.Iran
- Area: 1,648,195 km2
- Population: 82,913,910
- Capital: Tehran
Iran has coastlines that run along the Caspian Sea, the Gulf of Oman, and the Persian Gulf. Its population is roughly 83 million and it has a land area of 1,648,195 km2. The world's largest natural gas reserve and fourth-largest oil reserve are both found in Iran. The nation belongs to OPEC, the UN, as well as a number of other international associations. The services sector is essential to Iran's economy and gross domestic product (GDP).
5.Iraq
- Area: 438,317 km2
- Population: 39,309,780
- Capital: Baghdad
Iraq is largely a landlocked country, with the exception of a 36-mile stretch along the Persian Gulf. There are 39 million people living in the country, which has a total area of 438,317 km2. Iraq's economy has a GDP per capita of only $4,000 and an unemployment rate that ranges from 18% to 30% on average. Approximately 60% of all employment opportunities are in the public sector. Approximately 95% of Iraq's foreign exchange earnings come from the oil sector.
6.Israel
- Area: 20,770 km2
- Population: 9,053,300
- Capital: Jerusalem
Israel borders numerous nations, including Jordan, Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, and the Gaza Strip, and it has coastlines on both the Red and Mediterranean Seas. It has a population of about 9 million and a surface area of 20,770 km2. Around 74.7% of Israel's population self-identifies as Jewish. The nation is frequently referred to as the Jewish State because it was established as a homeland for people of Jewish ancestry and religion. The technology and industrial sectors are the foundation of Israel's economy, which is the most developed in the Middle East.
7.Jordan
- Area: 92,300 km2
- Population: 10,101,690
- Capital: Amman
Jordan has coastlines along both the Dead and Red Seas and is situated halfway between the continents of Europe, Africa, and Asia. It has a population of more than 10 million and a 92,300 km2 area. Almost all of the population (92%) self-identifies as a Sunni Muslim. The nation is renowned as a haven for local refugees who have fled their homes because of terrorism and political unrest. One of the most politically stable nations in the Middle East is Jordan.
8.Kuwait
- Area: 17,820 km2
- Population: 4,207,080
- Capital: Kuwait City
Kuwait occupies a region of 17,820 km2 at the northernmost point of the Persian Gulf. There are just over 4.2 million people living in this country, and about 70% of them are foreigners. The Kuwaiti petroleum industry, which employs many foreign workers, is primarily to blame for this high percentage of foreigners. At least 87% of the nation's exports are made from petroleum. The industry accounts for about 50% of Kuwait's GDP.
9.Lebanon
- Area: 10,400 km2
- Population: 6,855,710
- Capital: Beirut
With a total area of 10,400 km2, Lebanon is one of the smallest non-island nations in the Middle East. With a population of just over 6.8 million, it is known for having a diverse ethnic and cultural background. The economy of Lebanon managed to withstand the 2008 global financial crisis, growing at a rate of 8.5% in 2008 and 9% in 2009. The country's economy is dominated by the services sector, which also employs about 65% of the workforce.
10.Oman
- Area: 309,500 km2
- Population: 4,974,990
- Capital: Muscat
Oman has a lengthy coastline along the Arabian Sea due to its location on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. The population of the country, which has a total area of 309,500 km2, is approximately 4.97 million. All government duties are carried out by the Sultan, a hereditary position, and its government is regarded as an absolute monarchy. Oman's economy is reliant on the oil and petroleum sector, especially given that exports make up the majority of its GDP. However, Oman's tourism sector is expanding quickly.
11.Palestine
- Area: 6,020 km2
- Population: 4,685,310
- Capital: Ramallah1
Palestine has shared borders with Jordan and Israel as well as claiming sovereignty over the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Palestine has a population of 4.68 million people and a land area of 6,020 km2. The country and Israel have been at war for many years over the Israeli-occupied territories, which were governed by the Israeli Military Governorate from 1967 to 1982. 82% of Palestine's $10 billion GDP is made up of the services sector.
12.Qatar
- Area: 11,586 km2
- Population: 2,832,070
- Capital: Doha
Qatar occupies an area of 11,586 km2 and is located on the Arabian Peninsula's eastern coast. Over 2.83 million people call this country home, with 2.3 million of them being foreigners. The natural gas and oil industries, which hire a sizable number of foreign workers each year, are to blame for this high proportion of residents who were born outside of the country.
13.Saudi Arabia
- Area: 2,149,690 km2
- Population: 34,268,530
- Capital: Riyadh
The Middle East's largest nation, Saudi Arabia, spans an area of 2,149,690 km2. There are about 34 million people living there, and 90% of them identify as Arabs. Due to a higher-than-average birth rate, the nation's population had increased significantly since 1950, when it was only about 3 million. One of the three Arabic dialects—Najdi, Hejazi, or Gulf—is spoken by the vast majority of people in Saudi Arabia.
14.Syria
- Area: 187,437 km2
- Population: 17,070,130
- Capital: Damascus
Syria is a country in the Middle East's western region, and it has a total area of 187,437 km2. The estimated population of the nation is 17 million, though this figure may be off given the recent failure to conduct a reliable census. Given the large number of people who have been killed or fled the country as a result of civil war, military violence, and political instability, the population represents a decrease over previous years. Another 7.6 million people are internally displaced, and at least 5 million people have fled to other nations.
15.Turkey
*Area: 783,562 km2
*Population: 83,429,620
*Capital: Ankara
Turkey is regarded as a transcontinental nation because of its location halfway between Europe and Asia. It has a population of about 83.4 million and a surface area of 783,562 km2. Between 70 and 80 percent of this population claims Turkish ancestry. Turkey is a newly industrialized country with a $2.199 trillion GDP, more than half of which comes from the services sector.
16.United Arab Emirates
- Area: 83,600 km2
- Population: 9,770,530
- Capital: Abu Dhabi
Along the Arabian Peninsula's southern border is the United Arab Emirates (UAE). It has a population of about 9.7 million and a land area of 83,600 km2. With a GDP of about $377 billion, this nation has one of the largest economies in the Middle East. The UAE's economy is heavily reliant on the oil sector, like the majority of those in this part of the world.
17.Yemen
- Area: 527,968 km2
- Population: 29,161,920
- Capital: Sana'a
Yemen occupies a total area of 527,968 km2 and is located on the Arabian Peninsula's southwest coast. Nearly half of the nation's population, or over 29 million people, are under the age of 15. Yemen's population is anticipated to grow to 60 million people by 2050 as a result of these demographics and a number of other factors. Like many other Middle Eastern nations, Yemen's economy is centered on the petroleum sector, which accounts for 73% of its exports.
 How Many Countries Are There In South America? How Many Countries Are There In South America? What do you think of when we mention South America? Amazon Forest? Angel Falls? Tribes? Check out our article to know more about the updated ... |
 How Many Countries Are There in Africa: Full List, Population, Richest and Smallest How Many Countries Are There in Africa: Full List, Population, Richest and Smallest How many countries in Africa (Updated): Which one is the richest, poorest, smallest, latest population, Facts and Figures. |
 How Many Countries Are There In Europe: Full List, Population, Facts and Figures How Many Countries Are There In Europe: Full List, Population, Facts and Figures How many countries are there in Europe? 40,46, 48, 51? We have updated information for you to explore: Full List, Population, Richest, Smallest, Facts ... |


























