Top 15 Oldest Countries In History: Ancient Egypt, India, Xia Dynasty and More
♦ Top 5 Countries With The Longest Names In The World
♦ Top 10 Countries Have the Most Nuclear Reactors in the World Today
 |
| Egypt - The Oldest Countries In Human History |
What is a Country or Nation?
Definitions of "country," "state," and "nation" vary and are often vague. While the idea of a country is universal, the idea of a sovereign state is not. The political administrative entity of a country may already be a federal state or another type of state, depending on the definition.
In this context, the term "country" refers to a geographically defined region under the control of a central authority that has at least some discretionary power over the governed populace.
This government need not be apolitical or immune to outside pressure. A federal state is an independent nation with its own set of boundaries, government, and taxes, but it nevertheless answers to a higher authority. Even "sovereign" governments frequently rely on the economic and political support of other nations.
Nations belonging to the United Nations are the ones who officially recognize a region as an independent state. It's important to note that they do not independently recognize or reject a state. Each participating nation is free to make its own choice in the matter.
Consequently, the question of how to designate these areas irrespective of political interests or interests under international law must be resolved before the concept of countries can even be discussed.
The term "nation" is used to refer to a territory, its government, and the people who live there, all of whom are sovereign under international law. Those who embrace the foundational culture and history of the country share the same legal, economic, cultural, religious, linguistic, and written obligations as those who reject it. control of the government, and they work together to create a shared future in the region they control.
State sovereignty is the primary focus of international law. The current count of nations is somewhere around 195. Definitions of "state status" and "state execution" are common categories used when talking about what constitutes a nation. The Convention on the Rights and Obligations of States, signed in 1933, is often cited as the starting point for any discussion of what constitutes a country (referred to as the Montevideo Convention).
This Convention is a regional convention among 16 nations in the Americas, rather than a global multilateral agreement. The 1933 Montevideo Convention is the only international legal agreement that offers a national definition, notwithstanding its restricted universality.
♦ How Many Countries and Territories Are There In the World 2023: Full List, More in the Future
Which Ancient Country Has the Earliest State in the World?
Humans appeared on Earth about 200,000 years ago and went through many stages: tribes, primitive communes, city-states... until the formation of nations about 5,000 years ago.
According to the book "The History of World Civilization", Egypt is the oldest country in the world. The state in Egypt has been around since about 5,000 BC. After Egypt, new states gradually formed in Mesopotamia, India, and China.
Egypt is one of the countries with a rather special position in the world. Its territory stretches across 2 different continents (Africa and Asia). Most of Egypt's territory is in North Africa, but its northeastern part is in the Middle East (West Asia).
| There's a difference between the oldest countries and the oldest civilizations. Many of the oldest civilizations such as Egypt, Iraq, Persia, Greece, China, and India were neither united nor independent for large portions of their history. |
Join Knowinsiders.com to discover the Top 15 earliest ancient countries in human history.
1. Ancient Egypt
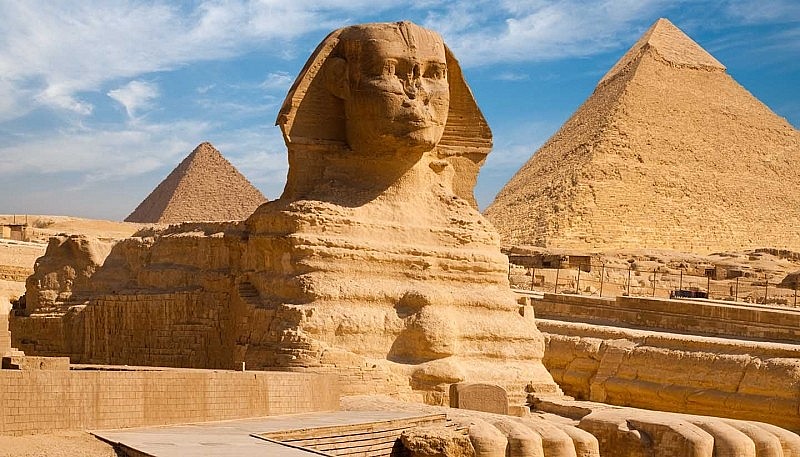 |
| Legacy left from ancient Egypt |
Topping the Top 15 ancient countries that appeared the earliest in human history is ancient Egypt. Ancient Egypt was officially unified from Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt with the ascension of the first Pharaoh around 3100 BC. The first pharaoh was named Narmer, commonly known as Menes.
The territory of ancient Egypt included a large area of Northeast Africa from the Nile basin to the Mediterranean. It was the fertile plains of the Nile River that created favorable conditions for people to focus on developing agriculture, thereby creating a new step in the development of human society.
Ancient Egyptian history includes major periods: Early Dynasty (3100-2686 BC), Old Kingdom (2686-2181 BC), First Intermediate (2181-2055 BC), Middle Kingdom (2055- 1650 BC), Second Intermediate (1650-1550 BC), New Kingdom (1550-1069 BC), Third Intermediate (1069-664 BC) and Late (664-332 BC). In it, ancient Egypt reached the peak of power, strength, and culture in the New Kingdom period, during the Ramsside period (English: Ramsey) (1186-1077 BC).
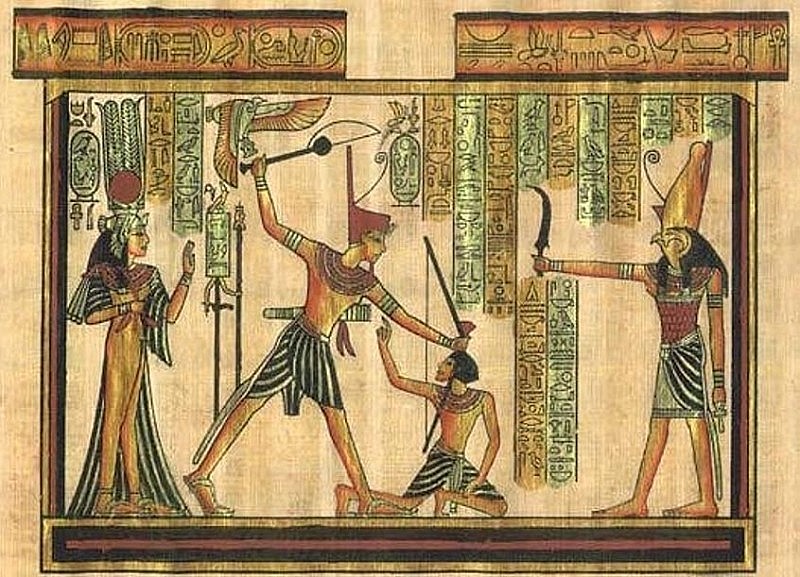 |
| Ancient Egyptian Society |
Ancient Egypt had many great civilizational achievements that are still preserved today. These are architectural works such as Pyramids, Sphinx, temples; the world's first primitive system of mathematics, early medicine, mummification, papermaking, and glassmaking. In particular, the most famous is the Giza Pyramid of Pharaoh Khufu - recognized by UNESCO as the 7 wonders of the ancient world.
