Who is the Father/Inventor of Artificial Intelligence: History and Timeline of AI
 5 Hottest and Scariest AI Technologies - Top Artificial Intelligence Tools 5 Hottest and Scariest AI Technologies - Top Artificial Intelligence Tools The technologies or tools of Artificial Intelligence (AI) such as ChatGPT, Lensa, Dall-E... are causing a global fever that makes people both curious and afraid. |
 How to Detect and Avoid AI-Generated Content How to Detect and Avoid AI-Generated Content The internet as we know it is advancing at a rapid pace. Several algorithms are capable of detecting natural writing patterns, and these tools have ... |
What is Artificial Intelligence - Definition of AI?
Rapid advancements in knowledge and artificial intelligence are creating a strong demand for new digital services to help this technology reach its full potential.
Improving existing products that we can all use in our daily lives will be critical to the future of artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the result of simulating human intellectual processes with machines, specifically computer systems. These processes include learning (acquiring information and rules for its application), systematic reasoning (applying rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-regulation. AI has specialized applications such as expert systems, speech recognition, and machine vision.
Who is the Father of AI?
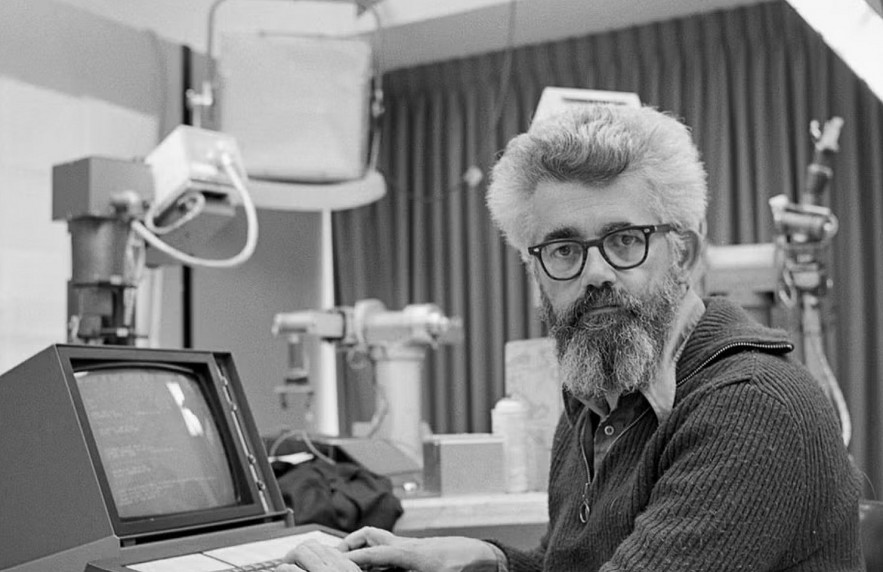 |
| John McCarthy is regarded as the inventor and father of artificial intelligence |
Since the 1880s, a few scientists have introduced the term artificial intelligence with the advent of telephones and computers. However, they are only the people who laid the foundation for later AI and are not the fathers of AI.
So When was AI Born and Who Created it?
In 1956, the phrase "artificial intelligence" was first mentioned at the "Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence". The conference, under the direction of John McCarthy, established the parameters and objectives of artificial intelligence as we know it today. Allen Newell and Herbert Simon demonstrate Logical Theorist (LT), the first reasoning program.
So, John McCarthy is regarded as the inventor and father of artificial intelligence for coining the term 'Artificial Intelligence'.
Read more: Top 120 Greatest Inventions That Have Changed the World Forever
History, Timeline of Artificial Intelligence
 |
| Timeline of Artificial Intelligence |
Regarding Ai's History, it can be divided into 4 stages as follows:
1950 - The time when everything began
Despite the fact that the concept had been around for decades, many people were still unfamiliar with it by 1950. John McCarthy, known as the founder of artificial intelligence, coined the term 'AI' in 1955.
McCarthy, along with Alan Turing, Allen Newell, Herbert A. Simon, and Marvin Minsky, are regarded as the fathers of AI. Alan made the first AI suggestion, stating that if humans can solve problems and make decisions using available information and rational thinking, why can't machines?
