17 Mightiest & Longest-Lasting Empires In Human History
 Top 5 Most Powerful Empires In History of the World Top 5 Most Powerful Empires In History of the World Throughout long human history, there are 5 most powerful and popular empires. Check out full details. |
 |
| Mightiest & Longest-Lasting Empires |
Throughout the history of mankind, hundreds of empires have arisen all over the world. Empires rise strongly and then decline as an inevitable law of human history.
People can learn a lot from the achievements and mistakes of the great empires created in the past.
1.Macedonian Empire (800 BC – 146 BC)
The Macedonian Empire was the name of an ancient kingdom in the north of Greece, bordered to the west by the kingdom of Epirus and the territory of Thrace to the east.
This kingdom was once a historical power in the Near East after Alexander the Great (also known as Alexander the Great) conquered most of the major countries in the world, beginning to form the Hellenistic period. in Greek history.
Alexander III of the Macedonian Empire, known as Alexander the Great, Alexander or Alexander (July 356 BC – June 11, 323 BC) was the 14th King of the Argead dynasty in the Macedonian kingdom (July 356 BC – June 11, 323 BC) period 336 BC - 323 BC).
And is considered one of the most successful generals in history, who conquered almost the entire world he knew before his death.
He is often considered one of the greatest military strategists in history.
Following the unification of the ancient Greek (Greek) city-states under the rule of his father Philip 2. Alexander conquered the Persian (Persian) empire. Including Asia Minor, Syria, Phoenician, Egyptian and all of ancient Mesopotamia and extending the frontiers of his empire as far as Punjap.
2.First Persian Empire (550 BC - 330 BC)
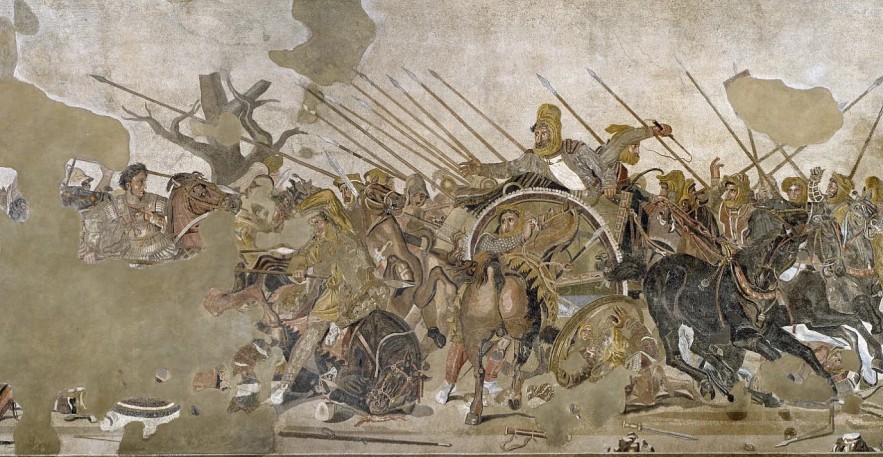 |
| The Battle of Issus between Alexander the Great and Darius III in 333 BC, leading to the fall of the Persian Empire. Leemage/Corbis/Getty Images |
The Achaemenid Persian Empire was founded by Cyrus the Great around 550 BC. This king has the title King of Kings (Shahanshah). Although the Persian Empire ended tragically at the hands of Alexander the Great (of the Kingdom of Macedonia) in 330 BC, it left a lasting legacy for the later development of civilizations. world and future empires. The Persian Empire was a key empire in human history, because it was the first real empire – it set the standards for what empires to be like for future empires.
The aforementioned Persian empire existed at a unique time in history, when much of the inhabited civilized world was concentrated in or near the Middle East. As a result, the Persian Empire, when it ruled most of the Middle East at the time, also ruled a larger proportion of the world's population than any other empire in history. Specifically, in 480 BC, this empire had a population of approximately 49.4 million people, equal to 44% of the world population at that time.
