How Many Royal Families Are There in the World

| Table of Content |
Countries With Royal Families
Of the 26 monarchies around the world, 12 are in Europe. Therefore, there are currently 12 royal families in Europe. Two of the monarchies are elective, and ten are hereditary.
Most monarchies in Europe are constitutional monarchies, meaning that the monarchs must exercise their power within limits prescribed in an established legal framework. Liechtenstein and Monaco are semi-constitutional, and Vatican City is a theocratic absolute elective monarchy.
The Current Monarchs in Europe
• Prince Macron of Andorra
• King Philippe of Belgium
• Queen Margrethe II of Denmark
• Prince Hans-Adam II of Liechtenstein
• Grand Duke Henri of Luxembourg
• Prince Albert II of Monaco
• King Willem-Alexander of the Netherlands
• King Harald V of Norway
• King Felipe VI of Spain
• King Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden
• Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom
• Pope Francis of Vatican City
One important thing to note is that Queen Elizabeth II, perhaps the most well-known monarch in the world, is commonly known as the queen of the United Kingdom. However, she is a monarch over the 16 commonwealth realms, which include:
Antigua and Barbuda, Australia
Bahamas
Barbados
Belize
Canada
Grenada
Jamaica
New Zealand
Papua New Guinea
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Solomon Islands
Tuvalu
United Kingdom
READ MORE: Who are Richest Royals in the Planet With Net Worth of Over $2.4 trillion
The List of 26 Countries In The World Where Royalty Still Rules
1. Andorra
The principality of Andorra is a small landlocked country located on the Iberian Peninsula, bordering France and Spain. Acting as co-princes, or co-regents, of the nation, are the Catholic bishop of Urgell, a Roman Catholic diocese, and the president of France. Presently the co-princes are bishop Joan-Enric Vives and President Emmanuel Macron, pictured.
2. Bahrain
The Kingdom of Bahrain is an island nation located in the Persian Gulf. The country is a constitutional monarchy led by the king, currently Sheikh Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa. He has been the ruling monarch since 1999.
3. Belgium
The Kingdom of Belgium is located in northwestern Europe with a constitutional monarchy form of government. The king, currently Philippe (or Filip in Dutch), is the ceremonial head of state. He has reigned since 2013.
4. Bhutan
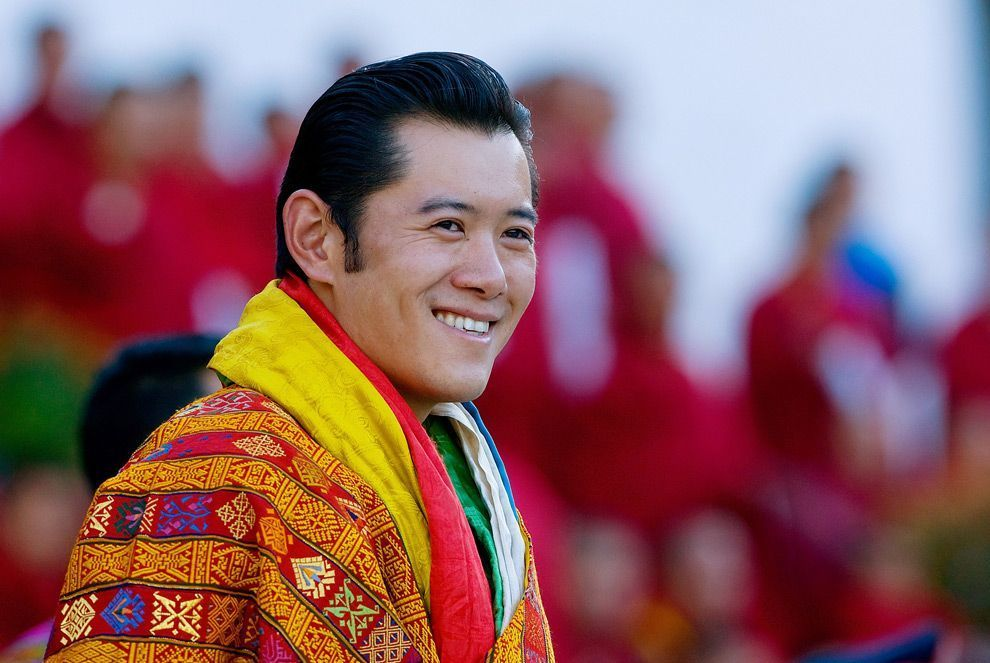

The Kingdom of Bhutan is a small landlocked nation in South Asia that is a constitutional monarchy. Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck is the “Druk Gyalpo,” or Dragon King, and is the head of state. He ascended the throne in 2006.
