Why Does the Moon Affect the Tides Though It is 384,000 KM from Earth
 |
| How does the Moon affect the tides despite being far from Earth |
| Contents |
The short answer is that the moon's gravity pulls the water in the earth's oceans toward it. Although the moon is very far away, it is large enough for its gravity to suck up the water on earth.
What is the Tide on Earth?
Science has confirmed that tides are the Moon's gravitational pull pulling the oceans (and us) towards it. Although the Moon is very far away, it is large enough to create a gravity strong enough to do so.
To be more specific, a tide is the rise and fall of the water level in the ocean, both in your ponds and cups, but only in the ocean that is clearly visible because of its enormous amount of water.
When the sea level rises to the highest point, we call it high tide. When it falls to its lowest point, it is called a low tide. The rise and fall of the tides is called the tidal cycle. If there is one high tide and one low tide per day, it is called a diurnal cycle. If there are two high tides and two low tides, it is called a semi-diurnal period.
The Moon has the biggest influence on the tides, but it's not the only factor that affects them. The Sun and Earth can also affect the tides.
How Far is the Moon from the Earth and How Does the Moon Affect the Tides?
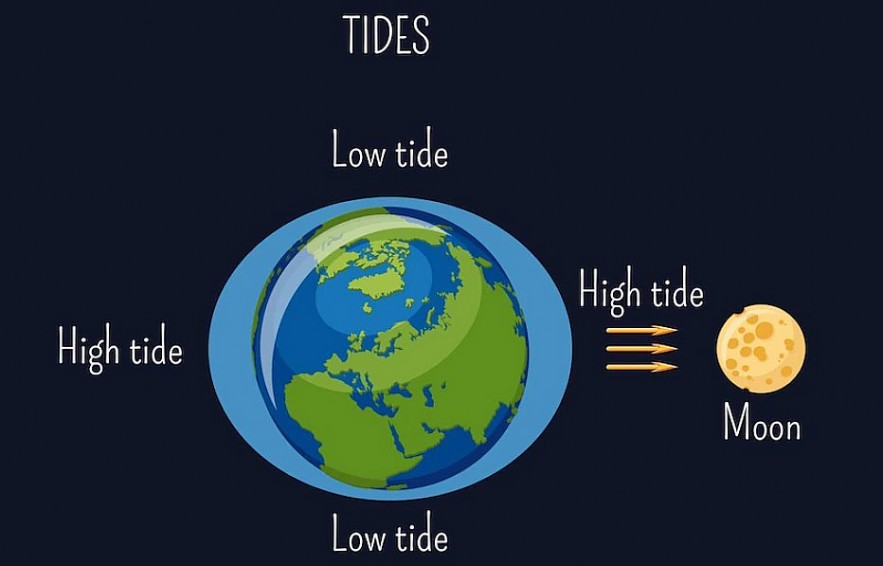 |
| The Moon affects the tides because of gravity |
The Moon is the closest celestial body to Earth in the universe. The average distance between the Moon and Earth is 384,400km. If man walked from the Earth to the Moon, it would take about 9 years. If you take a spaceship, it takes more than 7 days to go back from Earth to the moon every time.
The Moon affects the tides because of gravity. You will notice that every time you jump, you always land again. This is because Earth's gravity is pulling you down. The Moon has always had its own gravity, which pulls the oceans and us towards it.
The Moon's gravity is much weaker to us than Earth's, so we don't really notice it, but the Moon's effect on the liquid water of the oceans is very visible. .
If the Moon causes high tides on one side of the Earth on the opposite side, what causes high tides on the other side? The answer here is the rotation of the Earth, so we have both day and night.
The mutual attraction between the Moon and the Earth tends to bring them closer together. But this attraction is compensated by the centrifugal rotation of the Earth, as well as that of the Moon, around their centers of inertia.
The rotation of the Earth also means that another high tide occurs on the opposite side of the Earth from the Moon. These two high tides suck water out of the rest of the ocean, causing two low tides between the high tides.
Daily, there are 2 high tides and 2 low tides. Each day the tides appear about 1 hour later than the previous day. Because every day, the Moon has to make part of its rotation around the Earth, so the Moon is 1 hour different to return to the exact same point.
Tide boundaries (the difference in sea level at high tide and low tide) vary widely. In oceans, this amplitude is 1m, in closed and small seas it is less: about 30cm, but in estuaries and straits it can be up to 17m.
Interesting Facts about Tides
The Earth revolves around itself in 24 hours and the moon takes 27.3 days to orbit the Earth. Wherever you are on earth, after 24 hours, you have to wait for the moon to move for another 50 minutes before you see it again in a position directly above your head.
During both the new moon phases (dark, the moon is between the earth and the sun and is backlit by the sun) and the full moon (the brightest, the earth is between the moon and the sun), gravity on the earth Earth is the highest, equal to the sum of the effects of the sun and the moon. This explains why the tide phenomenon has 2 peak times: the new moon appears and the full moon day.
When the moon is in the phases of crescent (visible ¼) and waning moon (¾), the gravitational pull of the sun and moon on earth will form a 45 degree angle. When this total force is at its highest, the earth is somewhere between the moon and the sun.
The time it takes for the earth to move to this position can be several hours faster or slower than when the moon is highest in the sky. So the highest tides will occur before or after the moon is highest in the sky.
Low tide is the weakest tide, occurs when the moon is in the first or last phase or quarter ( visible), when the gravitational pull of the sun and moon on the earth forms a 90 degree angle are therefore almost completely mutually exclusive.
Tides are sometimes more difficult to predict because the moon does not orbit the earth directly at the equator, but its orbit is tilted at an angle of 5 degrees relative to the plane in which the earth orbits the sun. Earth's self-revolving orbit is also tilted 23.5 degrees from this plane, creating different seasons.
So the highest tides for each day will always be above or below the equator. That's why the tides only rise once a day in high tide areas.
Does the Sun Affect Tides on Earth?The Sun also has its own gravity that can affect the tides. Although the Sun is much larger than the Moon has also a greater gravity, it is also farther away, meaning its gravitational pull on the strong tides is only half that of the Moon. Although small, it still has an impact. When the Sun and Moon are in alignment with the Earth (which we often see a full moon or a new moon occurring) their combined gravity causes very high or very low tides. When the Sun and Moon are perpendicular to each other (when the moon is full or waning), the Sun helps to remove gravity from the Moon, causing lower high tides and higher than average low tides. |
Conclusion
So we clearly understand that theMoon has the greatest influence on the tides on Earth due to gravity. However, the gravity of the Sun and the rotation of the Earth also affect tidal levels.
Why do we have tides?
 Facts about the MOON: Top 12 Interesting Things Facts about the MOON: Top 12 Interesting Things At a distance of 384,400 km from the Earth, the Moon is our closest celestial neighbour and only natural satellite. Like the Earth itself, the ... |
 Facts about Cold Moon - Last Full Moon of the Year: Date, Timings, All you need to Know Facts about Cold Moon - Last Full Moon of the Year: Date, Timings, All you need to Know The upcoming lunar event Last Full Moon or also known as the Cold Moon, which is the highest full moon of 2020, last full moon ... |
 15 Strangest Places on Earth You Won’t Believe Exist 15 Strangest Places on Earth You Won’t Believe Exist Earth is an extraodrinary planet, and so are many parts on Earth. Let's take a look at top 15 strangest places that you wont believe ... |
 Where is the Coldest Place on Earth - According to NASA Satellite Where is the Coldest Place on Earth - According to NASA Satellite According to NASA, the coldest place on Earth is the East Antarctic Plateau with a temperature of -93.2 degrees Celsius. |