 Top 3 Most Beautiful Female Pharaohs In Ancient Egypt's History Top 3 Most Beautiful Female Pharaohs In Ancient Egypt's History |
2. Ancient India
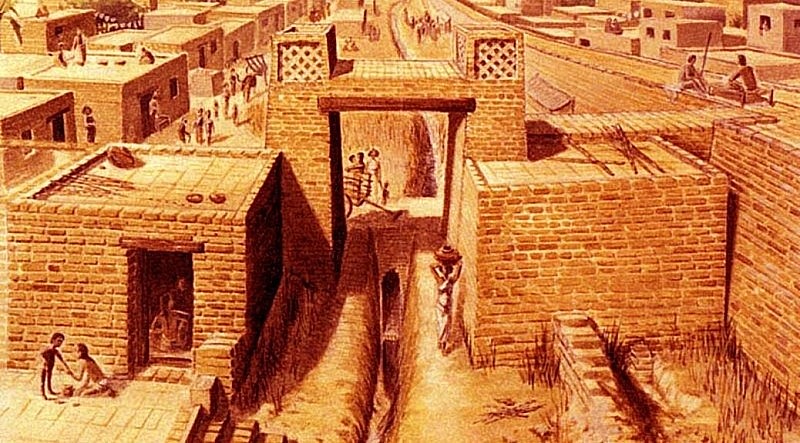 |
| Ancient Indian Society |
Scientists have found that the "cradle of Asia" is ancient India in the Indus basin around 3,000 BC.
According to the study, prehistoric humans appeared in India from about 200,000 to 500,000 years ago and modern humans settled in India at the end of the Ice Age, i.e. 12,000 years ago. The civilization of ancient India developed into a nation state around 3,000 BC. This civilization was distinguished by the construction of terracotta cities, sewers and multi-storey buildings.
Ancient Indian history experienced many events and overlapping stages, including an important historical milestone when the Aryans came down from the north, built the Vedic period in India. ancient. The pinnacle of this culture is the Vedas - the oldest surviving written text, written in 1,500 BC. Around 625 BC, a great Indian was born, that is Siddhartha Gautama, also known as Buddha, is Buddha Shakyamuni - the founder of Buddhism.
It can be said that ancient India had an extremely rich and strong religious culture, which has a profound influence until now, especially Buddhism is the most popular religion from South Asia to Asia.
3. Crete Island
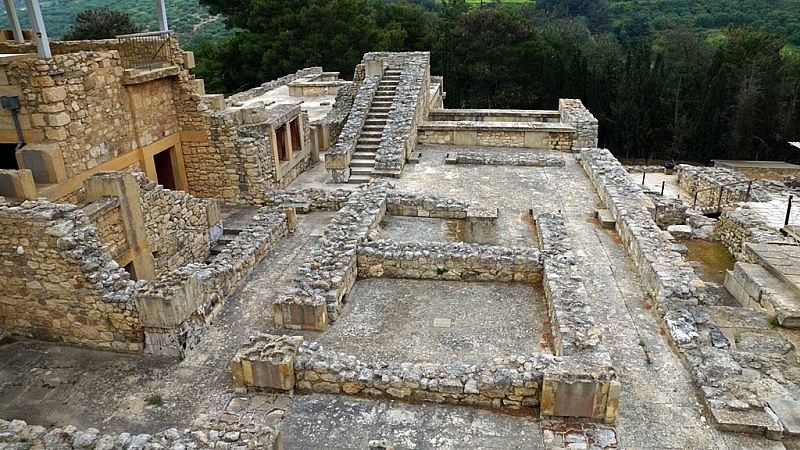 |
| Remains of the Ancient Civilizations of Crete |
Crete holds a significant place in history as the birthplace of ancient Greece. It was the pioneering land of advanced Western civilization and stands as the largest and most populous island in Greece.
Crete's civilization emerged in ancient times and eventually expanded throughout Greece, showcasing remarkable progress during the reign of the Minos civilization around 2,700 BC.
They have gained renown for their pioneering spirit and remarkable advancements in the maritime industry, thanks to their advantageous geographical position at the crossroads of major trade routes.
Crete's history, unfortunately, lacks the detailed records that historians crave. As a result, it has become intertwined with Greek mythology, with tales of legendary figures like Kings Minos, Theseus, and the fearsome Minotaur. These stories were passed down through the ages and immortalized by Homer, the renowned poet of ancient Greece around the 8th century BC. In the course of time, Crete became integrated into the realm of Ancient Greece.