The Persian Empire was the first to connect many regions of the world, including the Middle East, North Africa, Central Asia, India, Europe, and the Mediterranean region. This empire gave rise to the concept of empire in places like Greece and India.
Such a large empire could only be gathered through military might. The military achievements of the Persian Empire were remarkable, though they were often forgotten due to the empire's sudden defeat to the armies of Alexander the Great. Various Persian campaigns conquered many of the advanced civilizations of the world then such as Babylon, Lydian, Egypt, and the Hindu region of Gandhara located in present day Pakistan.
Excluding exaggerations and misinterpretations, the Persians still believed that they had achieved their goals in Greece and that there were more Greeks living in the Persian Empire than outside.
The Persian Empire ushered in a period of harmony and peace in the Middle East for 200 years – a feat rarely repeated.
In terms of imperial concepts, the legacy of the Persian Empire to the world included the use of a network of roads, a postal system, a unified administrative language (Aramaic was used throughout the empire). regime), self-government for minorities, and a bureaucracy. The Persian religion – Zoroastrianism – influenced the development of key concepts such as free will, heaven and hell in the Abrahamic religions to Judaism.
3.Persian Empire (550 BC – 1979 AD)
All the Empires of Babylon, Akkadians, Assyria, Sumer, Hitites, Bactrians, Scythians, Parthias, Medes, Elamites, Egypt, Ethiopia ... before being invaded by the Romans were territories belonging to the Persian Empire. .
They basically unified the whole of Central Asia which included so many different cultures, kingdoms, empires and tribes. The Persian Empire was the largest empire in ancient history.
At the height of its power under Cyrus the Great, the empire covered about 8,000,000 square kilometers and spanned three continents: Asia, Africa, and Europe.
4.Roman Empire (27 BC – 1453 AD)
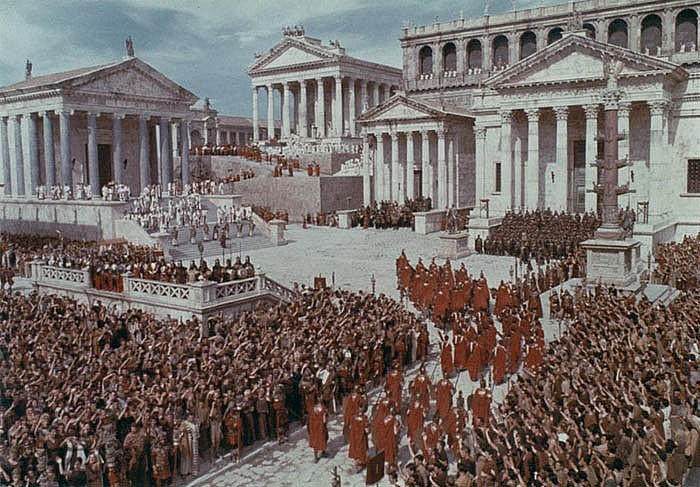 |
| Roman Empire |
The Roman Empire is not only one of the most famous but also the oldest in history. It lasted from 27 BC – 1453 AD. In total, this dynasty lasted for a period of 1,480 years. This empire extended its territory to include what is now Italy and much of the Mediterranean region.
The Western Roman Empire fell in 476 AD when the rule of the emperor Romulus Augustus was overturned. The Eastern Roman Empire continued to inherit the aura of the Romans in the centuries that followed. It is known by historians today as the Byzantine Empire. The empire was later overthrown by the Ottomans in 1453.
5.Holy Roman Empire (962 BC – 1806 BC)
The Holy Roman Empire existed from 962 BC – 1806 BC. The empire's territory consisted mainly of central Europe, especially most of Germany.
This empire was born when Otto I proclaimed himself king of Germany. Later, he became known as the first king of the Holy Roman Empire.
