Former Soviet Union (USSR): What Happened to the 15 Republics Today
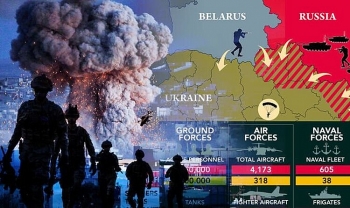 2022 Military Strengths of Russia and Ukraine in Comparison 2022 Military Strengths of Russia and Ukraine in Comparison |
 Fact-Check: Vanga Prediction for the Russian - Ukraine War? Fact-Check: Vanga Prediction for the Russian - Ukraine War? |
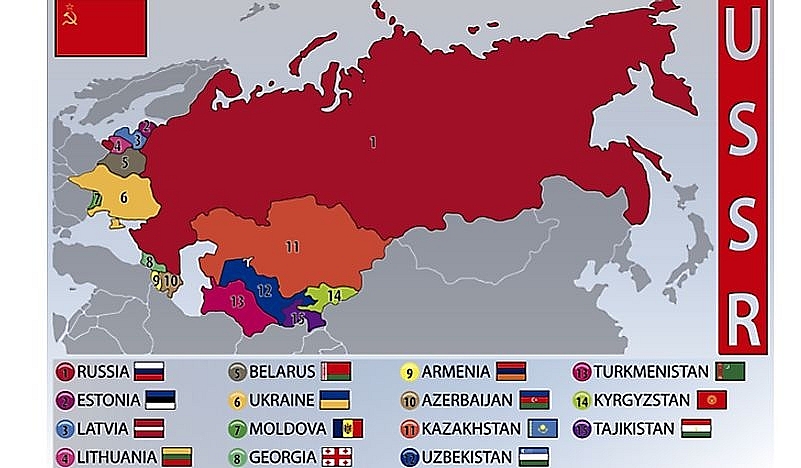 |
| What was Former Soviet Union (USSR) - Full List of Countries: Map and flags of the 15 republics of the former USSR. Getty Images |
| Table of Content |
What was the Former Soviet Union (USSR): Full List of Countries, History, Facts
Vladimir Lenin established the Soviet Union, also known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), as a socialist nation in 1922.
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), established in 1922 as a confederation of Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, and Transcaucasia (composed of Georgia, Azerbaijan, and Armenia), eventually expanded to 15 republics and became a global superpower.
The vast nation, which spanned 11 time zones, was home to nearly 130 ethnic groups.
The USSR held the title of largest country in the world for much of its existence. In 1991, the USSR disintegrated, leaving 15 modern independent states in its wake.
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), a federation made up of Russia, Belorussia, Ukraine, and the Transcaucasian Federation, is founded in post-revolutionary Russia (divided in 1936 into the Georgian, Azerbaijan and Armenian republics). The new communist state, also known as the Soviet Union, succeeded the Russian Empire and was the first nation in the world to be based on Marxist socialism.
The Bolshevik Party, led by Vladimir Lenin, controlled the soviet forces during the 1917 Russian Revolution and the three-year Russian Civil War, a coalition of workers' and soldiers' committees that demanded the creation of a socialist state in the former Russian Empire. The Communist Party maintained control over all levels of government in the USSR, and its politburo, led by its progressively more potent general secretary, effectively served as the country's executive branch. Agriculture was divided up into state-run collective farms, and Soviet industry was owned and run by the state.
The Russian-dominated Soviet Union expanded to include 15 republics, including Russia, Ukraine, Georgia, Belorussia, Uzbekistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia, in the decades that followed its founding.
