Where Is The Location of Liver In Your Body - Left Or Right?
 |
| What Is The Location Of Liver In Your Body? Left Or Right. Photo Human Anatomy |
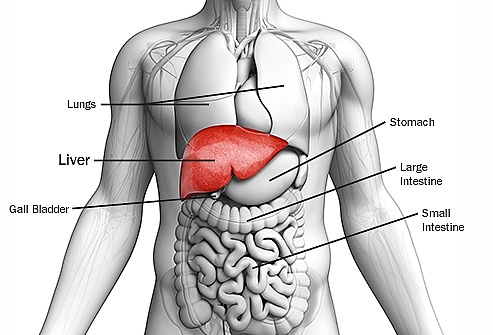
The liver is a large, meaty organ that sits on the right side of the belly. Weighing about 3 pounds, the liver is reddish-brown in color and feels rubbery to the touch. Normally you can't feel the liver, because it's protected by the rib cage.
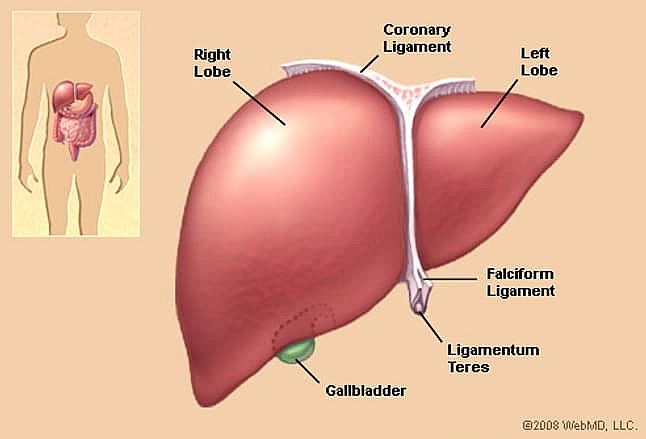
The liver has two large sections, called the right and the left lobes. The gallbladder sits under the liver, along with parts of the pancreas and intestines. The liver and these organs work together to digest, absorb, and process food.
Fast facts on the liver
The liver is classed as a gland.
This vital organ carries out more than 500 roles in the human body.
It is the only organ that can regenerate.
The liver is the largest solid organ in the body.
Alcohol abuse is one of the major causes of liver problems in the industrialized world.
What does the liver do?
 |
| Photo webmd |
It performs 500 tasks to keep the body healthy, says Hellan Kwon, M.D., a clinical assistant professor of hepatology at the University of Michigan.
The key ones are metabolic.
| “Anything that is eaten or consumed, whether it’s food, alcohol, medicine or toxins, gets filtered by the liver. Once we ingest food, it is digested by the stomach and intestine, gets absorbed into the blood and goes to the liver,” Kwon says. |
The liver is smart. It knows when to detoxify, when to usher the toxins out of the body through urine or stool, when to store the nutrients and when to release them back into the blood.
It also keeps the amount of sugar in the bloodstream constant, Kwon adds.
Another liver function is when the it processes a meal, it removes sugar from the blood and stores it in the form of glycogen. When a person’s blood sugar decreases, it converts that stored glycogen to glucose, adding the proper amount of instant energy into the bloodstream for the cells to use. Once the glycogen store is used, the liver will create glucose from other carbohydrates and a form of protein.
The liver is also a fat factory of sorts. It breaks down fats that are eaten, converting excess carbohydrates and protein into forms that are stored for later use, while synthesizing other fat, like cholesterol. The liver produces bile to help break down and absorb fats. Waste products and toxins are removed through bile. Bile, incidentally, gives stool its color, Kwon says.
The liver produces blood during fetal development and acts as a blood recycler during adulthood. It breaks down old or damaged blood cells. It knows to store the iron and various vitamins to use when those nutrients fall below what’s needed in the bloodstream. It’s also essential in releasing the plasma proteins necessary to clot blood.
The liver is truly an amazing organ in that it has the capacity to regenerate. This means that after an injury or surgery to remove tissue, the liver tissue can grow back to a certain extent. The liver starts growing back by having the existing cells enlarge. Then, new liver cells start to multiply.
Within a week after removing two-thirds of the liver, the liver can return to the same weight it was before surgery. The liver has been known to regenerate completely after as many as 12 partial liver removal surgeries.
READ MORE: How To Raise Low Blood Pressure Quickly with Food and Drinks
Where is the liver?
 |
| Photo healthline |
The liver is the second largest organ in the body, weighing in at approximately 3 pounds. It is a deep reddish-brown in color, and is situated on the right side of the abdominal cavity, just below the right hemi-diaphragm, to the left of the stomach.