The Holy Roman Empire was made up of about 300 territories. After the "30-year war" took place in 1648, the empire was divided and split into many independent states. In 1792, France also rebelled.
In 1806, Napoleon Bonaparte overthrew the last Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, Francis II, forcing him to abdicate. Later, the region was reorganized as the Confederation of the Rhine.
6.Han Dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD)
The Han Dynasty was the successor to the Qin Dynasty (221 BC – 207 BC), and was followed by the Three Kingdoms Period (220-280). This dynasty was founded by Liu Bang, a leader who rebelled against Qin rule.
For many Chinese, the reign of the Han Dynasty, which lasted 400 years, was one of the greatest periods in the entire history of China.
There are many opinions that the two empires of the same time, the Han Dynasty and the Roman Empire, are the two superpowers of the world.
7.Kush Empire (1070 BC - 350 AD)
The Kush Empire lasted from 1070 BC to about 350 AD. The land on which this empire was based is now the territory of the Republic of Sudan. Historians and scientists find very little information about the politics of this empire. They found very little documentation of the monarchy pursued by the empire in its final years.
The economy of the Kush empire was mainly based on the iron and gold trade. Some evidence suggests that the empire was attacked by desert tribes. However, others speculated that the empire was so dependent on iron resources that it destroyed forests. It forced people to leave their living places so that the government burned forests to find iron.
8.Arab Empire or Kingdom of Caliphate (632 AD - 750 AD)
The Arab Empire, also known as the Caliphate, was a political institution founded by the Islamic prophet Muhammad. This empire included most of the Arabian peninsula at the time of Muhammad's death in 632. It would be more reasonable to call it the Arab Empire than to call it the Islamic Empire, because while Islam was rooted and spread widely. from this empire, there were later many Muslim empires and were dominated by Muslims but not Arabs.
Muhammad was succeeded by four Caliphs selected by consensus until 661. Then the hereditary Umayyad Caliphate continued to rule until 750, followed by the Abbasid Caliphate, despite conquests. Restoration has ended at this point.
The Arab Empire essentially ceased to exist around 900, although the Abbasids maintained a religious role as Caliphs in Baghdad until the city was destroyed by the Mongols in 1258. After 900 AD, the empire disintegrated politically, with the rise of many rival dynasties, many of which were rivals of Turkic and Persian origin, as well as rival Caliphates in Spain and Egypt. .
In its day, however, the Arab Empire remained extraordinary, with its exploits and legacy. It is admirable that a loosely organized, tribal people on the fringes of world civilization could defeat the Byzantine Empire and overthrow the Sassanid Persian Empire – both of which had their own people. overwhelming number and resources compared to the Arabian Desert.
The Arab conquests are a prime example of how ideological enthusiasm can make up for technological and organizational weakness. The Arab generals of this period deserve to be ranked among the world's greatest military geniuses, especially the 3rd Caliph, Omar, who conquered the region from Egypt to Persia in 10 year. In 100 years, the Arab Empire grew to a size several times larger than the Roman Empire at its height.
Thanks to its location, the Arab Empire, like the Persian Empire before it, connected the centers of world civilization in Africa, Europe, Central Asia, India and China. As a result, goods and knowledge from all these regions can be combined for the first time, yielding new concepts such as algebra.
The final legacy of the Arab Empire was, of course, Islam, which today has over a billion adherents.