4. Akkadian Empire
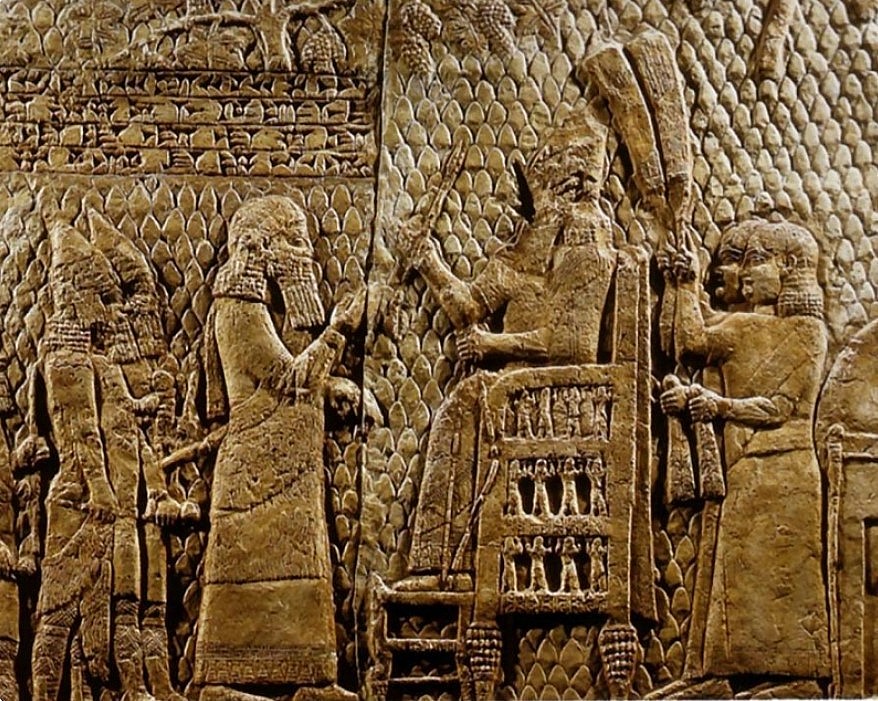 |
| Legacy from the Akkadian Empire |
The Akkadian Empire holds a significant place in history as the first Semitic-speaking ancient nation, and its mention in the Bible further solidifies its importance.
During the 3rd millennium BC, there was a fascinating intercultural exchange between the Sumerians and Akkadians, leading to a gradual shift in dominance from the Sumerian culture to the Akkadian culture. The Akkadian Empire emerged around 2334 BC and endured until approximately 2154 BC.
Located in Mesopotamia, the Akkadian Empire held its capital in the two countries of Syria and Iraq. The empire's reach extended to neighboring lands, including Bahrain, Oman, and parts of modern-day Arabia.
The Akkadian Empire marked the transition from city-states to nation-states in Mesopotamia, a significant development in one of the earliest civilizations.
The Akkadian Empire commenced with the conquest of King Sargon and concluded with King Shu-turul.
The Akkadian Empire paved the way for other renowned ancient empires, such as Assyria and later Babylon.
5. Xia Dynasty - China
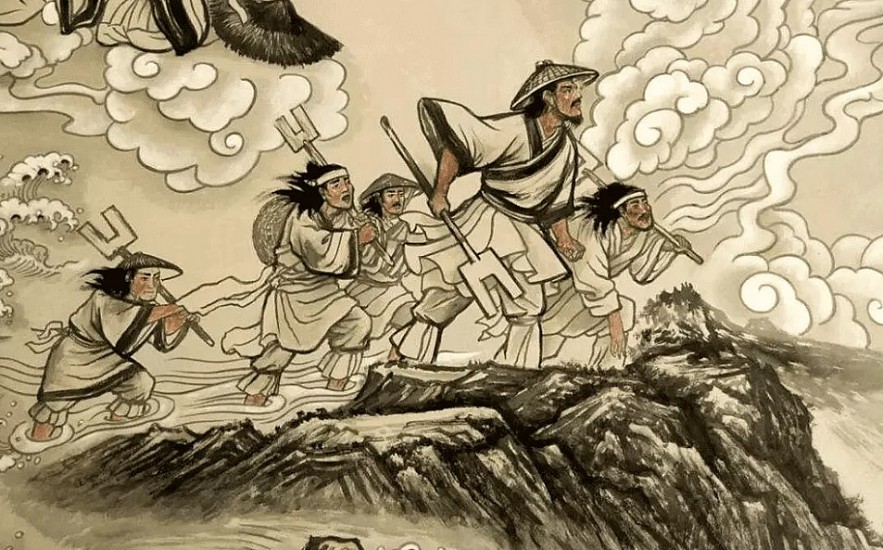 |
| The first Chinese dynasty was the Xia dynasty |
The records and existence of the Xia Dynasty (2070-1600 BC), China's earliest dynasty, have been a subject of ongoing debate. Chinese history suggests that a significant number of individuals can trace their lineage to the Beijing-Tianjin-Yellow River region in eastern China, despite the belief held by some that their ancestors originated from various parts of the world.
According to historical records, this dominion is said to have endured for a span of 400 years until it was eventually conquered by the Shang Dynasty in the year 1600. Examining historical documents and stories from over two thousand years ago provides a glimpse into the fascinating world of ancient culture.
During the period from 2070 to 1600 B.C., the Xia Kingdom experienced a period of prosperity. Extensive archaeological findings in the Yellow River Basin provide valuable insights into the various civilizations that thrived in this region. According to historical evidence, the presence of the Han people and their civilization can be traced back to approximately 4000 years ago in the region. Throughout history, researchers have dedicated themselves to deciphering the mysteries of ancient artifacts, hoping to uncover clues about their origins. However, the true origins of these finds continue to elude us, hidden within the intricate tapestry of historical mythology.
Experts in the field have a general understanding of the region where the Han civilization originated. However, there is ongoing debate among scholars regarding the specific details such as the exact location and timeline of the Han's rise along the middle and lower stretches of the Yellow River. For instance, the archaeological evidence regarding the origins of the Han is quite unclear. Despite the discovery of artifacts dating back over 3,500 years in the river basin area, the origins of the Han people have yet to be definitively identified by archaeologists.
In the middle Yellow River Valley, you can find traces of the Jiahu people, who lived from 7000 to 6600 B.C., and the Yangshao people, who thrived from 5000 to 3000 B.C. Settling along the shore in the lower sections of the river basin, the Qingliangang people established their presence during the period from 5400 to 4000 BC. The identity of these early ancestors of the Han people remains shrouded in mystery, as no written records documenting their existence have been found.
During the intermediate reaches, there was a thriving civilization known as the Longshan culture, which spanned from 3000 to 2000. Meanwhile, in the lower reaches, another culture called the Dawenkou culture (4300 to 2500) coexisted, but with distinct values and practices. Nevertheless, the absence of written records among their remains and artifacts makes it difficult to determine whether these individuals were indeed the ancestors of the Han.