5. Brunei
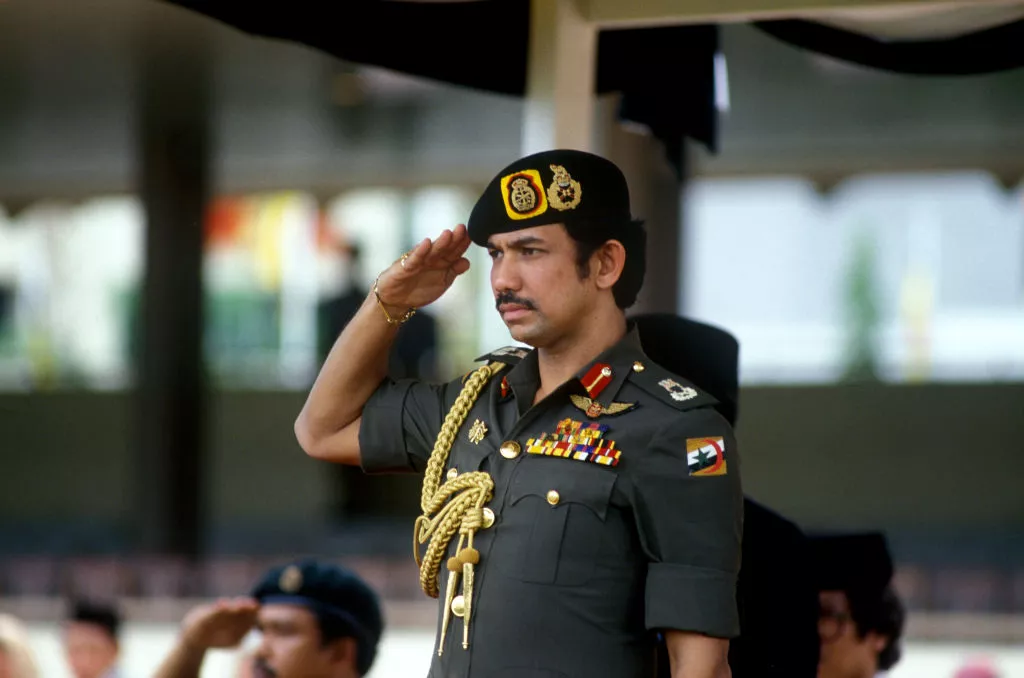

Brunei is a small country occupying part of the Southeast Asian island of Borneo. Hassanal Bolkiah is the current sultan, having ascended the throne in 1967. He is also the country’s only prime minister since the country became independent in 1984 and is thus the head of government.
6. Cambodia
The Kingdom of Cambodia is an elective constitutional monarchy located in Southeast Asia. Norodom Sihamoni has been the king of the country since 2004, having been named by the country’s throne council.