Political Map of Soviet Union
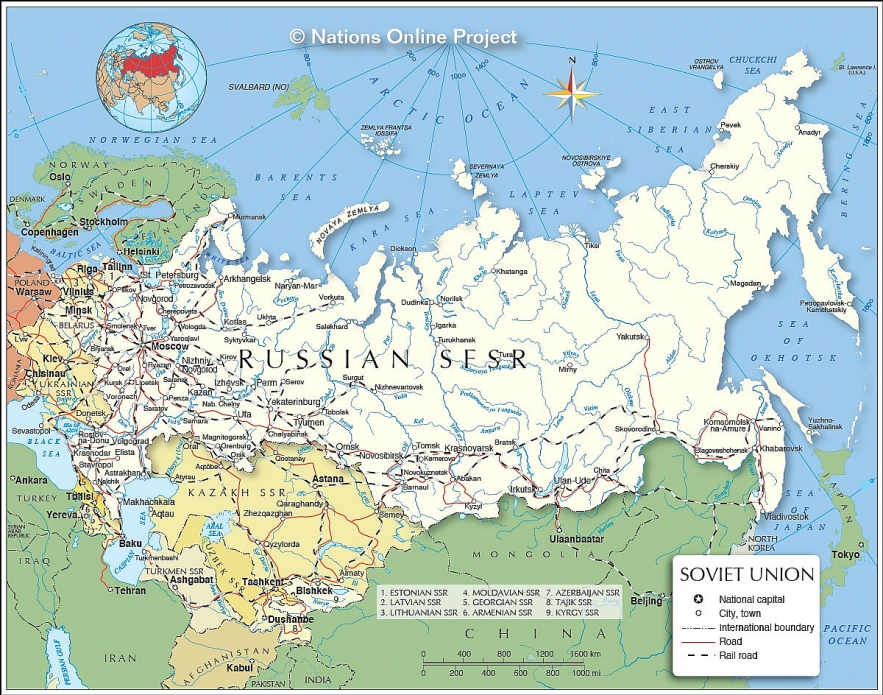 |
| Map of Soviet Union |
The map shows the Soviet Union and surrounding countries with international borders, the capital Moscow, Soviet Socialist Republics, major cities, main roads, railroads, and major airports.
Facts About Soviet Union
The Soviet Union, which occupied more than one-sixth of the Earth's landmass, was larger than the USA by more than two to one. However, a large portion of the nation was uninhabited or uninhabitable. Russia and the former Soviet Union both have extremely low population densities (8.5 people per square kilometer, compared to 226 in Germany and 33 in the United States). Nevertheless, there were close to 300 million people living in the USSR. In the USSR, Leningrad (now St. Petersburg), which was the second-largest city, was behind Moscow as the hub of political power, the center of culture, and the hub of trade.
The 15 Soviet Socialist Republics that made up the Soviet Empire were: Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Estonia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kirgiziya (now Kyrgyzstan), Latvia, Lithuania, and Moldavia (now Moldova).
The Soviet Union shared maritime borders with the USA and Sweden in addition to land borders with Afghanistan, Czechoslovakia (now the Czech Republic and Slovakia), China, Finland, Hungary, Iran, North Korea, Mongolia, Norway, Poland, Romania, and Turkey, totaling about 20,000 km of borders.
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact, a collective defense pact signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other socialist nations of the Eastern Bloc, including Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, and Romania, included the nations in the USSR's sphere of influence. After West Germany joined NATO in 1955, the Warsaw Pact was established in retaliation.
Geography of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union had a vast geographic range: 10,000 km from its western borders to the eastern coast of the Russian Far East at the Bering Street; 11 of the world's 24 time zones; 52 ethnic groups with populations greater than 100,000; 23 of these groups had populations greater than one million; 42,777 km of coastline; and, as already mentioned, the largest empire in history.
The Soviet Union had a diverse landscape. West of the Ural mountain range, which divides the country's Asian and European halves, is the European Plain, which is centered by Moscow. The majority of the population lived there.
Mountains
between the western coast of the Caspian Sea and the southern Black Sea in the southwest is the Caucasus Mountain Range. The Pamir Mountains are to the south of the Ural. Some of the tallest mountains in the world are found within this mountain range, which dominates the majority of present-day Tajikistan. It contained Communism Peak in Tajikistan, the highest mountain in the Soviet Union, with a peak elevation of 7,495 m (now Ismoil Somoni Peak) (24,590 ft).