9.Venetian Empire (697 AD - 1797AD)
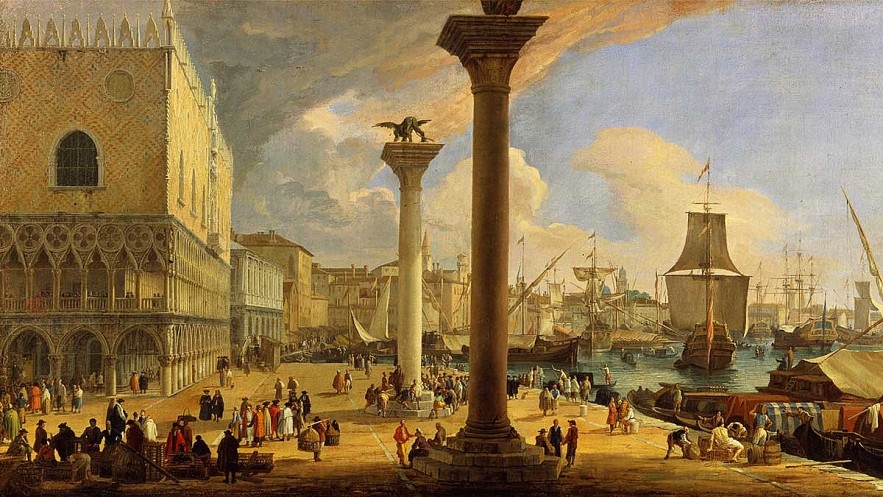 |
| Venetian Empire |
The pride of the Venetian Empire was in possession of a huge navy that allowed it to expand its territory across Europe and the Mediterranean. Eventually, the empire conquered lands of great historical significance such as Cyprus and Crete. The Venetian existed for a period of 1,100 years (from AD 697 to AD 1797). The land on which this empire was once based is now the territory of the Republic of Venice.
In 1797, Napoleon brought his army to destroy and took control of this empire. Unlike other empires that were destroyed by civil wars, the Venetians collapsed due to wars with neighboring countries. In addition, this empire was too complacent about its navy, so it distributed its forces too thin, making it easy for the enemy to break through the defenses.
The military technology that Venice had, along with the city's strategic placement on the key commercial routes of the period, provided Venice a number of powerful, mutually reinforcing advantages.
The Arsenal was the nerve center of the Venetian naval industry; it was a state-of-the-art weapons factory for ships that predated the assembly line by many centuries. As early as the thirteenth century, the Arsenal was a hotbed of inventiveness and enterprise in the galley-building industry.
The city's strategic placement provided a buffer against attacks from both land and water. Being a collection of islands in a swampy lagoon, there wasn't much arable land, thus the economy shifted around trade and lending money instead. Additionally, its strategic location at the head of the Adriatic Sea made it an important commercial crossroads between the Eastern and Western worlds across the Mediterranean.
10.Silla Empire (57 BC - 935 AD)
Historians find very little detail about the early stages of the Silla empire. But a number of documents recorded in the 6th century said that the social status and clothes of the people were based on genealogy. From there, it will decide which class does what work.
The name "Silla" (pronounced "Shilla") may have originally been closer to Seoya-beol or Seora-beol. This name appears in records of the Yamato Japanese and the Jurchens, as well as ancient Korean documents. Japanese sources name the people of Silla as the Shiragi, while the Jurchens or Manchus refer to them as Solho.
The Silla Empire began to form in 57 BC and is now the territory of Korea and Korea. Kin Park Hyeokgeose was the first to rule this land. Under his rule, the Silla empire continuously expanded its territory and conquered several other countries on the Korean peninsula. In the 7th century, this empire fought with the Tang dynasty (China) in the country of Goryeo. During that war, Silla still defended that territory.
However, a century-long civil war between high-ranking courtiers led to the destruction of the Silla Empire. By AD 935, the empire became part of Goryeo's territory.
Among the many accomplishments of the Unified Silla Kingdom is the first known example of printing. A Buddhist sutra, produced by woodblock printing, has been discovered at the Bulguksa Temple. It was printed in 751 CE and is the earliest printed document ever found.