7. Commonwealth Realms
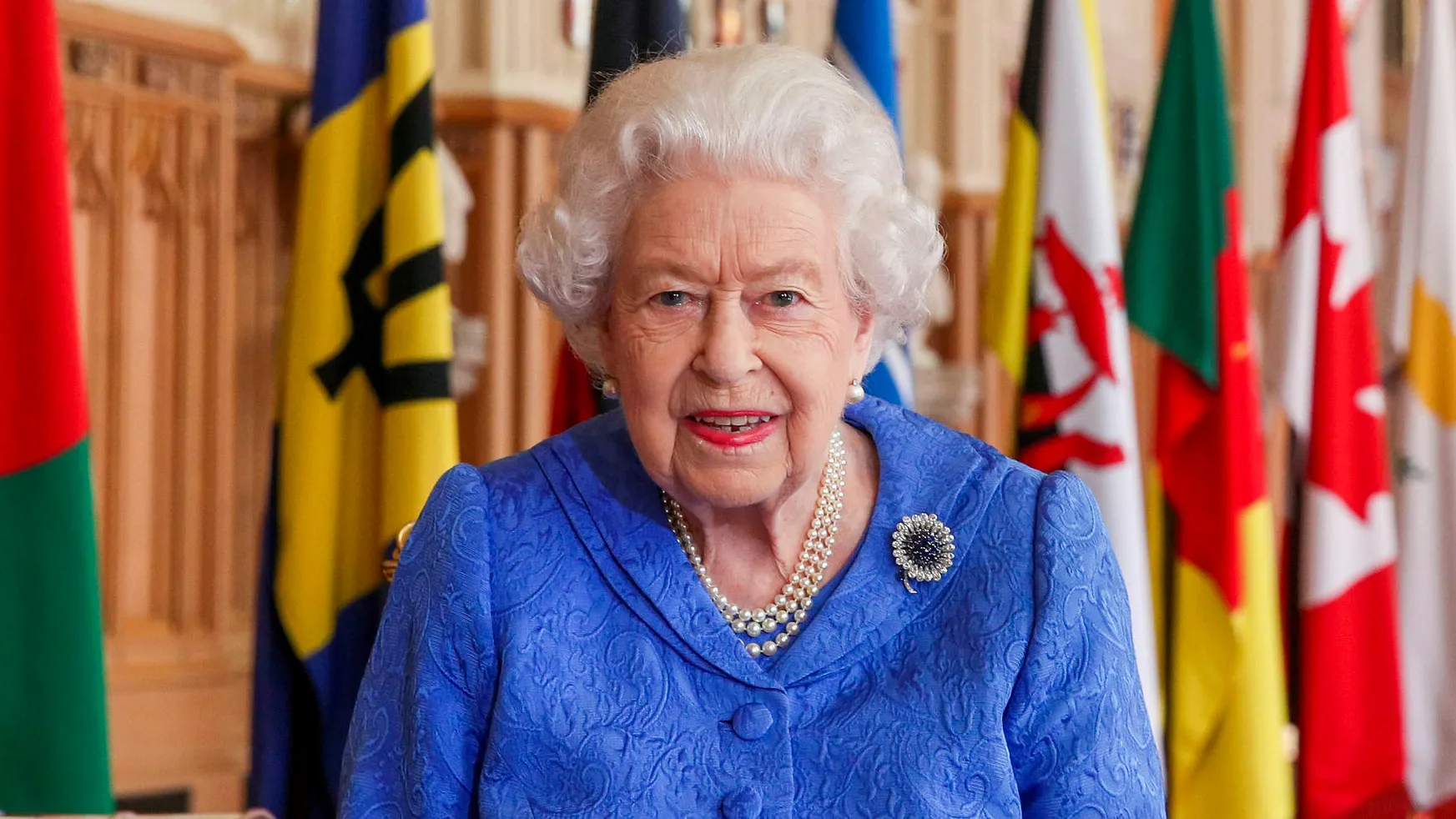

The British royal family, perhaps the world’s most well-known royals, rules over more than the United Kingdom. Queen Elizabeth II is the reigning constitutional monarch over 16 commonwealth realms: in addition to the U.K., the other 15 independent countries include Antigua and Barbuda, Australia, the Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Canada, Grenada, Jamaica, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, the Solomon Islands and Tuvalu.
Queen Elizabeth II ascended the throne in 1952.
READ MORE: The Full Statement issued by Buckingham Palace on Harry and Meghan interview
8. Denmark
The Kingdom of Denmark is the southernmost of the Scandinavian countries and is a constitutional monarchy. Margrethe II is the queen of the country and has reigned since 1972.
9. Eswatini
The Kingdom of eSwatini, also known as Swaziland, is a small landlocked country in Southern Africa. The country’s government is an absolute diarchy, meaning the nation is jointly ruled by the “Ngwenyama” (king) and “Ndlovukati” (queen). In 1986 Mswati III, pictured, became king and Ntfombi became queen.
10. Japan

Japan is an archipelago nation in East Asia that is a constitutional monarchy. Emperor Akihito ascended the throne in 1989 and is the 125th member of the world’s oldest reigning dynasty. On April 30, Akihito abdicates to allow his son Naruhito to become the newest emperor to sit on the Chrysanthemum Throne.
11. Jordan
The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan is a small landlocked Middle Eastern country located along the east bank of the Jordan River. The country is a constitutional monarchy and King Abdullah II has been the nation’s monarch since 1999.