The West Siberian Plain is located east of the Ural Mountains. The Altai Mountains and the Kazakh Uplands in the south, the Yenisey River valley and the Central Siberian Plateau in the east, and the Kara Sea in the north form the borders of the largest continuous lowland area in the world. The Stanovoy Mountains, Yablonovy Mountains, Verkhoyansk Range, Sikhote-Alin mountain range, Kolyma Mountains, and the mountainous Kamchatka Peninsula with a coastline at the Bering Sea and the Sea of Okhotsk are all found further east of the Soviet Union/Russia.
In 1991, the Soviet Union was dissolved following the collapse of its communist government.
Armenia
Moldova
Estonia
Latvia
Lithuania
Georgia
Azerbaijan
Tajikistan
Kyrgyzstan
Belarus
Uzbekistan
Turkmenistan
Ukraine
Kazakhstan
Russia
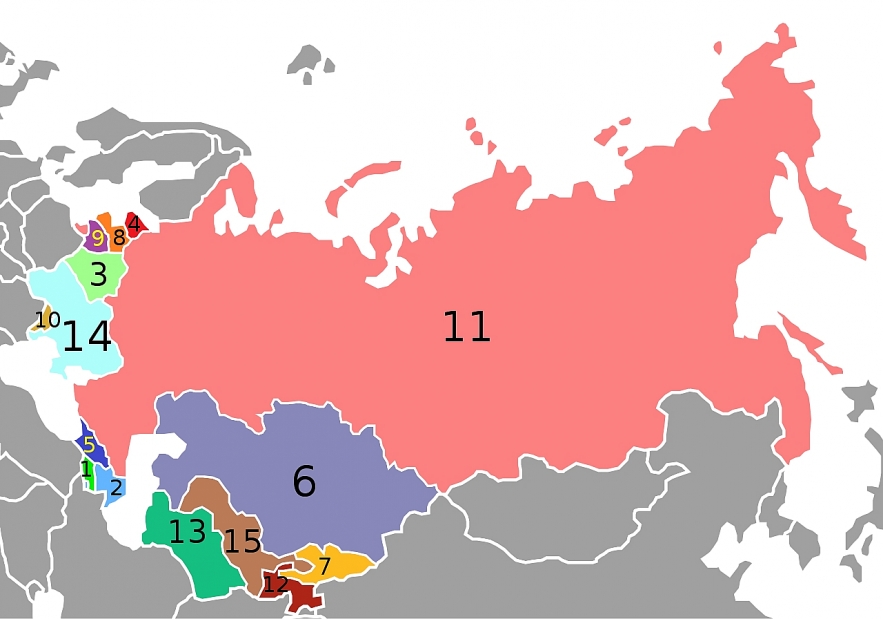 |
| Republics of the Soviet Union, numbered alphabetically by the English names of the post-soviet states: 1 Armenia, 2 Azerbaijan, 3 Belarus, 4 Estonia, 5 Georgia, 6 Kazakhstan, 7 Kyrgyzstan, 8 Latvia, 9 Lithuania, 10 Moldova, 11 Russia, 12 Tajikistan, 13 Turkmenistan, 14 Ukraine, 15 Uzbekistan |
Military Strengths of Russia and Ukraine in Comparison
What happened to the 15 republics in the decades after the USSR’s disintegration
1. Russian Federation
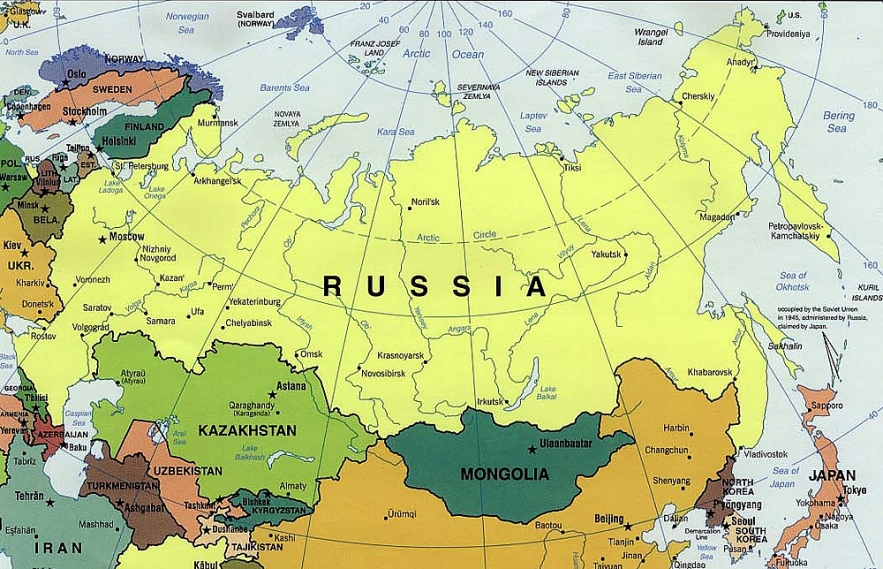 |
| Map of Russia |
Soviet Union
The Russian Federation, the largest nation in the world with 6.6 million square miles, is situated in Eurasia. The USSR was composed of Soviet Russia and the other Soviet Republics. With more than half of the population of the USSR, Russia was the largest member of the Soviet Union. Over the course of the Soviet Union's 69-year history, Soviet Russia ruled it.
The Soviet Union had the second-largest economy in the world prior to 1991, but inflation later had a significant impact. By 1991, the Soviet Union was in a state of political and economic upheaval, which led the Baltic Republics to sever ties with it.
After the USSR’s disintegration
After the USSR collapsed on December 25, 1991, Russia experienced a severe economic crisis that resulted in high mortality, low birthrates, and the disintegration of social services.
