Trump’s Healthcare Deregulation: Impact and Implications
 Top 10 Countries With The Best Healthcare System and Why Top 10 Countries With The Best Healthcare System and Why |
This approach prioritizes reducing federal oversight and allowing free-market forces to shape the healthcare system. While deregulation offers potential benefits like cost reduction and increased flexibility, it also raises concerns about accessibility, affordability, and the quality of care for vulnerable populations.
This article explores the impacts, beneficiaries, and challenges of Trump’s healthcare deregulation policies, alongside strategies to adapt.
Learn more: What Trump’s Education Policies Mean for You
Key Aspects of Healthcare Deregulation
 |
| Healthcare Deregulation: Impact and Implications |
1. Expansion of Short-Term and Association Health Plans
Trump’s administration emphasizes offering more affordable and flexible insurance options.
-
What It Means:
- Short-term health plans provide temporary coverage but are exempt from ACA requirements such as covering pre-existing conditions.
- Association health plans allow small businesses and groups to pool resources to negotiate cheaper insurance options for their employees.
-
Impacts:
- Pros:
- Lower premiums for young, healthy individuals who do not require comprehensive coverage.
- Increased affordability for small businesses seeking employee coverage.
- Cons:
- These plans often lack essential benefits such as maternity care, mental health services, and prescription drug coverage.
- Individuals relying on these plans may face high out-of-pocket costs during emergencies or chronic conditions.
- Pros:
2. Relaxation of ACA Mandates
Trump's administration plans to roll back key ACA provisions that require insurers to offer standardized benefits.
-
What It Means:
- Insurers would no longer need to include essential health benefits in every plan, such as preventive care, mental health services, and hospitalization.
- The individual mandate, which penalized uninsured Americans, has already been removed under Trump’s earlier presidency.
-
Impacts:
- Pros:
- Flexibility for insurers to create plans tailored to specific demographics.
- Reduced costs for insurance providers, potentially lowering premiums for minimal coverage.
- Cons:
- Patients with pre-existing conditions or chronic illnesses may face difficulty accessing affordable, comprehensive care.
- Uninsured rates could rise due to a lack of enforcement of coverage.
- Pros:
3. Deregulation of Drug Pricing
The Trump administration’s approach to reducing prescription drug prices relies on market competition rather than government intervention.
-
What It Means:
- Policies aim to increase competition among pharmaceutical companies by loosening regulations and accelerating drug approval processes.
-
Impacts:
- Pros:
- Potential for lower drug prices in the long term due to greater competition.
- Faster access to new medications through streamlined approval processes.
- Cons:
- Risks of prioritizing speed over safety in drug development.
- Limited short-term relief for patients facing high costs for existing medications.
- Pros:
4. Medicaid Reform through Block Grants
Medicaid, a lifeline for low-income individuals, is set to undergo significant changes.
-
What It Means:
- Medicaid funding would shift from per-enrollee payments to block grants, providing states with fixed federal funding and greater autonomy.
-
Impacts:
- Pros:
- States gain flexibility to design Medicaid programs that suit local needs.
- Potential for innovative state-led healthcare solutions.
- Cons:
- States with limited budgets may reduce benefits or tighten eligibility, leaving millions without adequate coverage.
- Funding caps may not account for population growth or rising healthcare costs.
- Pros:
 Rising Medicare Costs in 2025: What American Seniors Need to Know Rising Medicare Costs in 2025: What American Seniors Need to Know |
Who Benefits from Healthcare Deregulation?
-
Young, Healthy Individuals
- Short-term health plans provide cheaper alternatives for those needing minimal coverage.
-
Small Businesses
- Association health plans allow employers to offer affordable insurance with fewer regulations.
-
Pharmaceutical Companies
- Deregulation fosters innovation and allows companies to bring new drugs to market faster.
-
State Governments
- Medicaid block grants provide flexibility to customize programs without federal mandates.
Who Faces Challenges?
-
Low-Income Families
- Medicaid funding cuts and stricter eligibility requirements could reduce access to healthcare.
-
Patients with Pre-Existing Conditions
- Without ACA protections, these individuals may face higher premiums or coverage denial.
-
Elderly and Chronically Ill Patients
- Deregulated plans may not cover essential treatments, leading to increased out-of-pocket expenses.
-
Women and Reproductive Health Advocates
- Reduced federal funding for reproductive services could limit access to contraception and family planning resources.
Overall Implications of Deregulation
-
Accessibility
- Deregulation may widen disparities between those with access to affordable care and those left without sufficient options.
-
Affordability
- While premiums may decrease for some, out-of-pocket costs for comprehensive care are likely to rise.