12. Lesotho
The Kingdom of Lesotho is a small landlocked country enclaved within South Africa. King Letsie III has reigned since 1996 in a largely ceremonial role.
ALSO READ: Who are Prince and Princess of British Royal Family; Why Meghan and Philips’ Son not Given Title?
13. Liechtenstein
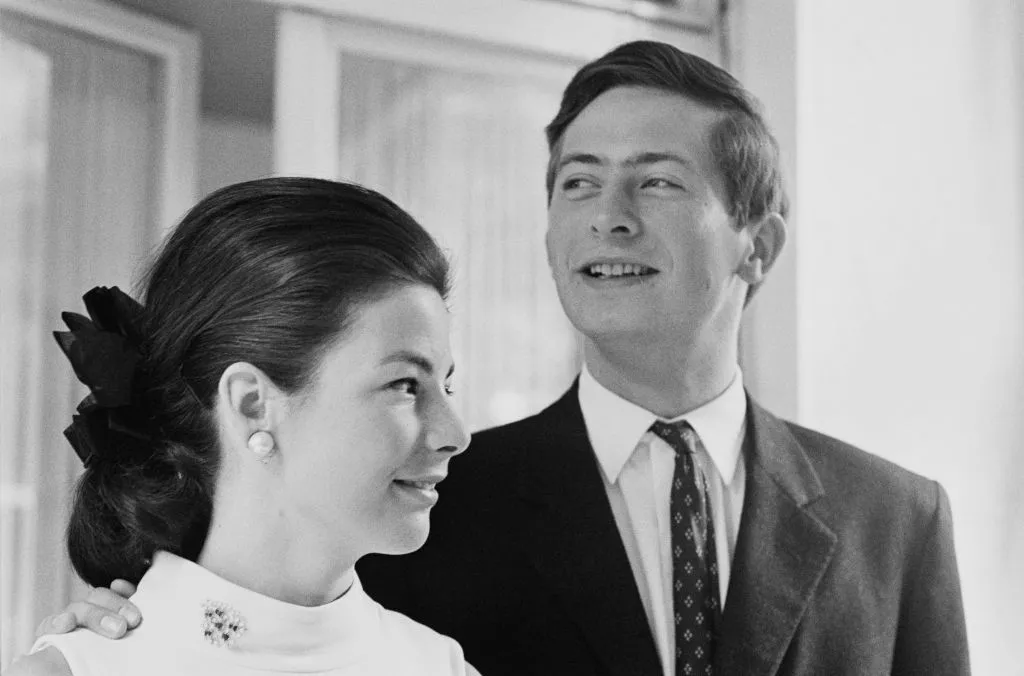

The Principality of Liechtenstein is a small country in Western Europe whose form of government is a constitutional monarchy. Prince Hans-Adam II has reigned since 1989.
14. Luxembourg
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg is a small landlocked nation in Western Europe.
Luxembourg is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy with one legislative house. While the grand duke appoints the prime minister, his powers are mainly formal. Grand Duke Henri has reigned since 2000.
15. Malaysia
Malaysia is a constitutional monarchy in Southeast Asia. Abdullah of Pahang is the 16th Yang di-Pertuan Agong (monarch) of Malaysia and the sixth Sultan of Pahang. He was proclaimed as Sultan on 15 January 2019, succeeding his father, Sultan Ahmad Shah, whose abdication was decided at a Royal Council meeting. On 24 January 2019, days after his accession to the throne of Pahang, he was elected as the 16th Yang di-Pertuan Agong of Malaysia. He was sworn in on 31 January. He was also a member of the FIFA Council from 2015 to 2019.
16. Monaco
The Principality of Monaco is a microstate located along the French Riviera in Western Europe, and is one of a small number of countries where the monarch is active in daily politics. Prince Albert II, son of the late American actress Grace Kelly, has been the head of state of the country since 2005.
17. The Netherlands
The Kingdom of the Netherlands is a constitutional monarchy with most of its territory located in Western Europe and with several small island territories in the Caribbean Sea. The monarch of the kingdom is the country’s head of state. King Willem-Alexander ascended the throne in 2013.
18. Norway
The Kingdom of Norway is a constitutional monarchy located in Northern Europe. King Harald V and Queen Sonja have reigned since 1991.