6. Assyrian Empire
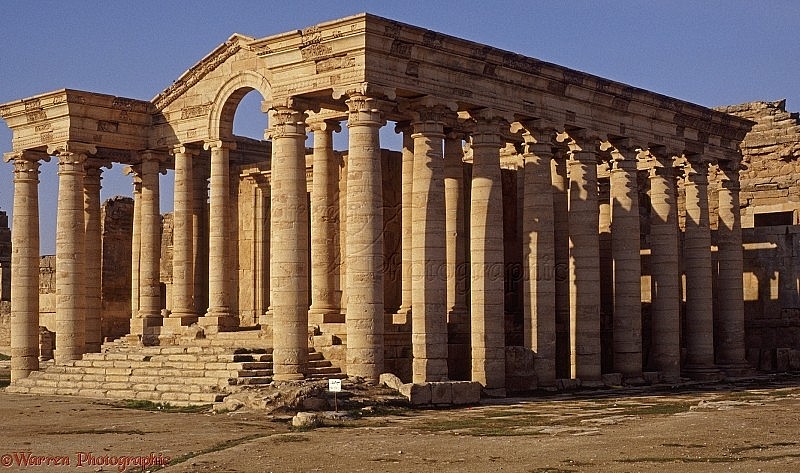 |
| Legacy from the Assyrian Empire |
When discussing the earliest civilizations in human history, it is impossible to overlook the significance of the Assyrian Empire. This empire was a formidable force during ancient times, leaving a lasting impact.
When the Akkadian Empire fell, the Assyrian Empire came to possess a vast expanse of Mesopotamia. During the reign of the Akkadian Empire, Assyria held the status of a relatively minor vassal state in close proximity. In the wake of the Akkadian Empire's collapse, Assyria experienced a gradual rise, engaging in fierce competition with other powers and ultimately evolving into the formidable Assyrian Empire around 2,000 BC. Located at the headwaters of the Tigris River, in northern Mesopotamia, the heart of the Assyrian Empire thrived in what is now northern Iraq.
After the Akkadian Empire crumbled, a multitude of powers emerged, vying for dominance. These included the Assyrian Empire, the Hittite Empire, and ancient Babylon.
Throughout history, the Assyrian Empire experienced significant growth, becoming a formidable force that rivaled both the Hittite Empire to the north and ancient Babylon to the south. During the reign of King Shamshi-Adad I (1813-1791 BC), the Assyrian Empire experienced a period of great prosperity. However, in 1756 BC, the empire was conquered and dominated by ancient Babylon. It wasn't until later, during the revival of the Assyrian Empire (911-609 BC), that they were able to reclaim their power and once again conquer and rule over Babylon. During this time, the Assyrian Empire experienced its peak of prosperity, as it extended its reach across Mesopotamia, reaching as far as Asia Minor and the Mediterranean.
The downfall of the Assyrian Empire can be attributed to its extensive territory and numerous colonies. As the empire grew larger and more difficult to manage, it eventually succumbed to defeat at the hands of its own colonies, such as Babylon, Scythia, Persia, and Yugoslavia.
7. Ancient Babylon
 |
| The Legacy of the Hanging Gardens of Ancient Babylon |
As per historical records, Babylon was initially a fortified city during the reign of the Akkadian Empire.
Following the decline of the Akkadian Empire, the territories once under its rule underwent a transformation, eventually giving rise to various ancient civilizations such as Babylon, the Assyrian Empire, and the Hittite Empire.
In 1894 BC, the Assyrian Empire set its sights on invading Asia Minor, leading to the emergence of ancient Babylon as an independent power. Located in present-day Arabia, about 85 kilometers from the Iraqi capital Baghdad, Ancient Babylon holds a significant place in history.
During the period from 1770-1670 BC, Ancient Babylon held the distinction of being the largest city in the world. It was the first city to have a population exceeding 200,000, and it is renowned for its iconic Hanging Gardens, which have been recognized by UNESCO as one of the 7 Wonders of the Ancient World.
In the annals of ancient Babylon, there emerged two distinct eras of dominance. The initial period, spanning from 1770 to 1670 BC, witnessed the mighty Babylonian empire triumphantly subjugating both the Assyrian Empire and, subsequently, enduring a period of counter-conquest by the Assyrians. During the period of 612-550 BC, ancient Babylon experienced a renaissance, commonly referred to as the Neo-Babylonian period.
In the era of King Nebuchadnezzar II of New Babylon, the mighty empire of ancient Babylon extended its reach to Jerusalem, resulting in the enslavement of numerous Jews. In 539 BC, ancient Babylon experienced a significant event when it was invaded by Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Persian Empire. This invasion marked the complete downfall of ancient Babylon.
8. Hittite Empire
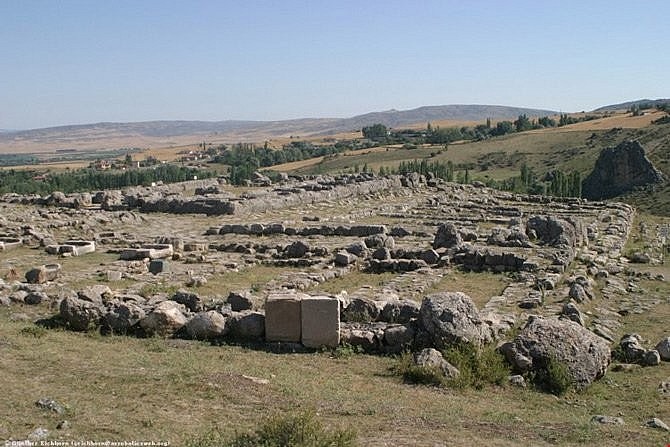 |
| Hattusa, the capital of the Hittite Empire |
The Hittite Empire emerged as one of the three empires that rose to power in Mesopotamia following the collapse of the Akkadian Empire. The formation of the Hittite Empire can be traced back to approximately 1600 BC, in the area of North Mesopotamia which encompasses present-day Turkey, Syria, and Lebanon.
During the 14th century BC, the Hittite Empire reached its pinnacle, engaging in numerous conflicts with Egypt and the Assyrian Empire as they vied for dominance over the Near East. The Hittite Empire, although not enduring as long as ancient Babylon and the Assyrian Empire, met its demise in 1,178 BC. It disintegrated into various independent cities before ultimately succumbing to the dominance of the Assyrian Empire.