-
Innovation and Efficiency
- Free-market solutions encourage innovation and efficiency in the healthcare industry, but concerns remain over consumer protections.
-
State-Level Variability
- Healthcare outcomes will depend on how effectively individual states manage deregulated systems and Medicaid block grants.
♦ Summary Table: Biden vs. Trump's Healthcare Policies
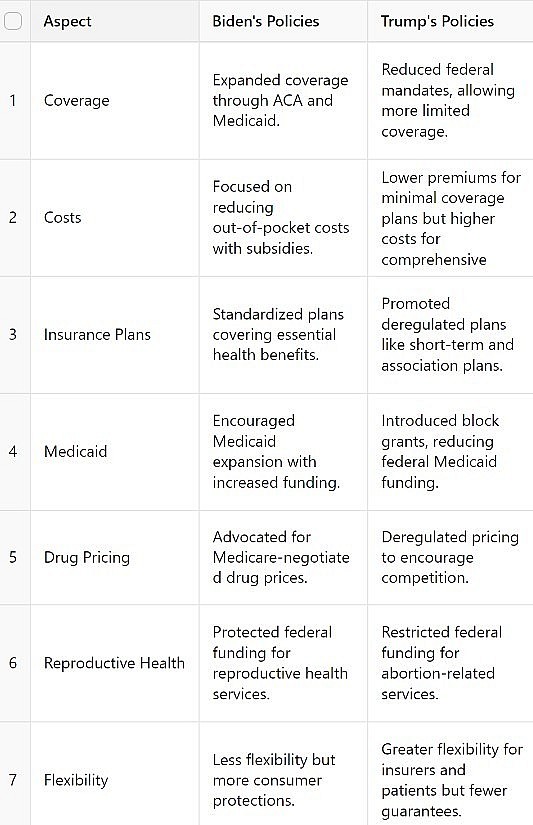 |
| Summary Table: Biden vs. Trump's Healthcare Policies |
Adapting to Trump’s Healthcare Policies
1. Explore Insurance Alternatives
- For Individuals: Evaluate plans carefully to understand coverage limitations. Short-term plans may be suitable for healthy individuals but inadequate for those with chronic needs.
- For Employers: Consider association health plans to offer affordable employee benefits.
2. Maximize Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- Utilize HSAs to save pre-tax money for healthcare expenses, providing a financial cushion against rising out-of-pocket costs.
3. Advocate for State-Level Solutions
- Engage in local advocacy to push for Medicaid programs that prioritize essential services and protect vulnerable populations.
4. Stay Informed
- Monitor policy changes and stay updated on healthcare options to make informed decisions.
How Trump’s Policies Could Affect Hospitals
Donald Trump’s healthcare policies, focused on deregulation, reduced federal oversight, and a market-driven approach, could significantly impact hospitals in the following ways:
1. Financial Pressure from Reduced Medicaid Funding
- Policy Changes: Transitioning Medicaid funding to block grants or per-capita caps reduces federal contributions.
- Impact on Hospitals:
- Hospitals in low-income areas, especially rural ones, may face increased financial strain as they treat more uninsured or underinsured patients unable to pay for care.
- Loss of Medicaid expansion funding may lead to fewer resources for uncompensated care, increasing the risk of closures for smaller hospitals.
2. Increased Demand for Emergency Care
- Policy Changes: Deregulated insurance plans may leave patients underinsured, leading them to rely on hospital emergency rooms for primary care.
- Impact on Hospitals:
- Higher volumes of non-emergency cases in ERs, causing overcrowding and increased operational costs.
- Reduced reimbursement rates if patients are uninsured or on low-coverage plans.
3. Shifts in Insurance Reimbursement
- Policy Changes: The promotion of short-term and association health plans could result in lower insurance reimbursements to hospitals due to limited coverage and stricter claims approvals.
- Impact on Hospitals:
- Reduced revenue from insurers, especially for high-cost treatments.
- Difficulty in sustaining specialized programs, such as maternity care or mental health services, which may not be covered under minimal plans.
4. Increased Competition from Privatization
- Policy Changes: Deregulation of healthcare markets could encourage private entities and urgent care facilities to expand, diverting patients away from hospitals.
- Impact on Hospitals:
- Greater competition for patients in profitable service areas (e.g., outpatient surgeries, imaging services).
- Hospitals may lose revenue from lucrative procedures while still shouldering the burden of high-cost emergency and chronic care.
5. Impact on Reproductive Health Services
- Policy Changes: Restrictions on federal funding for organizations providing reproductive health services, such as Planned Parenthood, could shift demand to hospitals.
- Impact on Hospitals:
- Increased patient volume for reproductive health services, potentially overwhelming existing resources.