19. Saudi Arabia
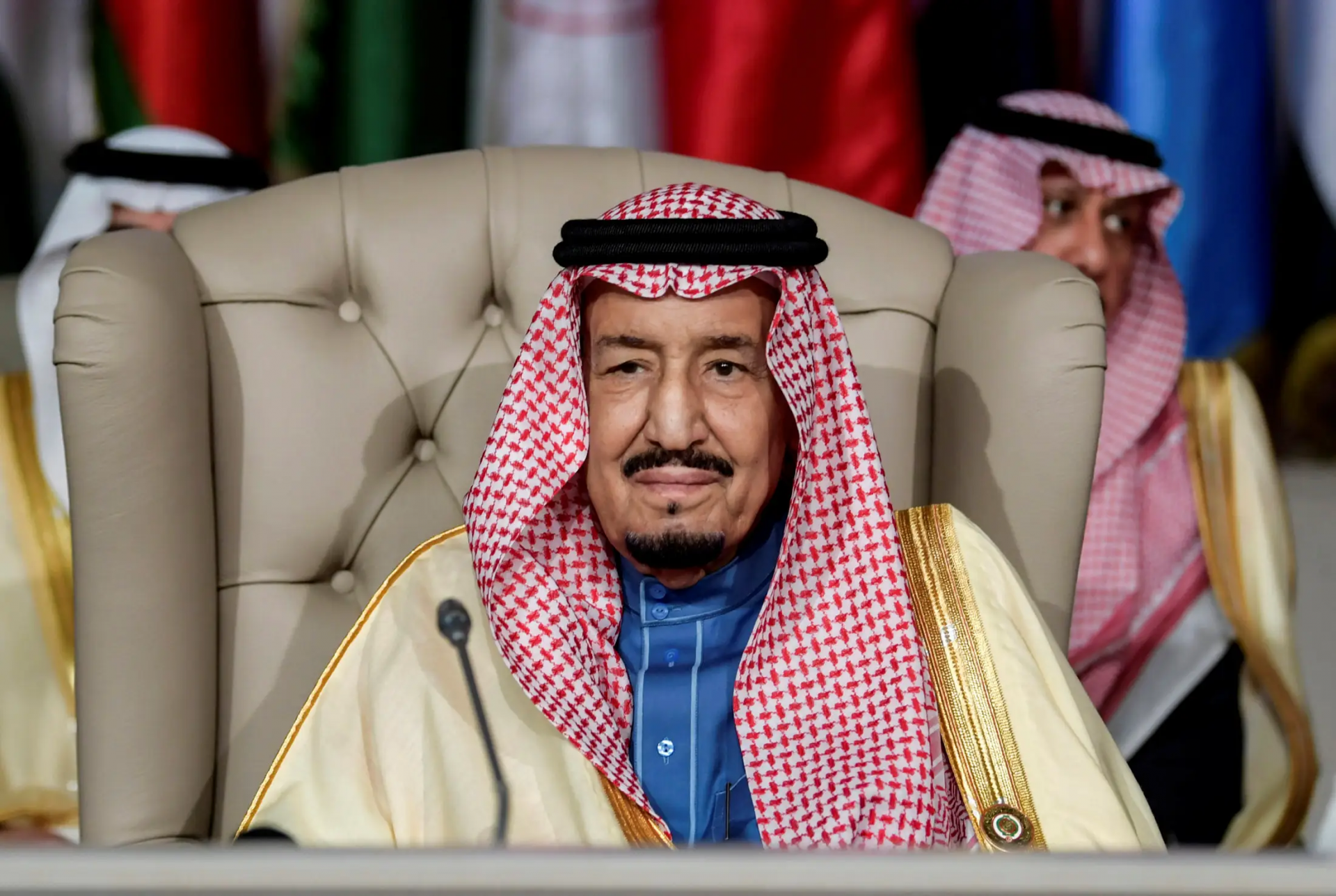

The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is located on the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East. The nation is an absolute monarchy, with King Salman bin Abdulaziz al-Saud acting as prime minister and head of state since 2015.
20. Spain
The Kingdom of Spain is a parliamentary monarchy primarily occupying part of Europe’s Iberian Peninsula and also including the Canary Islands and the Balearic Islands. King Felipe VI is the current head of state. He ascended to the throne in 2014 following the abdication of his father, King Juan Carlos.