Beginning in the 800s, Silla fell into a decline. Increasingly powerful nobles threatened the power of the kings, and military rebellions centered in the old strongholds of the Baekje and Goguryeo kingdoms challenged Silla authority. Finally, in 935, the last king of Unified Silla surrendered to the emerging Goryeo Kingdom to the north.
| The city of Gyeongju, the old Silla capital, still has many remarkable historical sites from that era. The Bulguksa Temple, the Cheomseongdae Observatory, the Tumuli Park, which has the burial mounds of Silla monarchs, and the Seokguram Grotto with its stone Buddha figure are some of the most well-known. |
11.Mongol Empire (13th - 14th Centuries)
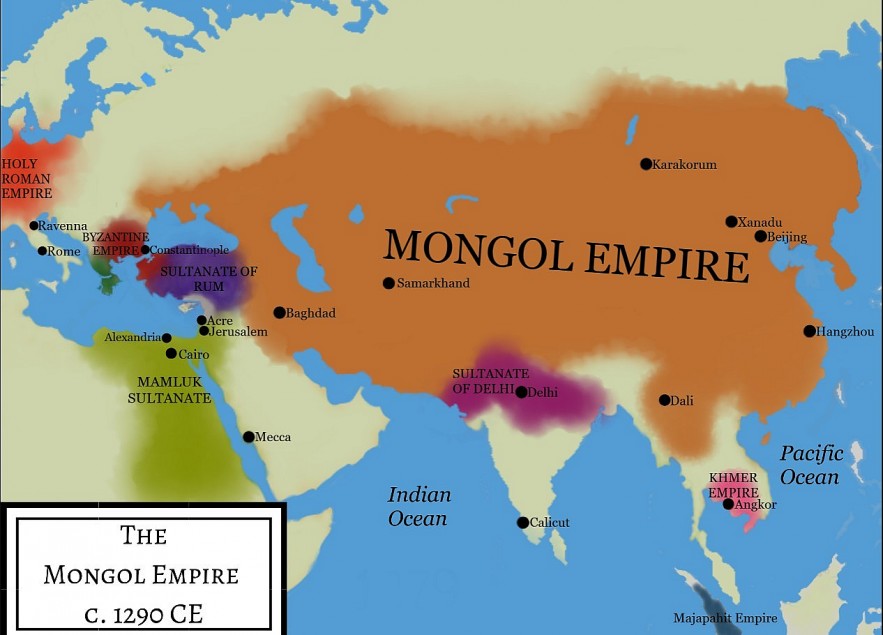 |
| The Mongol Empire during the reign of Kublai Khan (r. 1260 - 1294 CE). |
The Mongol Empire existed during the 13th and 14th centuries, and was the largest contiguous empire in human history.
It began with the unification of the scattered Mongol tribes of Genghis Khan. He then extended his vision to China and the lands to the west.
Khan was the founder of the Mongol Empire after uniting independent tribes in northeastern Asia in 1206.
Beginning in the steppes of Central Asia, the Empire eventually stretched from Eastern Europe to the Sea of Japan, including large parts of Siberia in the north and extending south to Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent and the Indian Ocean. India, the Iranian Plateau, and the Middle East.
At its peak, the Mongol Empire stretched 9,700 km, a territory of up to 24,000,000 km2 (equivalent to 16% of the land area of the Earth), and ruled over 100 million subjects.
The Mongol cavalry at that time was considered an extremely brave and ruthless fighting force, the image of the Mongols was depicted brutally and barbaric famous in history.
The Mongol Empire weakened shortly thereafter because of weaknesses in the management of such a large and multicultural territory.