9. Ancient Carthage
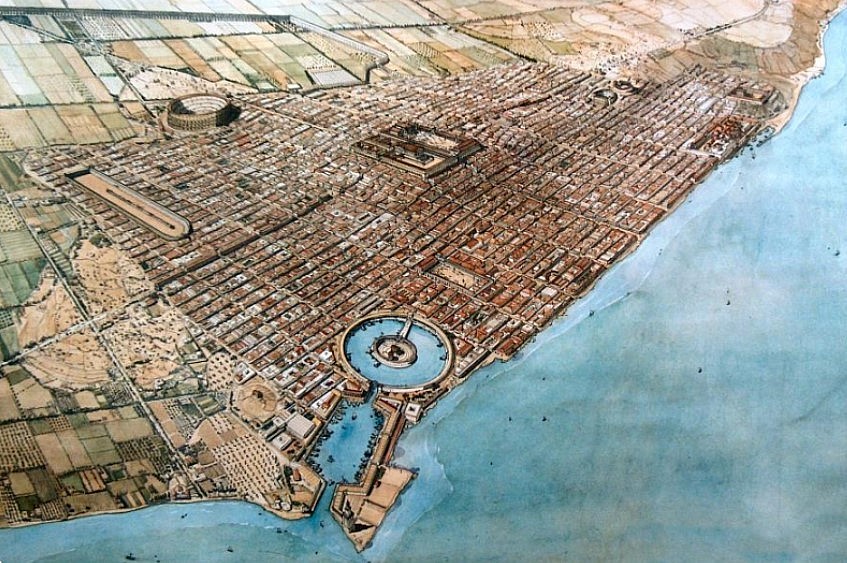 |
| Ancient Carthage |
Established in the year 814 BC, Ancient Carthage, also referred to as the Carthaginian Kingdom, came into existence.
Throughout its existence, Carthage controlled vast territories along the northern coast of Africa, reaching into the regions of France and Spain that would eventually fall under Roman rule. During that era, ancient Carthage emerged as a formidable nation, engaging in conflicts with ancient Greece and eventually contending with the mighty Roman Empire.
Throughout history, Carthage and the Roman Empire engaged in fierce battles, sparking a series of three Punic Wars. The Romans referred to the Carthaginians as "Punic" due to their Phoenician ancestry.
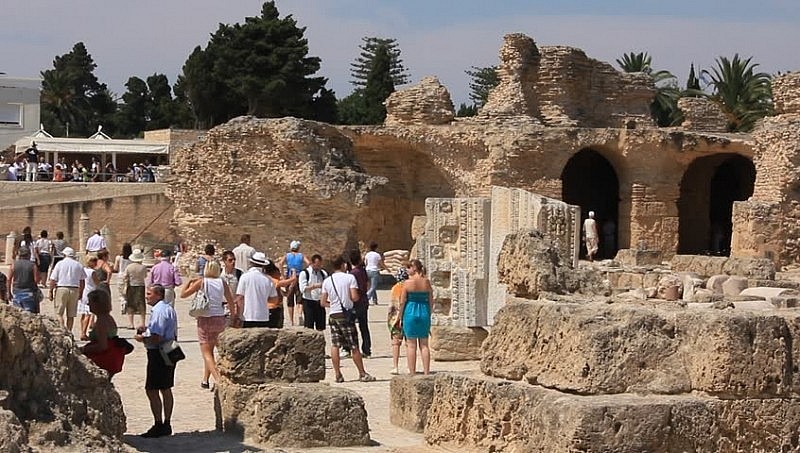 |
| Remains of Ancient Carthage |
At the end of the Third War, after more than a hundred years and the deaths of hundreds of thousands of soldiers on both sides, the Roman Empire conquered ancient Carthage and razed the city. Ancient Carthage ended in 146 BC.
10. Ancient Greek
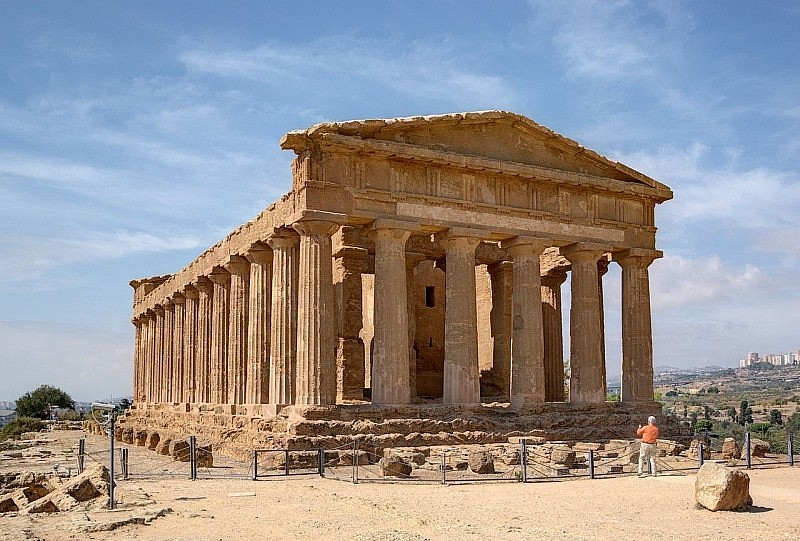 |
| Famous historical site left from ancient Greece |
With its roots in the island of Crete, the ancient European civilization gradually expanded its influence to the Mediterranean region, giving rise to the flourishing civilization known as Ancient Greece.
Ancient Greece stands as a truly emblematic civilization. These are the top 15 countries that emerged in the earliest stages of human history.
Throughout history, there existed city-states, but it wasn't until around 800 that Ancient Greece experienced a period of flourishing after enduring the dark ages. Athens occupies a significant position and is widely regarded as the capital of ancient Greece. Another renowned city, on par with Athens, is Sparta - a city known for its fierce warriors.
