When Will the US be Back to the Moon After More Than 50 Years
♦ Why Does the Moon Affect the Tides Though It is 384,000 KM from Earth
♦ Facts about the MOON: Top 12 Interesting Things
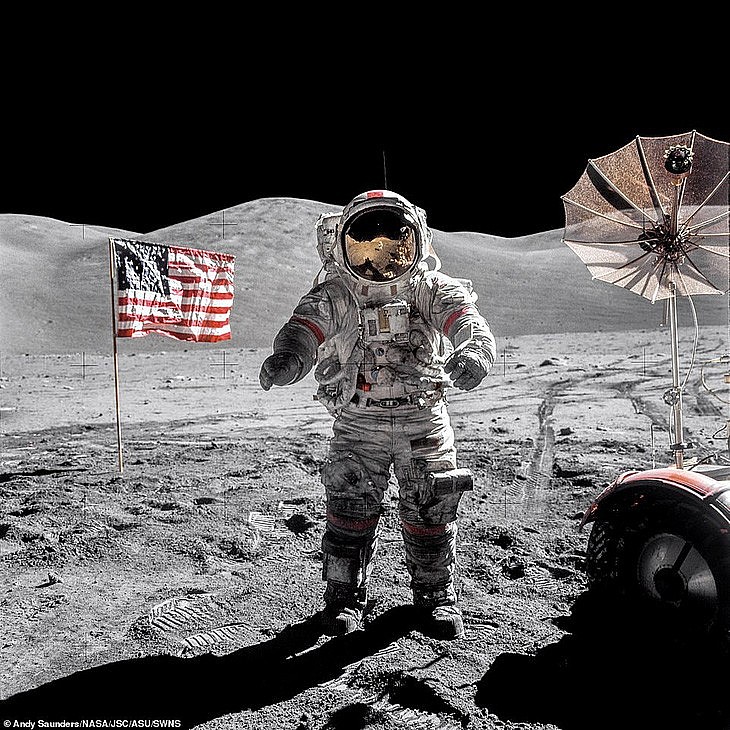 |
| Why Hasn’t The US Been Back To The Moon? Photo NASA |
| Contents |
How many times has someone walked on the Moon?
Between July 1969 and December 1972, twelve men walked on the Moon during the Apollo program's six Moon landings.
READ MORE: How NASA's Perseverance rover makes history land on Mars - Video
When was the first time and who was the first one to land on the Moon?
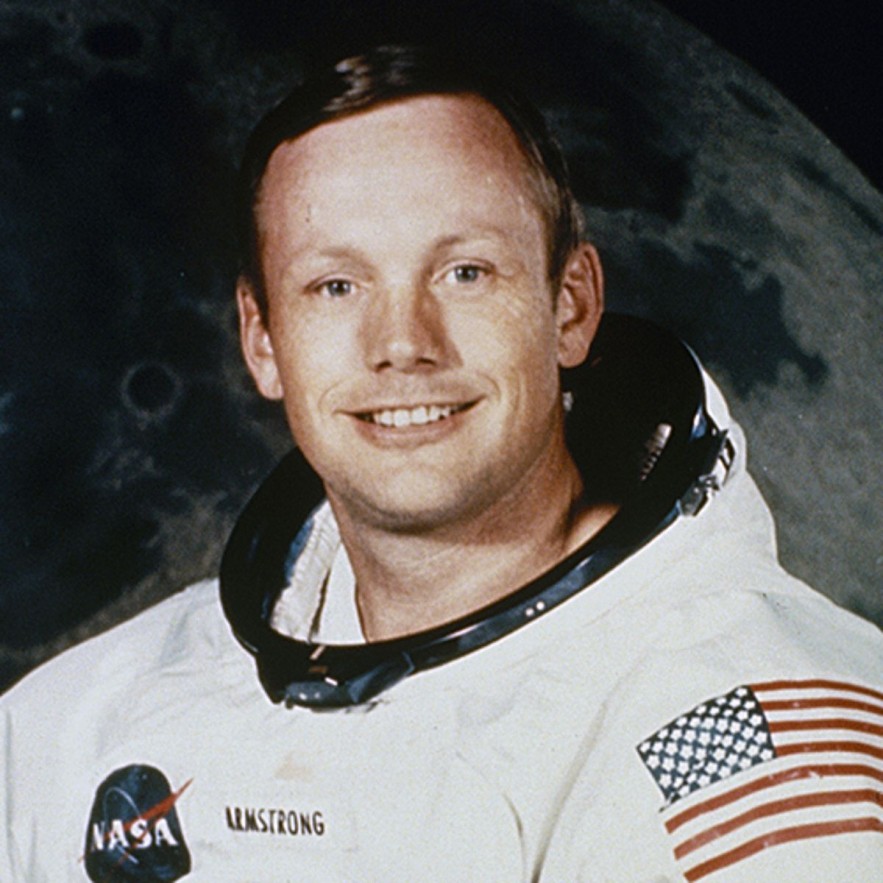 |
| American astronaut Neil Armstrong. Photo Getty |
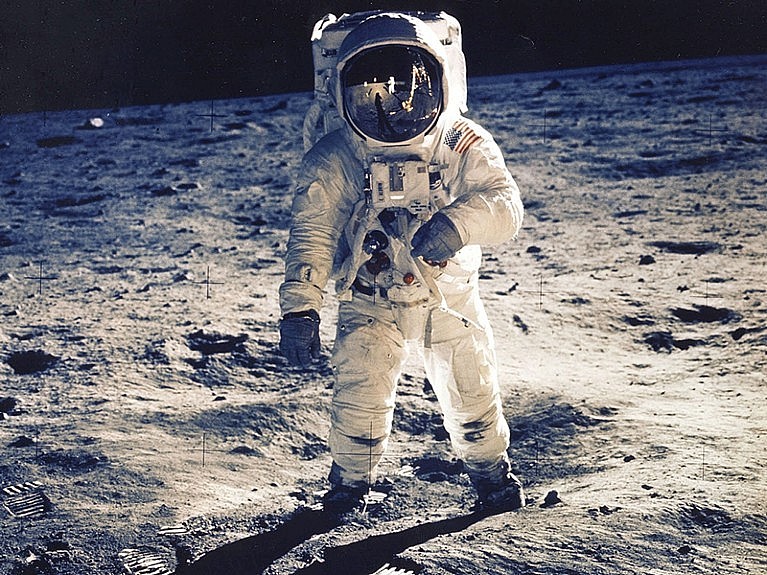
At 02:56 GMT on 21 July 1969, American astronaut Neil Armstrong became the first person to walk on the Moon. He stepped out of the Apollo 11 lunar module and onto the Moon's surface, in an area called the 'Sea of Tranquility.'
Armstrong reported the lunar module's safe landing at 20:17 GMT with the words: "Houston, Tranquility Base here. The Eagle has landed." As he put his left foot onto the Moon, Armstrong declared: "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind."
| At 03:15 GMT, Armstrong was joined by the lunar module pilot, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin. The two colleagues collected data and soil samples before planting the US flag at 03:41 GMT. They also unveiled a plaque bearing President Nixon's signature and an inscription reading: "Here men from the planet Earth first set foot upon the Moon July 1969 AD. We came in peace for all mankind. |