12.Kanem-Bornu Empire (700 AD - 1900 AD)
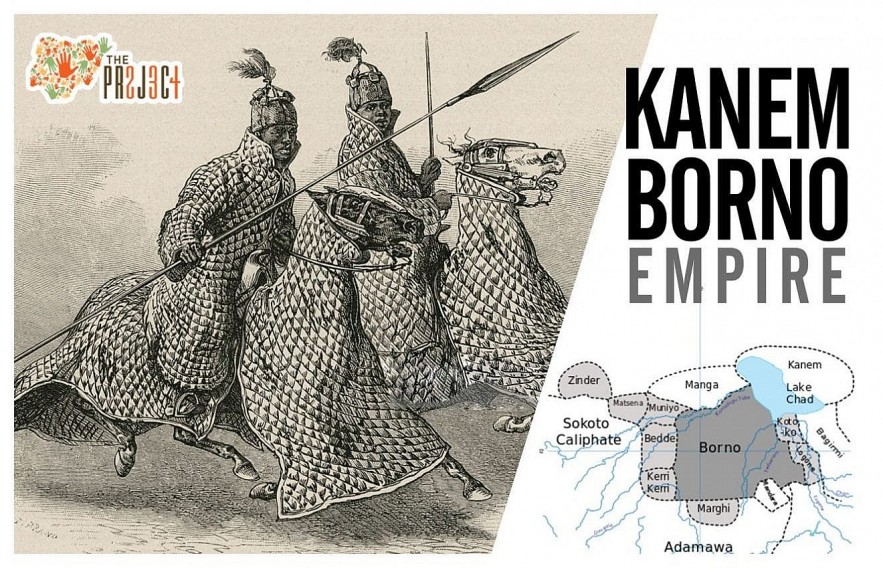 |
| Kanem-Bornu Empire |
The Kanem-Bornu Empire existed in modern day Chad, Nigeria, Niger, Libya and Cameroon from the 9th Century until 1900.
We know very little about the Kanem empire and most of it is based on a document discovered in 1851 called the Girgam.
This Islamic empire, with its capital in what is now Chad, Libya and partly in Niger, was founded around 700 AD and lasted until 1376 AD.
According to some accounts, the people of Zaghawa established their first capital in 700 AD and called it the city of N'jimi. The history of this empire is divided by two different dynasties, Duguwa and Sayfawa. Then a king declared a holy war against the surrounding tribes and at the same time to expand the territory.
The military system of that time was led by the aristocracy and passed down in a "heir apparent" fashion. As such, it weakened the Kanem Empire's power system and led to civil war. Bulala then invaded and quickly captured N'jimi in 1376. In the end, Bulala took control of the entire Kanem Empire territory.
The origin of the Kanem remains unclear. There are several theories that attempt to tell its story. One theory claims that the Kanem came about as a result of the collapse of the Assyrian Empire. Another popular theory (a more accepted theory) claims the Kanem Empire was created around 700AD under the Nomadic Tebu speaking Kanembu who were forced towards fertile lands around Lake Chad due to political pressure.
The area they were forced to was already occupied by the Sao culture and had an independent walled city. The Kanembu group adopted many of the Sao culture and customs but still dominated the Sao under the leadership of the Duguwa Dynasty. This domination resulted in war between the two cultures until the late 16th century.
The Kanem Empire is often referred to as the longest empire to rule in African history. It is also known for its wealth and contribution to pre-colonial African history. The empire was ruled by the Duguwa Dynasty and consisted of several ethnic groups skilled in iron and horsemanship. The capital of the Kanem capital was in Njimi. As a result of their strategic location between northern Africa and sub-Saharan Africa, the Kanem Empire benefitted from trade.
The Sayfawa Dynasty replaced the Duguwa Dynasty during the 11th century. The Sayfawa ruled until the 19th century. The Sayfawa Dynasty faced decades of internal conflicts and invasions from various groups such as the Bulala. In the end, they were forced out of Kanem due to invasion by outside groups. The Kanembu persisted and overcame several other attacks and moved their Empire to Bornu.
The Bornu Empire was a continuation of the Kanem Empire. It became bigger than the Kanem Empire at the peak of its greatest. It included areas in present day Chad, Niger, Nigeria and Cameroon. Although, the Sayfawa Dynasty overcame several invasions, their troubles did not stop when the Empire was moved to Bornu. Under the leadership of Dunanami, the Sayfawa Dynasty was able to consolidate and build a capital in Ngazargamu in present day Nigeria. By the early 16th century, the Sayfawa Dynasty was able to defeat the Bulala group and reclaim its former capital n Njimi.