The ancient Greek civilization flourished with remarkable architectural works and sculptures. It also served as the birthplace of the Olympic Games, which have now evolved into the largest sporting event in the world. When discussing ancient Greece, it is impossible to overlook Greek Mythology. This rich collection of folk tales encompasses stories about the gods, kings, and heroes of ancient Greece, passed down through generations by folk and troubadours. Ancient Greek poet.
In Homer's notable works, the Iliad and the Odyssey, we are transported back in time to witness the ancient Greek army, under the command of King Agamemnon, embarking on a momentous journey to besiege Troy. These epic tales also recount the arduous journey of the hero Ulysses as he makes his way back to his homeland after enduring years of warfare in Troy. These two works have established themselves as timeless classics and hold a significant place in the realm of world literature.
Throughout history, Ancient Greece has been renowned for its pivotal role in the development of Western philosophy and mathematics. This remarkable civilization produced a multitude of brilliant minds, including Euclid, Archimedes, Thales, Socrates, Plato, and Aristoteles... They were all mathematicians, renowned figures in the ancient world who made significant contributions to the fields of mathematics and philosophy.
During that period, Ancient Greece held a position of great influence and strength in the Mediterranean region. Throughout ancient times, the vast expanse of the Greek colony extended from the southern reaches of the Black Sea, spanning across Central Europe, all the way to Eastern Europe and neighboring Asia Minor. Nevertheless, ancient Greece faced formidable challenges during that era, including the invasion of the Persian Empire under the leadership of Emperor Xerxes.
With the backing of Sparta under the leadership of Leonidas I, Athens strategically withdrew from the impending Persian Empire's assault. This move allowed Ancient Greece to launch a remarkable counterattack, successfully defeating the Persian Empire both on the island and the mainland, reclaiming their lost territories.
Ancient Greece was conquered by Alexander the Great, who led the powerful Macedonian Empire. Regarded as a prominent figure in the annals of history, Alexander the Great left an indelible mark as a military genius. Through his conquests, he transformed the once modest Macedonian Empire into a formidable power, extending his dominion over ancient Greece, as well as the vast Persian and Egyptian Empires. In the course of time, Ancient Greece became integrated into the Roman Empire, as the latter rose to prominence as the dominant force in Europe.
11. Macedonian Empire
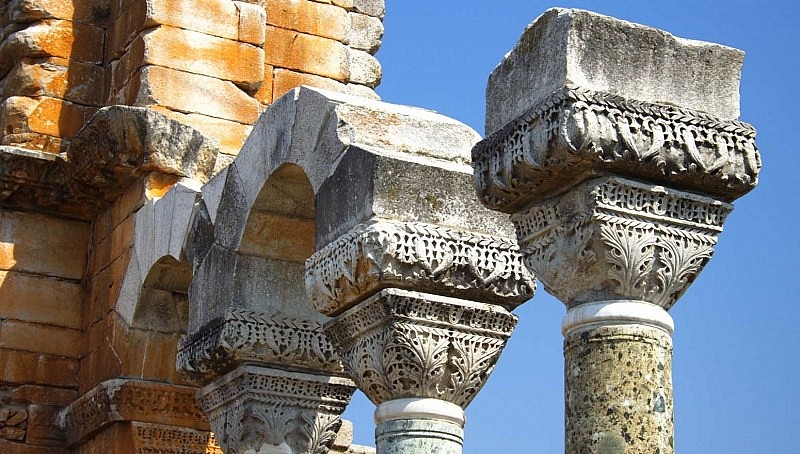 |
| Remains from the Macedonian Empire |
In the beginning, Macedonia was a modest territory that had been settled by ancient Greece. Greek immigrants settled in this region and engaged in land disputes with the native Macedonians. Following this, Macedonia transformed into a city-state and eventually gained autonomy as a sovereign entity situated in the northern region of Ancient Greece.
The establishment of the Macedonian Empire dates back to the 7th century BC, however, it was during the reign of King Phillip II that the empire truly gained significant strength and influence. In the annals of history, the formidable Macedonian Empire emerged as a dominant force, gradually asserting its control over numerous city-states of ancient Greece. Aiming to expand his dominion further, Philip II of Macedon set his sights on annexing the entirety of ancient Greece. However, fate intervened cruelly, as his grand ambitions were cut short by a tragic assassination before they could be fully realized.
Alexander the Great inherited the immense power of the Macedonian Empire. As Alexander the Great expanded his conquests, he set his sights on the nations of Asia Minor, ultimately bringing the Persian Empire and the southern region of Egypt under his control. During that period, the Macedonian Empire had gained control over a significant number of major countries in Europe and Africa.
Following the demise of Alexander the Great, the Macedonian Empire descended into a state of chaos and prolonged internal conflict. During this period, the Roman Empire emerged as a formidable force, ultimately conquering the Macedonian Empire in 168 BC. The Macedonian Empire was then officially incorporated into the Roman province in 149 BC, signifying the downfall of this once mighty empire.
12. Roman Empire
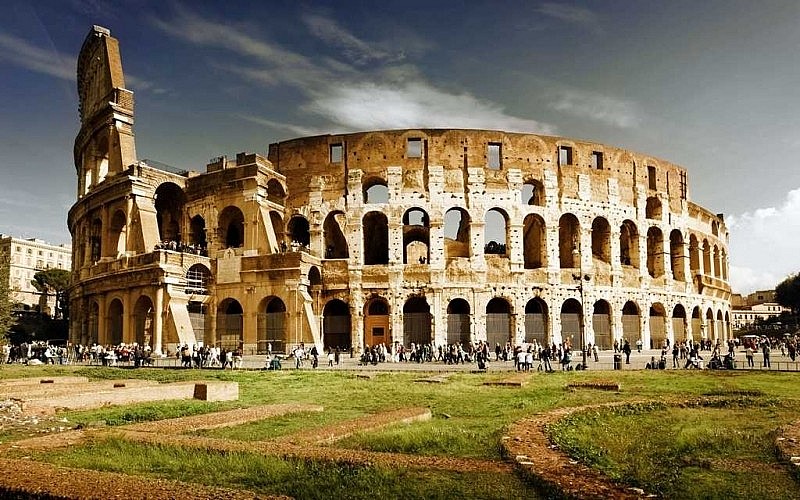 |
| Remains from ancient Roman times |
The Roman Empire originated on the Italian peninsula in 753 BC. According to historical accounts, the inaugural ruler of the Ancient Roman Empire was Romulus, who bestowed his name upon the city of Rome. In the ancient period, there were a total of 7 kings who ruled before the last king of Tarquin was overthrown in 510, marking the transition into the republic phase and the beginning of a new era for the Roman Empire.