1974 - Computers flourished
The computer wave gradually developed and then exploded. Computers are becoming faster, more affordable, and capable of storing larger amounts of data. The most important characteristic to discuss here is that computers can think abstractly, be self-aware, and perform natural language processing.
1980 - The year of AI
Artificial intelligence research resumed in 1980, with the expansion of investment funds and algorithmic tools. Deep Learning technology has allowed computers to gradually learn about their users' experiences.
2000's - Milestone
Despite all of the efforts and failures, the technology was successfully established, but it wasn't until the 2000s that we considered achieving the important AI goals. AI was thriving at the time, despite a lack of government funding and public attention.
1943: Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts publish the paper "The Logical Calculus of Intrinsic Ideas in Neural Activity," which discusses simple, idealized artificial neural networks (ANNs). chemistry, and how they can perform basic logic functions. Artificial neural networks were the forerunners of deep learning, which is now widely used.
1947: Statistician John Tukey used the term “bit” to refer to a binary digit - a unit of information stored in a computer.
1949: Donald Hebb proposed a theory of learning based on conjectures regarding neural networks, and the possibility that connections between neurons could strengthen or weaken over time.
1950: Claude Shannon published the paper “Programming a Chess-Playing Computer” – the first paper on developing a chess-playing computer software.
1950: Alan Turing publishes a famous paper titled “Can Machines Think?”, in which he introduces the concept of machine thinking and proposes the Turing Test – a test of the ability computer intelligence.
1952: Arthur Samuel develops a checkers program that is self-taught and can even beat professional chess players after training.
1955: Herbert Simon and Allen Newell created the first artificial intelligence program, "Logic Theorist." This program has proven 38 of the 52 mathematical theorems and discovered new and improved proofs for a few others.
1956: The term "artificial intelligence" was coined by American computer scientist John McCarthy at the Dartmouth Conference, signaling the official beginning of artificial intelligence.
1957:Frank Rosenblatt creates Perceptron, the first artificial neural network that recognizes patterns using a computer learning network (CLN) with two layers.
1958: John McCarthy develops the programming language Lisp, which becomes the most popular programming language used in artificial intelligence research.
1959: Arthur Samuel introduced the concept of “machine learning,” reporting on programming a computer “so that it learns to play a game of checkers better than the person writing the program can.”
1961: Unimate, the first industrial robot, began operating on an assembly line at a General Motors factory in New Jersey (USA).
1964: Daniel Bobrow develops STUDENT, a computer program that understands natural language.
1965: Joseph Weizenbaum developed ELIZA, an interactive program that could conduct dialogue in English on any topic.
1965: Edward Feigenbaum, Bruce Buchanan, Joshua Lederberg, and Carl Djerassi began developing the first expert system, DENDRAL, at Stanford University, aimed at studying hypothesis formation and the construction of Experimental induction model in science.
1966: Shakey, the first general-purpose mobile robot built at Stanford University, could reason about its own actions.
1968: Terry Winograd develops SHRDLU, an early natural language understanding computer program.
1970: The first intelligent humanoid robot was built at Waseda University (Japan), named WABOT-1. It includes a limb control system, a display system and a conversation system.
1972: MYCIN, an expert system designed at Stanford University to detect bacteria causing serious infections and recommend antibiotics for treatment.
1972: The logic programming language PROLOG is born.
1974-1980: The first “AI Winter” (AI Winter). The term “AI Winter” refers to a period when funding for artificial intelligence research projects is severely cut due to slow progress in AI development.
1980: Wabot-2 was built at Waseda University, Japan. This is a humanoid robot that can communicate with humans, read sheet music, and play melodies of medium difficulty on an electronic organ.
 |
| Who Invented Artificial Intelligence |
1981: Japan's Ministry of International Trade and Industry allocates a budget of $850 million to the '5th Generation Computer' project, which aims to develop computers that can carry out conversations, translate languages, understand visualize and reason like humans.
1984: Released the film Electric Dreams about a love triangle between a man, a woman, and a personal computer.
1985: The first business intelligence system was developed for Procter & Gamble by Metaphor Computer Systems to link sales information and retail scanner data.
