What is Emotet - World's Most Dangerous Malware?
 |
| Emotet. Photo: bankinfosecurity.com |
History of Emotet
Emotet was first documented by FortiGuard Labs’ own Joie Salvio, who was at Trend Micro at the time. The infection vector was simple – it was delivered via social engineering techniques, such as malspam, with a link to a malicious download. The resulting download contained two payloads: one was a configuration file that contained a list of predetermined banks. The other was a DLL file that could be injected into various processes to intercept outbound network traffic and as well as gather details within a web browser.
The first iteration of Emotet relied on corrupting the registry of a targeted devices, and it continues to do so as a method of evasion as any exfiltrated data is encrypted and stored in the registry. Not only is this method highly effective in thwarting discovery, it allows the attackers to maintain persistence on the targeted machine due to the complexity of finding any indicators of compromise.
Emotet is part of a group that includes – and is loosely related to – the Bugat/Feodo/Geodo/Heodo/Cridex/Dridex malware banking families that have had their fair share of publicity over the span of several years due to their widespread and destructive campaigns. Over the past several years, Emotet has also been seen distributing AZORult, IcedID, ZeuS Panda, and TrickBot. Emotet has now gained the serious attention of the AV industry, law enforcement, and researchers alike for its ability to simultaneously include multiple malware families in its distribution syndicate, according to Fortinet.
What is Emotet?
Emotet is a Trojan that is primarily spread through spam emails (malspam). The infection may arrive either via malicious script, macro-enabled document files, or malicious link. Emotet emails may contain familiar branding designed to look like a legitimate email. Emotet may try to persuade users to click the malicious files by using tempting language about “Your Invoice,” “Payment Details,” or possibly an upcoming shipment from well-known parcel companies.
Emotet has gone through a few iterations. Early versions arrived as a malicious JavaScript file. Later versions evolved to use macro-enabled documents to retrieve the virus payload from command and control (C&C) servers run by the attackers.
Emotet uses a number of tricks to try and prevent detection and analysis. Notably, Emotet knows if it’s running inside a virtual machine (VM) and will lay dormant if it detects a sandbox environment, which is a tool cybersecurity researchers use to observe malware within a safe, controlled space.
Emotet also uses C&C servers to receive updates. This works in the same way as the operating system updates on your PC and can happen seamlessly and without any outward signs. This allows the attackers to install updated versions of the software, install additional malware such as other banking Trojans, or to act as a dumping ground for stolen information such as financial credentials, usernames and passwords, and email addresses, reported Malwarebytes.
Who does Emotet target?
Emotet targets private individuals, as well as, companies, organizations, and authorities. In 2018, after being infected with Emotet, the Fuerstenfeldbruck hospital in Germany had to shut down 450 computers and log off from the rescue control center in an attempt to control the infection. In September 2019, the Berlin Court of Appeal was affected, and in December 2019 the University of Giessen. The Medical University of Hannover and the city administration of Frankfurt am Main were also infected by Emotet.
These are just a few examples of Emotet infections, the undisclosed number of affected companies is estimated to be much higher. It is also assumed that many infected companies didn't want to report their breach for fear of damaging their reputation.
It’s also worth keeping in mind that while in the early days, Emotet mainly targeted companies and organizations, the Trojan is now primarily targeting private individuals.
Which devices are at risk from Emotet?
Initially, infections by Emotet were only detected on more recent versions of the Microsoft Windows operating system. However, at the beginning of 2019 it became known that computers made by Apple were also affected by Emotet. The criminals lured users into a trap with a fake email from Apple support. Claiming the company would "restrict access to your account" if you didn’t respond. Victims were then told to follow a link to allegedly prevent the deactivation and deletion of their Apple services, cited Kaspersky.
How Does Emotet Malware Spread?