During the era of the republic, a notable development was the emergence of the principle of separation of powers within the republican system. The Senate assumed the authority to make decisions, while the leadership was shared between two consuls who held equal power. This institution is a crucial aspect of contemporary modern politics, serving as a safeguard against excessive authoritarian power.
During the republic era, the Roman Empire significantly grew its territory by triumphing over Carthage, Macedonia, Greece, and the northern barbarians in regions that now encompass England, France, and Germany. Julius Caesar, a renowned figure in the Roman Empire, held a prominent position as one of the consuls, alongside Pompey Magnus. Alongside another formidable figure, Marcus Crassus, these three individuals came together to establish what is known as the First Triumvirate.
With the demise of Crassus, the Triumvirate met its end, paving the way for Julius Caesar to emerge victorious over Pompey Magnus and claim ultimate power over the Roman Empire. In a significant turn of events, Julius Caesar took on the title of "Dictator for Life", a decision that ultimately led to the downfall of the republic.
Shortly thereafter, Julius Caesar met his untimely demise in the Senate. In the annals of history, the Roman Empire witnessed a momentous division, giving rise to three prominent figures: Caesar Augustus, the adopted son and designated successor of Julius Caesar; Mark Antonius, the esteemed supreme general and trusted confidant of Julius Caesar; and Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, a distinguished Roman nobleman. These three individuals came together to establish the 2nd Tam Hung Alliance.
Following Aemillus Lepidus' defeat, Julius Caesar assumed control of Rome, compelling Mark Antony to retreat to Egypt. In his quest for power and love, Marcus Antonius found himself entangled in a tumultuous marriage with Queen Cleopatra. Despite his valiant efforts to defend against Rome's attacks, his ultimate downfall was inevitable. In the annals of history, the mighty Roman Empire expanded its dominion to encompass both Egypt and saw the rise of Caesar Augustus as its inaugural emperor, marking the end of the republic.
Caesar Augustus's significant constitutional changes transformed the Roman Empire into an imperial state, even though a considerable portion of the colony had been under Roman control since the days of the republic. In the imperial period, the Roman Empire had dominion over a vast territory that spanned across Europe, encompassing Western Europe with countries like England, France, and Germany, as well as Spain, Portugal, Italy, Greece, and even extending to North Africa, including Egypt, and Asia Minor, all the way to Jerusalem, which is now known as Israel and Palestine.
The Roman Empire stands as a testament to a remarkable civilization, boasting renowned structures like the Colosseum of Rome. Throughout history, the Roman Empire left a lasting impact on humanity with its sophisticated political and legal system, which served as the foundation for Western politics. Additionally, the empire made significant advancements in military science, leaving behind a rich legacy. The literature and mythology of the Roman Empire was heavily influenced by Greek culture, with Latin letters being adopted as the writing system. These Latin letters have since become the foundation of the modern language, which is now widely spoken in various countries, including Vietnam. In the context of history, it is worth noting that during the time of the Roman Empire, there emerged a significant individual who hailed from Jerusalem and embarked on a mission to spread his teachings. This individual, known as Jesus Christ, played a pivotal role in the birth and subsequent rise of Christianity. Today, Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism are among the most prominent religions globally.
The collapse of the Roman Empire was a result of various factors, including the expansion of colonies beyond control, the discontent among the people, particularly the Barbarian uprising and the Viking attack in the Northern region. Additionally, the rise of Christianity also played a role in the decline of the Roman Empire. The Roman Empire underwent a significant division in 285, resulting in the establishment of the Eastern and Western Roman Empires. Over time, these colonies eventually evolved into various nations, including England, France, Prussia, and others. Additionally, the Empire faced significant conflicts, such as the Holy War with the Kings. Islam emerged in the Middle East, marking the beginning of a significant era in Europe's history.
The Roman Empire is widely regarded as one of the most formidable empires among the earliest civilizations in human history.
13. Persian Empire
 |
| Remains from the Persian Empire |
The Persian Empire held immense influence in ancient West Asia, establishing itself as a formidable force. In 550 BC, Cyrus the Great established the Persian Empire, which swiftly conquered the ancient city of Babylon. From that point forward, the rulers of the Persian Empire adopted the title "Kings of Kings." During the reign of Darius I, the Persian Empire achieved a remarkable feat by becoming the first Asian empire to conquer Europe. In the time of Xerxes I, the Persian Empire engaged in conflict with ancient Greece and launched an assault on the city of Athens. However, they were ultimately forced to withdraw due to a fierce counterattack by the ancient Greeks. Similar to a historian, it is worth noting that the formidable army of the Persian Empire possessed a unique advantage - their strategic utilization of a significant number of elephants in warfare, which greatly enhanced their destructive capabilities.
During its peak, the Persian Empire held immense power, surpassing even the vastness of ancient Greece. Throughout history, the Persian Empire emerged as a remarkable force, successfully unifying and exerting its influence over the vast expanse of the Middle East and West Asia. This empire brought about a sense of order and organization to the region, leaving a lasting impact. The Persian Empire constructed numerous awe-inspiring cities, reflecting a deeply rooted Middle Eastern culture. The culture of the Persian Empire had a profound impact on regions spanning from the Middle East and West Asia to North Africa, India, and even China.
In 330 BC, the Persian Empire met its downfall as Darius III suffered a defeat at the hands of Alexander the Great. Throughout the course of history, the Persian Empire underwent various transformations. It eventually became a part of the Macedonian Empire, only to regain its independence and form Parthia after the Roman Empire triumphed over Macedonia. In the course of history, Parthia and the Sassanid Empire, also referred to as the Neo-Persian Empire, emerged as significant forces in the Middle East, engaging in conflicts with the Roman Empire. During the Neo-Persian Empire, the Roman Empire held a position of equality, with the Roman Emperor even referring to the Emperor of New Persia as "Brother". After the Muslim armies launched their attack in 651, the New Persian Empire met its downfall. Iran was the neighboring country to the current Persian Empire.