1986: The first driverless car (a Mercedes-Benz van) equipped with cameras and sensors, built at the Bundeswehr University in Munich under the direction of Ernst Dickmanns, can reach high speeds of 55 mph on empty roads.
1987-1993: The second "AI winter". Once again, investors and governments stopped funding AI research due to high costs but not the expected results.
1995: Richard Wallace creates the A.L.I.C.E chatbot, inspired by Joseph Weizenbaum's ELIZA program, but with the addition of natural language sample data collection on an unprecedented scale, facilitated by the Web.
1997: IBM's Deep Blue becomes the first computer program to defeat a world chess champion (Garry Kasparov).
1998: Dr. Cynthia Breazeal at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) launched Kismet, an intelligent robot that can recognize and respond to human emotions.
2000: Honda launches the humanoid robot ASIMO that can walk as fast as a human, delivering trays to customers in a restaurant setting.
2002: Robots first appeared in homes in the form of the Roomba, an automated vacuum cleaner developed by iRobot.
2006: AI appeared in the business world. Companies like Facebook, Twitter, and Netflix are starting to use AI.
2009: Computer scientists at Northwestern University's Information Intelligence Laboratory develop Stats Monkey, a program that writes sports news without human intervention.
2011: Watson, IBM's question-answering computer, competes in the television game show Jeopardy! and defeats two previous champions. Watson has demonstrated the ability to understand natural language and solve difficult questions quickly.
2011: Apple integrated Siri, an intelligent virtual assistant with a voice interface, into the iPhone 4S.
2014: Chatbot Eugene Goostman passes the Turing test with 1/3 of the judges believing Eugene is human.
2014: Amazon launches Alexa, an intelligent virtual assistant with a voice interface that supports customer shopping activities.
2016: The first "robot citizen" was introduced to the public. Sophia is a humanoid robot created by Hanson Robotics that can recognize faces, communicate verbally, and express emotions through facial expression.
2017: Google DeepMind's AlphaGo defeats Go champion Lee Sedol, becoming the first computer program to win against a professional Go player.
2020: OpenAI releases the GPT-3 natural language processing model that can generate AI-based text.
2021: OpenAI relies on GPT-3 to develop DALL-E to generate images from text prompts.
May 2022: DeepMind introduces Gato, a multimodal AI system trained to perform hundreds of different tasks, including playing video games, captioning images, and stacking blocks with robotic arms.
November 2022: OpenAI introduces ChatGPT, an AI chatbot that can interact in a conversational mode and respond in natural language. The tool gained 100 million users in just two months of launch, making it the fastest growing consumer app in history.
2023: ChatGPT's launch has sparked a global race to research, develop, and apply AI, involving major technology companies like Microsoft, Google, Alibaba, and Baidu.
2024: AI baby and AI lover
Artificial intelligence boyfriends and girlfriends are thriving, even generating significant profits for their owners and the companies that own them.
Chinese scientists created the world's first baby, AI Tong Tong, who possesses exceptional abilities, particularly the ability to experience happy and sad emotions and to think and act independently.
 Who is Lexi Love And Who Created A Most Famoust AI Model Who is Lexi Love And Who Created A Most Famoust AI Model A model created by artificial intelligence (AI) is causing a worldwide sensation due to her beauty, attractiveness, and exceptional ability to profit from lonely men. ... |
 How To Create An AI-Powered Virtual Girlfriend To Share Everything How To Create An AI-Powered Virtual Girlfriend To Share Everything Artificial intelligence has advanced significantly in recent years and its applications have exceeded our wildest dreams. Building AI-powered virtual girlfriends is one such use. Check ... |
 Who is 'Little Girl' Tong Tong - First AI Child in the World with Full Emotions of Joy and Anger Who is 'Little Girl' Tong Tong - First AI Child in the World with Full Emotions of Joy and Anger Tong Tong, the world's first artificial intelligence (AI) girl created by Chinese scientists, has the same behavior and abilities as a three- to four-year-old child ... |
 AI-Generated 'Fake' Photos Cause a Stir Worldwide And How to Detect AI-Generated 'Fake' Photos Cause a Stir Worldwide And How to Detect Furthermore, alongside the fervor for generating content from written material, we are observing the rapid increase of artificial intelligence systems that produce lifelike images based ... |