That is, it is pressing against the domed right half of the diaphragm, which separates it from the right side of the thoracic cavity. It is roughly triangular in shape, and fills almost the whole right side of the upper abdomen. Its lower border extends in front to just the level of the right ribcage margin, while at the back it extends downwards to the top of the right kidney.
The liver is covered almost completely by a fibrous capsule, and then by a peritoneal fold. The smooth glistening peritoneum encloses almost all organs within the abdomen. The peritoneum condenses in four places to form sturdy thickenings or peritoneal ligaments, which help to support the liver and keep it in place.
| The surface marking of the liver is as follows: The following three points are marked; 1.25 cm below the right nipple, 1.25 cm below the tenth rib tip and 2.5 cm below the left nipple. The line joining the first and third points marks the upper surface of the liver. The line joining the first and second points represents the lateral border of the liver. The line joining the second and third points represents the lower border. The liver has four lobes or parts: the right and the left lobes, the caudate and the quadrate lobes. The liver cells produce bile, which is released into microscopic canals between the cells called bile canaliculi. These join as they go on to form bile ducts. Bile ducts from the different parts of the liver flow together to form the right and the left hepatic ducts, which join into the common hepatic duct. |
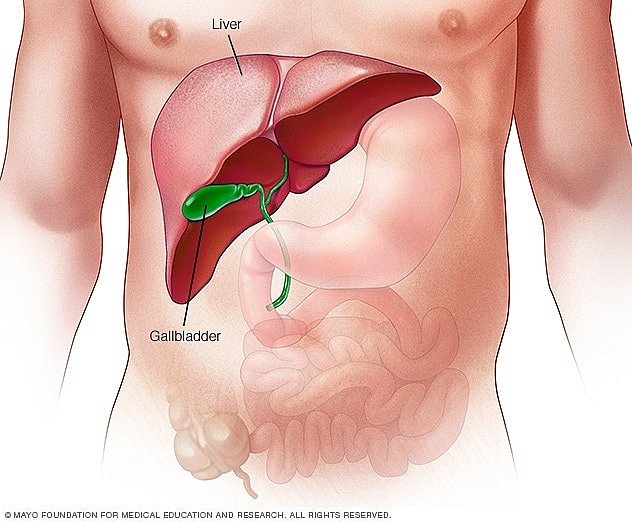
Just below the liver, tucked into its own fossa or niche, is the gallbladder which stores the intensely bitter dark green fluid called bile. Its duct, called the cystic duct, joins with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct that empties bile into the duodenum as required for digestion of food.
Most of the bile that arrives via the common hepatic duct, however, goes into the gallbladder for storage till needed. Other impressions on the undersurface of the liver are made by the lowest part of the esophagus, the stomach, and the right kidney.
Live Diseases - Symptoms
There are more than 100 types of liver diseases. Many conditions begin as flu-like symptoms and progress to more severe signs of liver damage, such as jaundice and dark-colored urine.
Other symptoms of liver problems include:
fatigue
loss of appetite
nausea
vomiting
joint pain
stomach discomfort or pain
nose bleeds
abnormal blood vessels on the skin
itchy skin
weakness
a low sex drive
More serious symptoms include:
yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
confusion and difficulty thinking clearly
abdominal swelling (ascites)
swelling of the legs (edema)
impotence
gynecomastia (when males start to develop breast tissue)
enlarged liver (hepatomegaly)
dark urine
pale-colored stools
If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, see your doctor immediately.
How to Keep Your Liver Healthy
 |
| Photo healtblog |
Below are some recommendations to help keep your liver working as it should:
Diet: As the liver is responsible for digesting fats, consuming too many can overwork the organ and disturb it from other tasks. Obesity is also linked to fatty liver disease.
Moderate alcohol intake: Avoid consuming more than two drinks at a time. Drinking too much alcohol causes cirrhosis of the liver over time. When the liver breaks down alcohol, it produces toxic chemicals, such as acetaldehyde and free radicals. For serious damage to occur, it takes the equivalent of a liter of wine every day for 20 years in men. For women, the threshold is less than halfTrusted Source of that.
Avoiding illicit substances: When last surveyed in 2012, close to 24 million people in the United States had consumed an illicit, non-medical drug within the last month. These can overload the liver with toxins.
Caution when mixing medications: Some prescription drugs and natural remedies can interact negatively when mixed. Mixing drugs with alcohol puts significant pressure on the liver. For example, combining alcohol and acetaminophen can lead to acute liver failure. Be sure to follow the instructions on any medications.
Protection against airborne chemicals: When painting or using strong cleaning or gardening chemicals, the area should be well ventilated, or a mask should be worn. Airborne chemicals can cause liver damage because the liver has to process any toxins that enter the body.
Travel and vaccinations: Vaccination is essential if you are traveling to an area in which hepatitis A or B might be a concern. Malaria grows and multiplies in the liver, and yellow fever can lead to liver failure. Both diseases can be prevented by oral medication and vaccination.