What vehicles did the astronauts use to land on the Moon in 1969?The Lunar Roving Vehicle is a small electric vehicle that allows Apollo mission astronauts to drive in the vicinity of the solar module's landing site, to make geological observations, to collect rock specimens and to use musical instruments. |
When was the last time someone walked on the Moon?
Apollo 17, which took place from December 7 and 19, 1972, was the last human mission to the Moon.
READ MORE: NASA’s Dragon Launched to the ISS: Date, How to Watch?
Who has been to the moon?
The list of astronauts who've walked on the moon during the Apollo era are:
Neil Armstrong (Apollo 11)
Buzz Aldrin (Apollo 11)
Charles "Pete" Conrad (Apollo 12)
Alan Bean (Apollo 12)
Alan Shepard (Apollo 14)
Edgar Mitchell (Apollo 14)
David Scott (Apollo 15)
James Irwin (Apollo 15)
John Young (Apollo 16)
Charles Duke (Apollo 16)
Eugene Cernan (Apollo 17)
Harrison Schmitt (Apollo 17)
How important for humans to land on the moon?The human landing on the moon is a national project that has put the United States at the forefront of the technology of the planet, but has also benefited all of us, because science creates develop. |
Why Hasn’t the US Been Back To The Moon?
 |
| Why Hasn’t the US Been Back To The Moon? Photo nature |
High cost
The first reason is the high cost. NASA's 2022 budget is $24 billion, and the Biden administration is asking Congress to increase that number to nearly $26 billion in the 2023 budget.