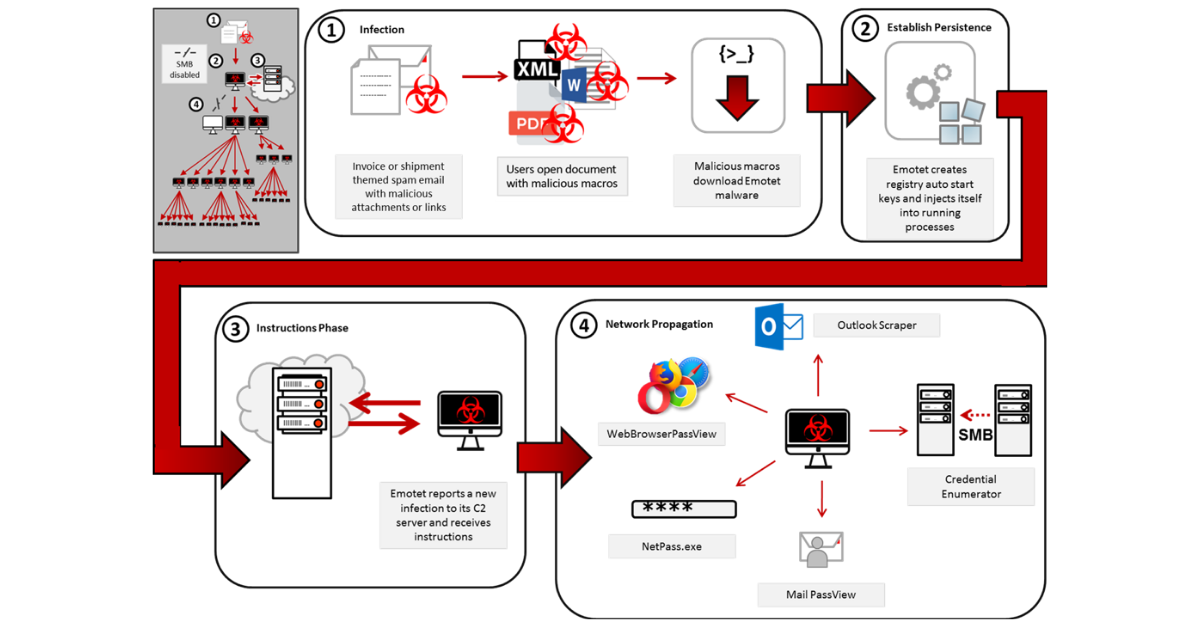 |
| Photo: cisecurity.org |
Emotet malware infiltrates computers through a network spreader component which consists of several spreader modules. Five known spreader modules power the malware as per the findings of the aforementioned and quoted technical alert:
- NetPass.exe, a legitimate password recovery tool developed by NirSoft. It can retrieve all passwords stored in a system for a logged-in user, as well as those kept on external drives.
- WebBrowserPassView, another password recovery tool that operates in most known web browsers. The list includes Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, and Safari.
- MailPassView, a third password recovery tool that gathers information from popular email providers such as Gmail, Microsoft Outlook, Hotmail, Yahoo! Mail, Windows Mail, and Mozilla Thunderbird.
- Outlook scraper, a malicious utility that scrapes credentials from the users’ Outlook accounts and uses this info to send out further phishing emails.
- A credential enumerator, which is a self-extracting archived .RAR file composed of a service component and a bypass component. By harnessing information collected by the four modules mentioned above, it either tries to brute force access accounts or locate writable share drives with the help of Server Message Block (SMB). When it eventually finds an available system, it writes the Emotet service component onto the network, which infects the entire disk, according to Heimdalsecurity.
Disruption of EMOTET’s infrastructureThe infrastructure that was used by EMOTET involved several hundreds of servers located across the world, all of these having different functionalities in order to manage the computers of the infected victims, to spread to new ones, to serve other criminal groups, and to ultimately make the network more resilient against takedown attempts. To severely disrupt the EMOTET infrastructure, law enforcement teamed up together to create an effective operational strategy. It resulted in this week’s action whereby law enforcement and judicial authorities gained control of the infrastructure and took it down from the inside. The infected machines of victims have been redirected towards this law enforcement-controlled infrastructure. This is a unique and new approach to effectively disrupt the activities of the facilitators of cybercrime. |
How to prevent Emotet
Described by the Department of Homeland Security as “among the most costly and destructive malware affecting state, local, tribal, and territorial governments, and the private and public sectors”, there’s no doubt we all have a responsibility to take Emotet very seriously.
Here are some tips of Clario you can implement to protect yourself and your organization from Emotet.
- Stay educated
If you’re reading this you’ve completed the first step! Make sure you and your colleagues are fully aware of the dangers of opening infected email attachments and links and just how well disguised they can be. Make sure all staff are aware of the dangers associated with opening some email attachments. Even simple tips like hovering over links to verify their destination could make a big difference.