Safe sex: There is no vaccination for hepatitis C, so caution is advised in regards to safe sex, tattoos, and piercings.
Avoid exposure to blood and germs: Receive medical attention if you are exposed to the blood of another person. It is also important not to share personal items related to hygiene, such as toothbrushes, and to avoid dirty needles.
Liver is on the right so what is in the left?
Left lobe of the liver
Most of your liver is on the right side of your body. Only a small lobe of the liver is on the left. It’s located above and in front of your stomach and below the diaphragm.
Your liver is about as large as a football and weighs three pounds.
| What it does The liver is a very hardworking organ. The liver: regulates metabolic functions generates energy converts substances removes toxins |
The liver manages chemical levels in the blood and sends some waste products away as urea or within the bile it produces. It processes nutrients, too. It stores some of them, eliminates others, and sends some back to the blood.
The liver also plays a role in breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins and storing vitamins and minerals.
Your liver sends bile out into the small intestine, which helps aid the digestion and absorption of fats into the body. Bile is eliminated in feces. Blood byproducts are sent to the kidneys, where they’re eliminated in your urine.
You can’t live without a liver, but your liver has the ability to regenerate its cells.
Left lung
Your left lung has only two lobes compared with your right lung, which has three lobes. This asymmetry allows room for your heart on the left.
| What it does The lungs are your breathing apparatus. They take in oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide. The lungs sit inside your rib cage. The lungs are made up of a spongy pink material. The lungs expand and contract as you breathe. The parts of the lungs involved in air intake are: bronchi bronchiole tubes alveoli Heart Your heart sits in the middle of your chest, to the left. The heart is a muscle at the center of your circulatory system. The average adult heart is about the size of a fist: 5 inches long, 3.5 inches wide, and 2.5 inches deep. |
Spleen
The spleen is located in the upper left of your abdomen, under your diaphragm and behind the top half of your stomach. It’s fist-sized, about 4 to 5 inches long, and purple in color.
| What it does As part of your lymphatic system, the spleen filters your blood. It recycles red blood cells and sends out white blood cells (lymphocytes) to help fight infections. The spleen also produces substances that help reduce inflammation and promote healing. |
Structure of Liver
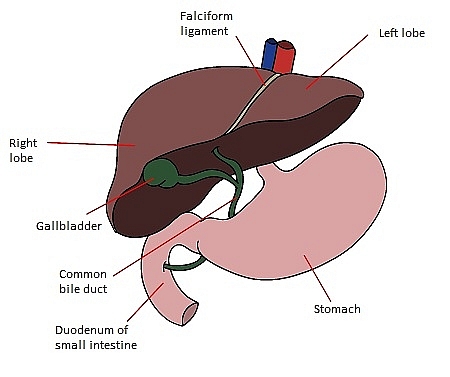 |
| Anterior view of the liver and surrounding organs |
The liver is a large, dark, multi-lobed organ in the top of the abdominal cavity. Where is the liver within the abdominal cavity? It stretches across the entire abdominal cavity from right to left but resides mostly on the right side of the body. The inferior surface of the liver sits atop the stomach and sandwiched between the stomach and liver is a small organ known as the gallbladder.
The liver needs proper blood circulation to complete its role. It receives fresh oxygenated blood via the hepatic artery. It receives blood from the digestive system via the hepatic portal vein. Blood coming via the hepatic portal vein is carrying important substances absorbed from organs like the stomach, small intestines, and colon. The liver processes this blood and sends it (plus the now deoxygenated blood it received from the hepatic artery) out through the hepatic veins.
The liver sends bile out via the hepatic ducts. These hepatic ducts come together to form the common hepatic duct. The common hepatic duct joins with the cystic duct of the gallbladder, and together these two ducts work to deliver bile into the duodenum of the small intestines.
The human liver has four lobes. The right and left lobe are separated by a tendon known as the falciform ligament. The falciform ligament keeps the liver in place by attaching it to the abdominal wall. On the inferior surface of the liver reside the caudate and quadrate lobes. The caudate lobe is posterior to the quadrate lobe.
 Top 10 Bizarre-Looking Foods But Absolutely Healthy Top 10 Bizarre-Looking Foods But Absolutely Healthy The KnowInsiders has rounded up all the strangest, best, most delicious food pairings you can imagine to stay healthier and younger. Read on to ... |
 Effective Home Treatment to Improve Low Blood Pressure Effective Home Treatment to Improve Low Blood Pressure Low blood pressure can put your life at risk. There are effective treatments for low blood pressure you can apply. |
 20 unknown facts about blood, the fluid in our body 20 unknown facts about blood, the fluid in our body Blood plays a crucial role in supplying our organism with oxygen and nutrients every single seconds. However, blood is much more than just a red ... |