The Sayfawa Dynasty became more powerful than before with the control of both capitals, the capitals were consolidated but political and economic authority was in Bornu. This merging of Kanem and Bornu led to the name – Kanem-Bornu Empire.
Alooma’s son Umar could not match his father’s political, military and economic skills, so he delegated to a team of advisors. The Kanem-Borno Empire was in decline by the 19th century. They faced invasion from the Fulanis who under the leadership of Usan Da Fodio who was ranging a jihad. The Fulanis were able to capture the capital of Ngazargamu. The Kanem-Borno Empire was also faced with administrative disorganization and other internal conflicts. The Sayfawa Dynasty ended but the Kanem-Borno Empire continued but faced a continuing decline in power. They suffered other invasion from militants from the East. In the end, the European division of the continent absorbed them under the British rule.
13.Ethiopian Empire (1270 AD - 1936 AD)
The Ethiopian Empire began around 1270 AD when the Solomonid dynasty overthrew the Zagwe dynasty. At that time, Solomonid claimed possession of the lands believed to belong to King Solomon
In 1895, the Italians declared war on the Ethiopian empire and the empire began to shake. In 1935, Benito Mussolini ordered Italian troops to invade Ethiopia. That war lasted for 7 months and the victory belonged to the Italians. During 1936-1941, Italy ruled Ethiopia.
14.Khmer Empire (802 AD - 1432 AD)
Little is known about the Khmer empire however the city at Angkor is said to be awe-inspiring and is part of the way to the famous temple of Angkor Wat - one of the world's largest religious monuments. This building was built during the height of the Khmer empire. The Khmer Empire began around AD 802 when Jayavarman II proclaimed himself monarch in the area now called Cambodia. This empire lasted for 630 years and was destroyed in 1432.
Most of the empire's dynasties waged wars to protect and expand their territory. Angkor became the capital of this empire in the second half of the dynasty. Later, neighboring civilizations fought for control of Angkor as the Khmer empire's power began to wane. There are many different theories about the decline of the Khmer empire. Some people believe that a king adopted Hinayana Buddhism to rule the country, leading to the weakening of the governing system, causing the empire to perish. Others say that the Thai kingdom of Sukhothai conquered Angkor in the 1400s.
15.Ottoman Empire (1299 AD – 1922 AD)
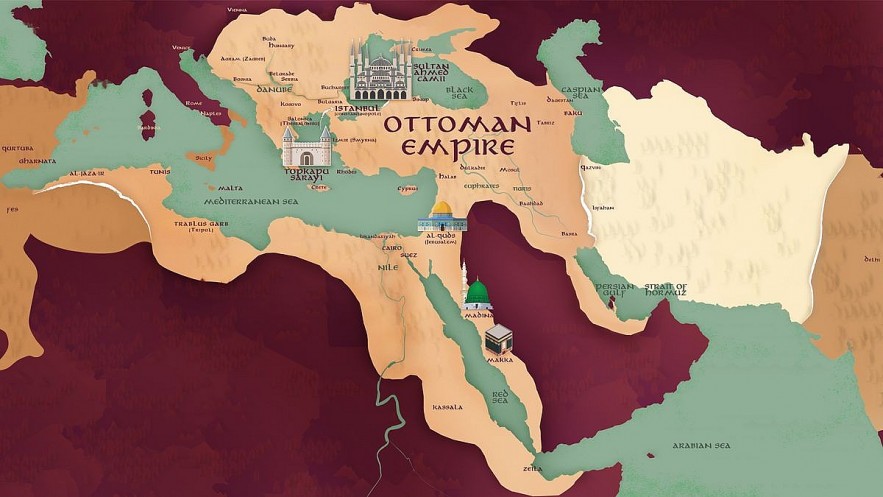 |
| Ottoman Empire |
At its height, the Ottoman Empire "covered" on 3 continents and included many cultures, religions, and languages. Despite its differences, the empire governed the colonies and prospered for 623 years (AD 1299 – AD 1922).