21. Sweden
The Kingdom of Sweden is a constitutional and parliamentary democracy located in Northern Europe. The long history of Swedish monarchs date to the late 10th century and King Carl XVI Gustaf is the current head of state, ascending the throne in 1973.
21. Thailand
The Kingdom of Thailand is located on the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia. Although it calls itself a constitutional monarchy, the country has a modern history dotted by frequent coups, the latest placing the nation under the rule of a de facto military dictatorship. Maha Vajiralongkorn has been king since 2016 and his official coronation takes place May 4-6.
22. Vatican City
Vatican City is a city-state located within Rome and the world’s smallest independent state. The government is an absolute elective monarchy run by the Roman Catholic Church, effectively making the pope an elected non-hereditary monarch. Pope Francis was elected into the position in 2013.
23. Oman
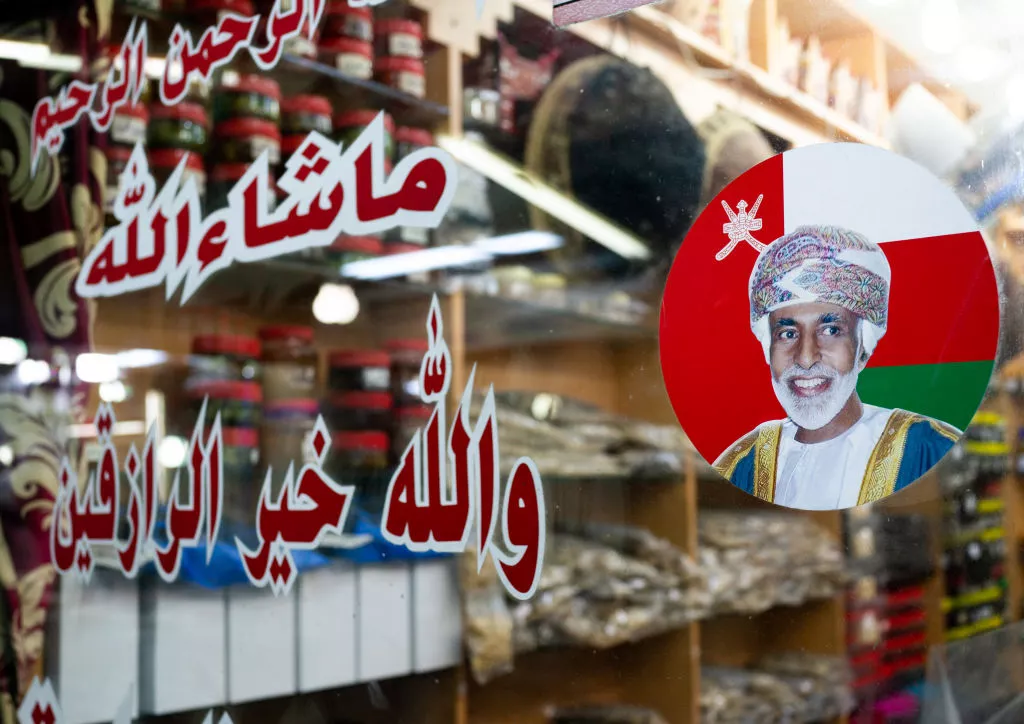

Yet another nation on the Arabian Peninsula to have a king (actually the official title here is “sultan”), Oman has been ruled by Qaboos bin Said al Said since 1970. He came to power in a palace coup, overthrowing his father, who was exiled to England where he died two years later. Recently, Sultan Qaboos has brought about political reforms, allowing parliamentary elections for the first time. Despite its status as an absolute monarchy, Oman has enjoyed a reasonable level of prosperity under the Sultan. The country is considered more open and liberal than other theocratic Arabian Peninsula nations, and healthcare and education are a major part of government spending. Critics have likened Qaboos to a dictator, however, saying he has more absolute control over his country than any other monarch in the world.
24. The United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates is a federation of seven different kingdoms (emirates), each with its own ruler. Dubai and Abu Dhabi are the most well-known of the emirates and their absolute monarchs hold the most power of the seven members. However, all seven emirs sit on the Federal Supreme Council, which, in effect, oversees all operations of the country. This group appoints various ministers, advisors, and 20 members of the 40 member National Council. The other 20 National Council representatives are elected, but by members of an electoral college, not by popular vote. Dubai and Abu Dhabi, and to a lesser extent the other emirates, are known for their rapid pace of modernization, with the emirs commissioning massive and ambitious construction projects to draw investment and tourism.