After some of its republics broke away, the country that was left of the Soviet Union, now known as the Russian Federation, is still the largest in the world, occupying more than 11% of the planet's inhabited space.
Meanwhile, poverty in Russia increased from 1.5% to roughly 39 to 49%, affecting millions of people. The 1990s in Russia were marked by violent crime, egregious corruption, criminal gangs, and lawlessness.
While oligarchs amassed enormous wealth, the majority of Russians experienced high inflation and a lack of supplies. After ordering the army to shell the nation's legislative building to end a constitutional crisis in 1993, Russian Federation President Boris Yeltsin started a disastrous war in the breakaway republic of Chechnya.
Following a cease-fire in 1997, Yeltsin’s government ordered a second attack of Chechnya in 1999 after Russian authorities asserted that bombings in Moscow and other cities were linked to Chechen militants. Then-Prime Minister Vladimir Putin led the military response against Chechnya.
On December 31, 1999, Yeltsin announced his resignation and named Putin acting president. Since taking office and serving as president, prime minister and again as president, Putin has consolidated authority. In seeking to re-establish Russia as a global power and limit Western influence in the former Soviet republics, Putin continued the war in Chechnya, annexed Crimea from Ukraine in 2014 and attack Ukraine in 2022.
How Strong Is The Russian Army - 2nd Strongest Militaries in the World
2. Ukraine
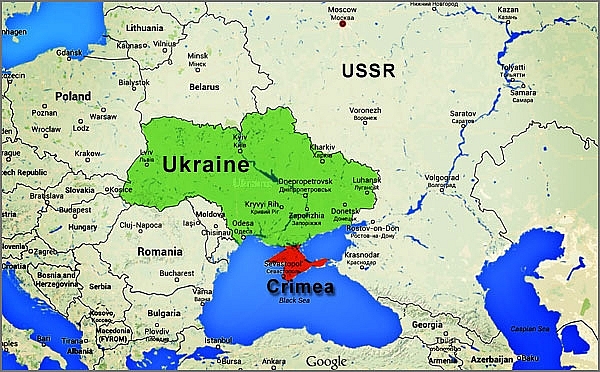 |
| Map of Ukraine showing Crimea with Blak Sea and neighbouring countries, USSR, Belarus, Romannia, Poland, Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary, Geogia. |
Soviet Union
A sovereign nation, Ukraine has an area of 233,000 square miles. On December 30, 1922, the Ukrainian SSR, also known as UkSSR, was admitted as one of the Soviet Union's constituent republics. Soviet Ukraine was a founding member of the UN, but in disputes involving nations that were not a part of the USSR, the All-Union state served as its legal representative.