- Review Microsoft Office macro settings
Organizations should review the use of macros and consider blocking macros from the internet.
- Implement an antivirus program
Using a trusted antivirus with automatic updates will help prevent infection by Emotet.
- Keep operating systems up to date
Regular patches improve security, fix bugs and improve functionality. This will help to restrict opportunities for Emotet to move around your network and infect others, should you have a breach.
- Ensure your network is segmented
Similarly, partitioning your organization’s network into multiple smaller networks, as opposed to one large one, will help to contain an Emotet outbreak.
- Back up daily
Keeping up to date backups offline could be highly valuable should you lose access to your files and get hit with ransomware.
- Use email content scanning
Scanning emails will help prevent malicious content reaching users in the first place. Your organization could also mark external mails with a banner highlighting they are from an external source, making it easier to spot malspam.
- Adhere to the principle of least privilege
Not everyone needs administrative privileges to do their work. Keep your systems safe by granting the minimum necessary level of access. This will limit the number of sources Emotet could steal credentials from.
How to remove the Emotet virus
 |
| Photo: linuxsecurityblog.com |
Emotet is not a new threat, but its constant evolution has made it particularly difficult to tame. If you do get infected with Emotet, follow the below first steps to help contain the virus and bring in security specialists to start work on your recovery.
- Identify, shutdown, and remove the infected devices from the network
- If possible, take the network temporarily offline to prevent reinfections, and stop the Emotet spreading
- Clean the infected devices
- Be mindful the infection could have already spread to your network so clean all devices.
Fun Facts About Emotet1. It has other names. Just to make the Emotet family tree seem even more complicated, Emotet also has other names: Geode, and a personal favorite, Mealybug. 2. It had a book named after it. Well, not exactly a book, but a playbook. Actually, there have been several, but this just speaks to how menacing and insidious Emotet is. In fact, the US Department of Homeland Security identifies Emotet as “among the most costly and destructive malware affecting state, local, tribal, and territorial (SLTT) governments, and the private and public sectors.” Emotet playbooks describe the Emotet infection process and its subsequent behavior after it has infected its targeted device. 3. It changes. In an effort to evade signature-based detection, Emotet changes itself every time it’s downloaded. This is one reason why it’s critical to install comprehensive anti-malware software that uses not only signature-based detection for detecting known malware, but also advanced detection technologies such as behavior-based and heuristics-based detection that detect new and emerging malware. Anti-malware solutions that rely on several detection technologies can better perform malware analysis, including Emotet malware analysis, and therefore more successfully deter, detect, and remove malware. 4. Its unique and central role in malware delivery is based on a Software as a Service (SaaS) business model. Yes, much like Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) business models that host legitimate applications and make them available to customers over the Internet, Emotet is based on a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) business model, only Emotet is anything but legit. A better name would be malware mercenary. The latest variant of Emotet earns its revenue primarily by selling access to its botnet infrastructure of other Emotet-infected computers so criminal actors can infect them with more malware. 5. It does not discriminate. Emotet targets everyone including individuals, large, medium and small businesses, banking sites, and government entities. And it doesn’t care about geographic boundaries either. It has happily targeted the US, Italy, Spain, Germany, Brazil, Mexico, Japan, Vietnam and many other countries, according to Reasonsecurity. |
 Facts about COVID Tongue: Peculiar virus Symptoms, Signs of Infection Facts about COVID Tongue: Peculiar virus Symptoms, Signs of Infection Facts about COVID Tongue: Is a swollen tongue or bumpy tongue a symptom of COVID-19? This COVID symptom is a serious mouthful? |
 Facts about Dogecoin: Forecast, True Value, Joke Cryptocurrency that became Real Facts about Dogecoin: Forecast, True Value, Joke Cryptocurrency that became Real Facts about Dogecoin - Forecast, True Value: WallStreetsBets, the social media mob that pumped up GameStop, is now dabbling in cryptocurrency and craze pushes Gogecoin ... |
 What is Wallstreetbets (WSB) Reddit Group and Who is Jaime Rogozinski What is Wallstreetbets (WSB) Reddit Group and Who is Jaime Rogozinski What is Reddit Group - History, Campaigns, Who is: The WallStreetBets Reddit community, which upended the stock market this week with its GameStop campaign, has ... |