25. Luxemburg
Henri is the Grand Duke of Luxembourg, reigning since 7 October 2000. He represents, in the words of the official government Web site, "a symbol of stability, a single figure at the head of state, above the daily political business. In 2019, his net worth was estimated at around US$4 billion.
26. Greenland
Greenland is part of the Kingdom of Denmark, though it has governed itself through an elected parliament since 1979. Denmark's Queen Margrethe II is still the queen in name there, however; the 73-year-old queen has reigned since 1972 and is to eventually pass the throne to her son Frederik.
What is Monarchy?
A monarchy is a form of government in which total sovereignty is invested in one person, ahead of a state called a monarch, who holds the position until death or abdication. Monarchs usually both hold and achieve their position through the right of hereditary succession (e.g., they were related, often the son or daughter, of the previous monarch), although there have been elective monarchies, where the monarch holds the position after being elected: the papacy is sometimes called an elective monarchy.
There have also been hereditary rulers who weren’t considered monarchs, such as the stadtholders of Holland. Many monarchs have invoked religious reasons, such as being chosen by God, as a justification for their rule. Courts are often considered a key aspect of monarchies. These occur around the monarchs and provide a social meeting place for monarch and nobility.
Titles of a Monarchy
Male monarchs are often called kings, and females queens, but principalities, where princes and princesses rule by hereditary right, are sometimes referred to as monarchies, as are empires led by emperors and empresses.
Levels of Power
The amount of power a monarch wields has varied across time and situations, with a good deal of European national history comprising a power struggle between the monarch and either their nobility and subjects. On the one hand, you have the absolute monarchies of the early modern period, the best example being French King Louis XIV, where the monarch (in theory at least) had total power over everything they wished. On the other, you have constitutional monarchies where the monarch is now little more than a figurehead, and the majority of power rests with other forms of government. There is traditionally only one monarch per monarchy at a time, although in Britain King William and Queen Mary ruled simultaneously between 1689 and 1694. When a monarch is either considered too young or too ill to take full control of their office or is absent (perhaps on crusade), a regent (or group of regents) rules in their place.
The Modern Age
After the absolute era, a period of republicanism took place, as secular and enlightenment thinking, including the concepts of individual rights and self-determination, undermined the claims of the monarchs. A new form of “nationalist monarchy” also emerged in the eighteenth century, whereby a single powerful and hereditary monarch ruled on behalf of the people to secure their independence, as opposed to expanding the power and possessions of the monarch themselves (the kingdom belonging to the monarch).
In contrast was the development of the constitutional monarchy, where the powers of the monarch were slowly passed down to other, more democratic, bodies of government. More common was the replacement of monarchy by a republican government within the state, such as the French Revolution of 1789 in France.
 Who are Prince and Princess of British Royal Family; Why Meghan and Philips’ Son not Given Title? Who are Prince and Princess of British Royal Family; Why Meghan and Philips’ Son not Given Title? The questions around who is the prince and princess of the British Royal Family while Archie- Meghan and Harry’s son are not given the Royal ... |
 The Full Statement issued by Buckingham Palace on Harry and Meghan interview The Full Statement issued by Buckingham Palace on Harry and Meghan interview A statement issued by Buckingham Palace said the Queen Elizabeth was "concerned" and "saddened" by the revelations from the couple in the Meghan and Prince ... |
 Meghan and Harry Interview: What is Buckingham Palace's reaction and Little Known Facts About Meghan and Harry Interview: What is Buckingham Palace's reaction and Little Known Facts About Little Known Facts about Meghan Markle and Prince Harry’s Oprah Interview: Viewed by 12.4 million making it the biggest TV show of the year; What ... |
 UK’s Prince Philip in hospital: What did Buckingham Palace say, How is he now? UK’s Prince Philip in hospital: What did Buckingham Palace say, How is he now? Prince Philip, 99, husband of Queen Elizabeth has admitted to hospital after reportedly feeling unwell. What did Buckingham Palace announce and how is he now, ... |