Ukraine provided a quarter of the agricultural output for the USSR and was once referred to as Europe's breadbasket due to its large wheat fields.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Society, UkSSR was renamed as Ukraine and its new constitution was approved on June 28, 1996. Post independence the country has retained its seat in the UN and continues to pursue allegations in foreign courts against the Russian Federation in hopes of recovering its foreign property share.
Since independence, the country’s politics have lurched between pro-Russian and pro-European governments. In 1994 Ukraine became the first former Soviet republic to peaceably transfer power through an election, and it transitioned toward capitalism over the next decade.
After pro-Russian candidate Viktor Yanukovych declared victory in a presidential election beset by fraud in 2004, the peaceful Orange Revolution forced a new vote that was won by pro-Western candidate Viktor Yushchenko, who sought membership in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). When Yanukovych, who subsequently won the presidency in 2010, backed away from signing an association agreement with the European Union (EU) in 2014, the Maidan street protests forced him to flee to Russia as a pro-Western coalition took power. Weeks later, Russia annexed Crimea while pro-Russian rebels launched an insurgency in eastern Ukraine. In 2019, a former actor and comedian Volodymyr Zelenskyy was elected the nation's new president.
In 2022, Russian President Putin claimed that Ukraine never had stable statehood and said the country was instead part of Russia’s “own history, culture, spiritual space.” Days later, Russia attacked Ukraine in the largest European military operation since World War II.
How Strong Is The Ukrainian Army - 22nd Strongest Militaries in The World
3. Kazakhstan
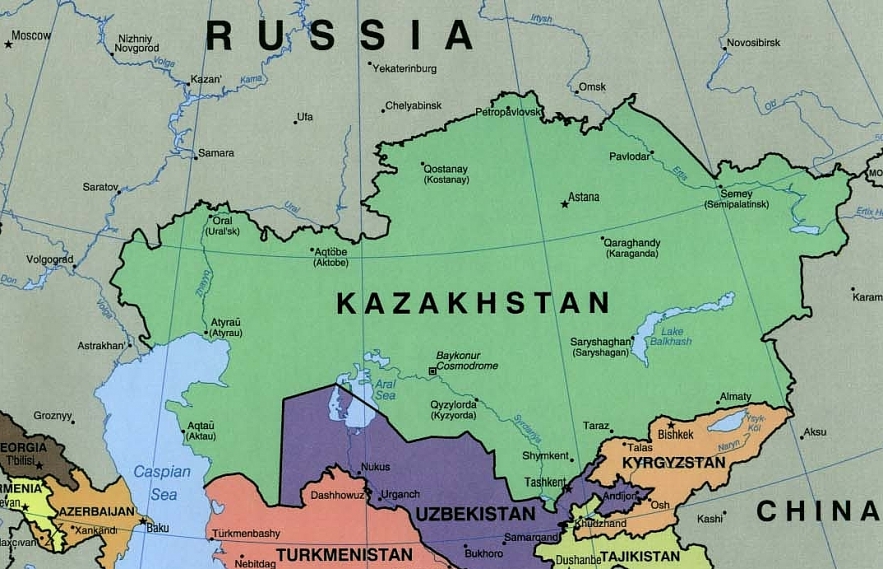 |
| Map of Kazakhstan |
The Republic of Kazakhstan, which spans 1.05 million square miles, is the world's largest landlocked nation. It is a transcontinental nation that is situated in northern Central Asia and Eastern Europe.