14. Ancient Korea
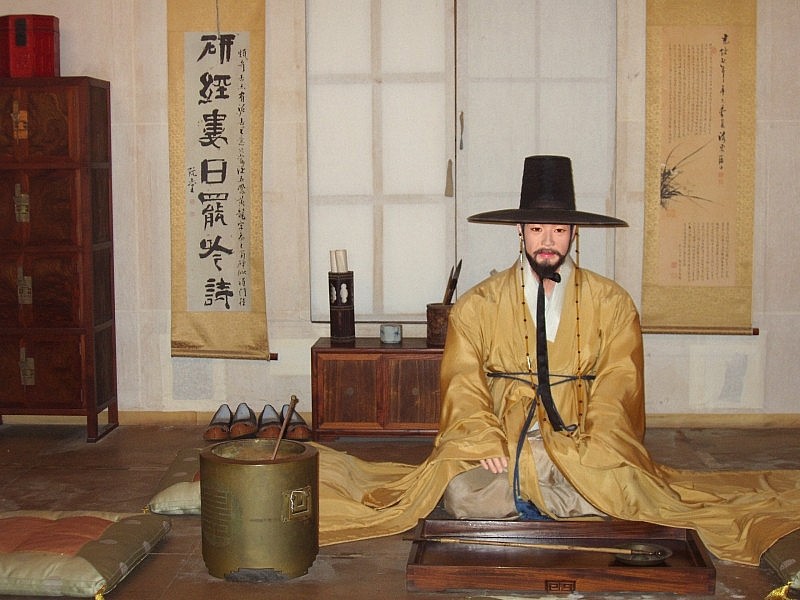 |
| Paintings of people in Ancient Joseon |
Gojoseon was an ancient nation that spanned the peninsula of East Asia, encompassing the territories of present-day South Korea and North Korea.
Legend has it that Gojoseon was established in 2333 BC, although historians believe that these were likely just tribes. The state of Gojoseon, as we understand it, was founded around the 4th century BC. It was during this time that Gojoseon declared itself a dynasty and engaged in warfare with the Zhou dynasty of China. In ancient times, the culture of China played a major role in shaping the history of Joseon. Additionally, there were instances when China engaged in military actions and exerted control over the region.
Throughout its rich history, Ancient Joseon experienced numerous transformative periods, marked by the rise and fall of various dynasties and interactions with neighboring nations. One of the most renowned among these was the illustrious Goguryeo. At a later point, it fell under the occupation of Japan. After its liberation, the Korean peninsula was split into two separate nations, North Korea and South Korea, as it remains today. Gojoseon, being one of the earliest countries in East Asia, holds a significant place in history, alongside China.
15. Aksumite Kingdom
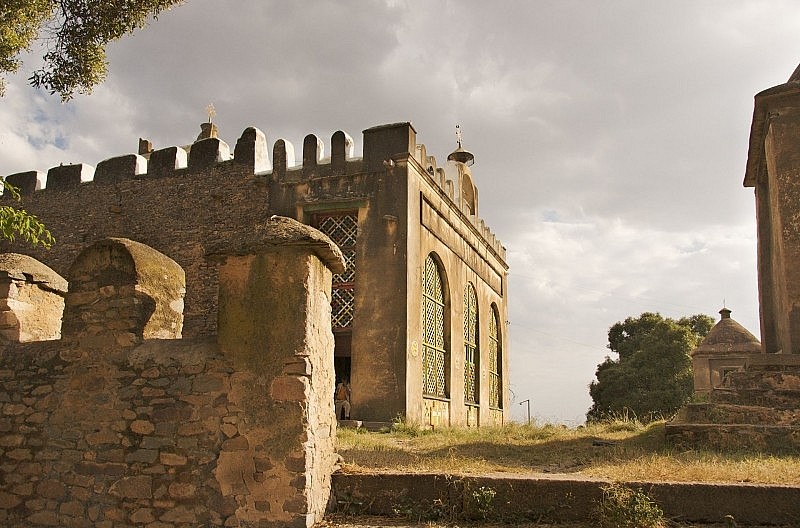 |
| Aksumite Kingdom |
The Aksumite Kingdom, which appeared early in human history, is ranked last among the Top 15 ancient countries. The Aksumite Kingdom, situated in North Africa, specifically present-day Ethiopia, holds a significant place in ancient history.
The Aksumite Kingdom had a remarkable lifespan, spanning from 100 BC to 940. During its time, the Aksumite Kingdom held great importance as a nation and managed to avoid the Roman Empire's assault thanks to its secluded position and considerable sway in North Africa. Formed a strong diplomatic relationship with the Roman Empire.
During ancient times, the Kingdom of Aksumite played a crucial role as a hub for trade and commerce, connecting the Roman Empire with various South and East Asian nations like India and China.
 Top 12 Most Mysterious Deaths In The World History Top 12 Most Mysterious Deaths In The World History In the world history, some famous people died without clear reasons. The reasons behind their deaths have been so far mysteries. Check out Top 10 ... |
 17 Mightiest & Longest-Lasting Empires In Human History 17 Mightiest & Longest-Lasting Empires In Human History Human history has produced many great empires through different periods, of which the 17 most powerful and longest-lasting empires stand out in general. |
 Top 13 Most Creepy And Mysterious Mysteries That Have Finally Been Explained Top 13 Most Creepy And Mysterious Mysteries That Have Finally Been Explained There have been lots of creepy mysteries about specific people and places on Earth. Some happened accidentally, making haunted stories. Others happened for reasons. |
 The Great Mysteries in History That Are Still Unsolved The Great Mysteries in History That Are Still Unsolved The city of Helike completely disappeared, the fall of the Minoan Empire, the disappearance of a Roman legion... are the greatest mysteries in history, which ... |
 Top 7 Biggest Unsolved Mysteries on the Planet of All Time Top 7 Biggest Unsolved Mysteries on the Planet of All Time The Earth has many mysteries that make us extremely surprised while scientists have not been able to explain why. Let’s discover the most mysteries phenomena ... |

