- Ethical and political pressures on hospitals to navigate conflicting state and federal regulations.
6. Potential Innovation in Service Delivery
- Policy Changes: Reduced regulations might encourage hospitals to innovate and adopt cost-effective practices to stay competitive.
- Impact on Hospitals:
- Opportunity to streamline operations and invest in telemedicine, outpatient services, and other efficient care models.
- Hospitals with resources to adapt quickly could thrive, while those unable to compete may struggle or close.
7. Unequal Impact Across Hospitals
- Policy Changes: Market-driven policies favor well-funded institutions in urban areas while disadvantaging rural or underfunded hospitals.
- Impact on Hospitals:
- Larger hospitals or healthcare systems with diversified revenue streams may adapt and even benefit from deregulation.
- Smaller, rural hospitals are more likely to close, exacerbating healthcare access disparities.
Adaptation Strategies for Hospitals
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Focus on high-demand services while minimizing waste in operations.
- Expand Outreach Programs: Partner with community organizations to address gaps in uninsured or underinsured care.
- Invest in Telemedicine: Leverage technology to reduce costs and expand service access, especially in rural areas.
- Advocate for State Support: Collaborate with state governments to secure funding or tailored Medicaid programs.
Trump’s healthcare policies are likely to create significant challenges for hospitals, particularly those serving vulnerable populations. While some institutions may thrive by adapting to a deregulated market, others could face closures or financial strain, further deepening disparities in healthcare access.
How Deregulation Affects Patients in Healthcare
Deregulation in healthcare, a key focus of Trump’s policies, involves reducing federal oversight, relaxing insurance mandates, and encouraging market-driven solutions. While this approach offers benefits like lower premiums and increased flexibility, it also poses challenges for patients, especially those who rely on comprehensive care or public assistance.
1. Reduced Access to Comprehensive Coverage
- What Changes: Deregulated plans (e.g., short-term health insurance) are not required to cover essential health benefits such as maternity care, mental health services, or prescription drugs.
- Impact on Patients:
- Young, Healthy Individuals: Benefit from cheaper insurance options with limited coverage.
- Patients with Chronic Illnesses: May face difficulties finding affordable plans that cover necessary treatments.
- Pregnant Women: Limited coverage for maternity care may increase out-of-pocket expenses.
2. Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs
- What Changes: Reduced federal mandates allow insurers to offer plans with higher deductibles, co-pays, or coverage exclusions.
- Impact on Patients:
- Patients may struggle to afford routine care, preventive services, or treatments for chronic conditions.
- Out-of-pocket costs for medications, especially for rare or expensive treatments, are likely to increase.
3. Increased Difficulty for Individuals with Pre-Existing Conditions
- What Changes: Without ACA protections, insurers may charge higher premiums or deny coverage based on health history.
- Impact on Patients:
- Individuals with pre-existing conditions (e.g., diabetes, heart disease) may face limited or unaffordable options.
- Risk of medical debt rises for patients requiring frequent or ongoing care.
4. Unequal Access to Care
- What Changes: Medicaid block grants reduce federal contributions, giving states more control over healthcare programs but potentially limiting overall funding.
- Impact on Patients:
- Low-income individuals may lose access to Medicaid due to stricter eligibility criteria.
- Disparities between states could lead to unequal access to healthcare, with poorer states offering fewer services.
5. Limited Protections for Consumers
- What Changes: Relaxed regulations reduce oversight on insurance companies and healthcare providers.
- Impact on Patients:
- Consumers may face deceptive practices, such as plans that appear comprehensive but exclude key benefits.
- Increased reliance on out-of-network providers due to narrowed insurance networks.
6. Potential for Cheaper, Flexible Plans
- What Changes: Deregulation allows for the creation of affordable, customizable insurance plans tailored to individual needs.
- Impact on Patients:
- Healthy Individuals: Gain access to low-cost plans, particularly if they require minimal healthcare services.
- Older Patients or Those with Medical Needs: Face challenges balancing affordability and coverage adequacy.
7. Increased Reliance on Emergency Care
- What Changes: Underinsured patients may delay routine or preventive care due to costs, leading to increased use of emergency rooms for treatable conditions.
- Impact on Patients:
- Emergency rooms become overburdened, reducing efficiency and increasing wait times for all patients.
- Delayed care often results in more severe health issues and higher medical bills.
8. Prescription Drug Pricing Variability
- What Changes: Deregulation aims to increase competition among pharmaceutical companies rather than imposing price controls.
- Impact on Patients:
- Some patients may benefit from lower costs due to increased competition.
- Others, especially those reliant on expensive or rare medications, may see minimal relief.