That money is divided among all the agency's activities and ambitious projects, such as: the James Webb space telescope, the massive rocket project called the Space Launch System (SLS) and distant missions to the Sun, Jupiter, Mars, the asteroid belts, the Kuiper belts, and the edge of the Solar System.
Meanwhile, the US military has a budget of about 858 billion USD in 2023.
Compared to the federal budget, NASA's share of the budget is smaller than it used to be.
NASA's share of the federal budget only peaked at 4% in 1965. Over the past 40 years, it has remained below 1%, and over the past 15 years, it has been toward 0.4% of the budget, said former Apollo 7 astronaut Walter Cunningham.
Political factors
The process of designing, building, and testing a spaceship typically spans more than a presidential term.
But new presidents and legislators often dismiss their predecessors' space exploration priorities.
In 2004, the Bush administration tasked NASA with figuring out how to replace the soon-to-be retired space shuttle and return to the Moon at the same time. The agency launched the Constellation program to send astronauts to the Moon using a rocket called Ares and a spacecraft called Orion.
NASA spent $9 billion over five years designing, building, and testing the hardware for that spaceflight program.
However, after former President Barack Obama took office, he canceled the Constellation program and replaced it with the SLS missile program.
By the time of former president Trump, he did not eliminate SLS but changed his goal, from sending astronauts to an asteroid to prioritizing missions to the Moon and Mars.
Such frequent changes resulted in cancellations after cancellations, costing about $20 billion in losses, a waste of time and motivation.
Public indifference and lack of succession team
Public interest in lunar exploration has always been indifferent.
Even at the height of the Apollo program, after astronauts Aldrin and Neil Armstrong stepped onto the surface of the Moon, only 53% of Americans said they thought the program was worth it.
Another problem is the legacy team. Today many American children polled say they dream of becoming YouTube stars more than astronauts.
| American researchers and entrepreneurs have long pushed for the creation of a space station on the Moon. A lunar base could evolve into a fuel depot for deep space missions, leading to the creation of space telescopes, making it easier for humans to live on Mars and solving scientific mysteries. long-standing study of the Earth and the Moon. It could even boost a space economy like space tourism. |
When will the US be back to the Moon?
 |
| NASA's initial goal was to reach the moon again by 2024. Photo NASA |
NASA sees a return to the moon as the first step on the path to a manned mission to Mars and Artemis is the boots it will use for the journey.
NASA's initial goal was to reach the moon again by 2024, but the date has been pushed back to no sooner than 2025.
With a strained economic outlook for the US and the world, firing humans into space may be the least important thing on many Americans’ agenda. Each launch costs $4 billion. However, NASA has used a lot more private investment for its latest round of space explorations including the use of rockets from SpaceX and Blue Origin, controlled by Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos respectively.
The real aim for NASA is to do something so far unaccomplished by humans; reach Mars. the red planet has had a number of unmanned missions onto the surface in the form of rovers, but so far it has been impossible to translate that to a human footprint. Musk has made Mars a focus of SpaceX’s mission and the lessons from the Moon could help him realise this goal.
 What Is The First Spaceship In The World? What Is The First Spaceship In The World? Flying into space was one of important missions that human has completed. Let's take a look at the history of spaceflight, and the first spacecraft ... |
 What is the Oldest Spacecraft of NASA - Voyager 1 What is the Oldest Spacecraft of NASA - Voyager 1 First launched in 1977, the Voyager duo is NASA's longest-running mission. |
 Where is the Coldest Place on Earth - According to NASA Satellite Where is the Coldest Place on Earth - According to NASA Satellite According to NASA, the coldest place on Earth is the East Antarctic Plateau with a temperature of -93.2 degrees Celsius. |
