The beginning of the Ottoman Empire was a small Turkish state after the weakening of the Byzantine Empire and withdrawal from the region. After that, the Ottoman Empire increasingly expanded its territory through a strong judicial, educational, and military system as well as possessing a unique method of transferring power. Inflation, competition and unemployment were key factors in the fall of the Ottoman Empire.
16.Portuguese Empire (1415 AD - 1999 AD)
The Portuguese Empire is known for having one of the strongest navies in the world. This empire existed for 584 years, was the first global "coverage" empire in history, spanning 4 continents. It all started in 1415 when the Portuguese conquered Cueta – a Muslim city in North Africa. They then continued to expand their territories in Africa, India, Asia, and eventually the Americas.
After World War II, many European countries struggled to break free from the Portuguese empire. By 1999, Portugal had lost control of Macau to China, signaling the end of this mighty empire.
17.British Empire
The British really played an important part in creating the modern world. Britain's representative democracies inspired French enlightenment philosophers such as Montesquieu to create modern political doctrines that had a profound influence on modern European nations.
The main features of America - its strong attachment to liberalism, the rule of law, civil and commercial rights - were inherited from the British and spread to the world. Most of these features have evolved organically over Britain's long history rather than as the result of some master plan.
It was these same characteristics that helped the British Empire grow, prosper and keep the territory it controlled. Moreover, its example is widely studied, whether for the financial or naval power of the empire.
At its height in the 20th century, the British Empire spanned a quarter of the world – the largest empire (in terms of area) in history. This feat was achieved largely by the organizational victories and financial strength of England, and then by the role of a large army. For example, the British conquest of India was mainly carried out by Indian soldiers who received British salaries and benefits to serve Britain. London also demonstrated an excellent ability to handle multiple wars at once. The British rarely lost a battle.
Conclusion: America's Greatest Empire?How does America compare to these giants? Militaryly, the US is unmatched. America blends liberalism, British business, and continental resources. Americans, like Romans, have a fascinating culture. The US can strike like the Mongols. Like the Arabs, the US spreads a global ideology. America united cultures like the Persian Empire. The US will remain a superpower for these reasons. If America doesn't want to repeat the sins of past empires, it must remember their lessons. Rome fell despite a strong army. Empires can fall to internal strife. The Persians lost because of poor leadership, not weakness. The Mongols won the battle, but they failed to preserve their rule in peacetime. The Arabs built a great society, but the intruders took their best and pulled them down. The British were weary from advancing their interests, the world order, and the European system. |
 Top 6 Most Mysterious 'Mass Hysteria' Cases in the World History Top 6 Most Mysterious 'Mass Hysteria' Cases in the World History Group dancing, group laughter... are mysterious "epidemics" that have occurred in many places in world history that scientists are still trying to explain. |
 Top 6 Biggest Mysteries in the World History That Probably Never be Solved Top 6 Biggest Mysteries in the World History That Probably Never be Solved Not all mysteries will have an answer to it, and some will remain secret forever. Here are the world's biggest historical mysteries that have never ... |
 Top 10 Most Mysterious Events In The World of All Time Top 10 Most Mysterious Events In The World of All Time Throughout the world history, there have been lots of events that so far we are unable to explain why. Read on to know Top 10 ... |
 Top 10 Crazy Prophecies That Came True In The World History Top 10 Crazy Prophecies That Came True In The World History There were many prophecies that seemed crazy and frightening but finally came true. Check out Top 10 Crazy Prophecies That Came True. |
 Top 12 Most Mysterious Deaths In The World History Top 12 Most Mysterious Deaths In The World History In the world history, some famous people died without clear reasons. The reasons behind their deaths have been so far mysteries. Check out Top 10 ... |