Who Benefits from Deregulation?
- Young, Healthy Patients: Lower-cost, minimal coverage plans work well for those with infrequent healthcare needs.
- High-Income Individuals: Can afford flexible plans and out-of-pocket costs.
- Patients in Competitive Markets: May benefit from price reductions due to increased market competition.
Who Faces Challenges?
- Low-Income Families: Risk losing Medicaid coverage or access to affordable care due to funding cuts.
- Patients with Chronic Illnesses: May find fewer comprehensive plans or face prohibitively high costs.
- Elderly Patients: Higher out-of-pocket expenses for medications and long-term care.
Adapting to Deregulated Healthcare
- Research Insurance Plans: Understand what is and isn’t covered, particularly in short-term or limited plans.
- Utilize Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): Save pre-tax funds for medical expenses to offset rising costs.
- Advocate for State Programs: Support initiatives that expand coverage and maintain essential benefits.
Conclusion
Trump’s healthcare deregulation policies aim to increase market efficiency, reduce federal oversight, and provide more affordable options for certain demographics. However, these changes could also marginalize low-income families, women, and individuals with chronic health conditions. Striking a balance between innovation and equitable access will be critical in adapting to this new healthcare landscape. While the impacts will vary widely, proactive measures at both individual and state levels can help mitigate potential challenges and ensure better outcomes for all.
FAQs: Understanding Trump’s Healthcare Deregulation
1. What is healthcare deregulation?
Healthcare deregulation refers to reducing federal oversight and requirements in the healthcare system. It gives more control to states, insurers, and private entities, allowing for more flexibility but potentially less uniformity in care standards.
2. How will deregulation affect my health insurance options?
- If you’re young and healthy: You may have access to cheaper insurance plans, such as short-term or association health plans.
- If you have pre-existing conditions or need comprehensive care: Finding affordable coverage might become more challenging as fewer plans are required to meet ACA standards.
3. Will drug prices decrease under deregulation?
Trump’s policies aim to lower drug prices by increasing competition and accelerating drug approval. While this could reduce costs in the long term, immediate price reductions may not be significant for consumers.
4. How does Medicaid reform impact low-income families?
Medicaid reforms, such as block grants, allow states to design their own programs with fixed federal funding. However, states with budget constraints may reduce benefits, tighten eligibility, or limit access for low-income families.
5. What changes can I expect in reproductive healthcare?
- Federal funding for abortion services and family planning organizations may be restricted.
- Access to contraception and related health services could be reduced, especially in areas with limited local funding.
6. Who benefits most from healthcare deregulation?
- Young and healthy individuals: Benefit from cheaper insurance plans.
- Small businesses: Gain access to affordable insurance through association health plans.
- Pharmaceutical companies: Enjoy faster drug approvals and fewer restrictions.
7. Who is most negatively affected?
- Low-income families: Could lose Medicaid benefits or face stricter eligibility requirements.
- Patients with chronic illnesses: May struggle to afford or access comprehensive care.
- Women: Could see reduced access to reproductive health services.
8. What are Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), and how can they help?
HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts that allow individuals to set aside money for medical expenses. They are especially useful for those on high-deductible plans, as they can offset rising out-of-pocket costs.
9. How can I adapt to these changes?
- Research thoroughly: Understand your insurance options and the coverage they offer.
- Use HSAs: Save pre-tax money for medical expenses.
- Advocate locally: Push for state-level programs to fill gaps in federal funding.
10. What should I do if I lose Medicaid coverage?
- Explore alternative insurance options, such as subsidized plans through private insurers or short-term health plans.
- Seek community health centers or nonprofit organizations that offer free or low-cost healthcare services.
 Top 10 States With The Best Healthcare in the US Today Top 10 States With The Best Healthcare in the US Today Depending on where they live, some Americans have better health care options than others. If you want to learn more about which states have the ... |
 Why Is There No Universal Healthcare In The US Why Is There No Universal Healthcare In The US Universal healthcare does not exist in the US while the healthcare costs people have to pay are so high. Why is that? |
 10 Highest-Paying Healthcare Administration Jobs In The US Today 10 Highest-Paying Healthcare Administration Jobs In The US Today You aren't sure which 10 healthcare administration jobs in the United States pay the highest salaries. Take a look at the following list, which features ... |
 Top 10 Hottest Healthcare Trends To Rule The World In 2024 Top 10 Hottest Healthcare Trends To Rule The World In 2024 The healthcare industry is one that is always changing, with many new obstacles to overcome. Check out Top 10 Hottest Healthcare Trends To Rule The ... |