The Slavic settlers who colonized the Kazakh SSR, which became a republic in 1936, farmed wheat on its grasslands and served as the focal point of the nation's space program.
The nation was the last of the Soviet Union's constituent republics to declare independence during the USSR's dissolution.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Since Kazakhstan's independence, Nursultan Nazarbayev has served as its president. Human rights violations and the repression of political opposition have been hallmarks of the current president's administration.
Kazakhstan privatized its economy after gaining independence, and as a result, it saw tenfold growth in 20 years thanks to oil reserves that were the largest of any former Soviet republic aside from Russia.
Kazakhstan has strong ties with both the West and Russia, which it enlisted in 2022 to help put an end to widespread demonstrations against rising inequality and the price of liquefied gas.
4.Turkmenistan
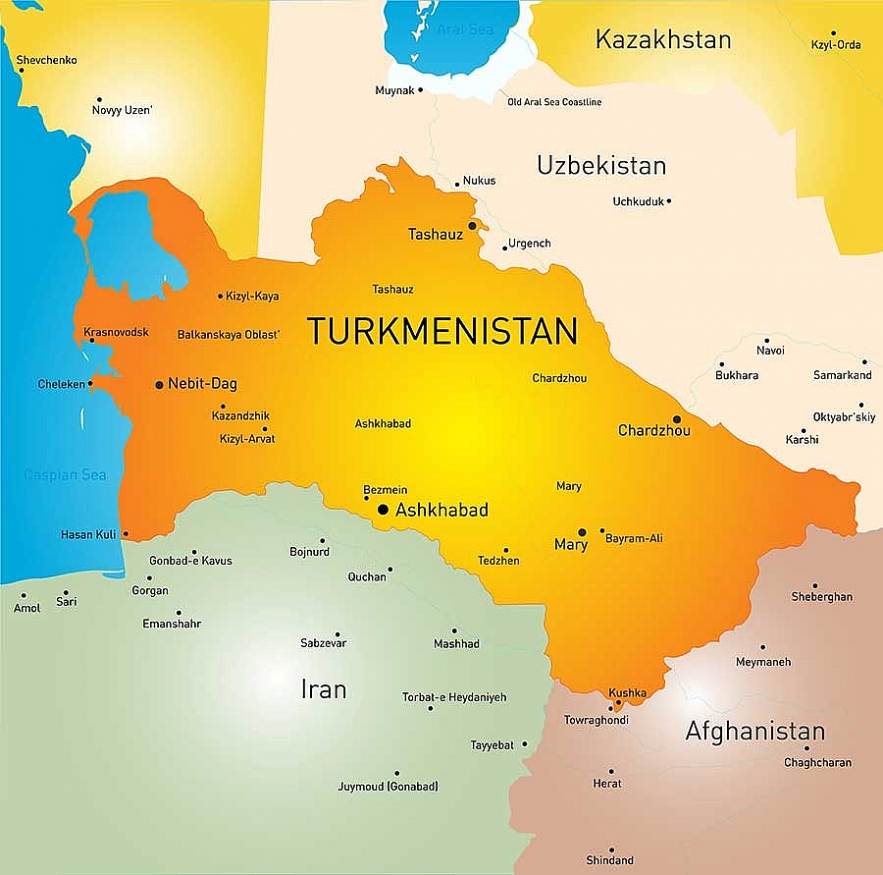 |
| Map of Turkmenistan |
Turkmenistan, formerly known as Turkmenia, covers an area of 190,000 square miles. Turkmenistan was annexed into the Russian Empire and was later established as one of the Soviet Union's constituent republics in 1924. The Soviet Union reorganized agricultural practices thus destroying the nomadic lifestyle in the country.
The Turkmen and Uzbek SSRs joined the Soviet Union in 1925, followed by the Tajik SSR in 1929 and the Kirghiz SSR in 1936. Soviet leaders transformed the majority-Muslim region through forced collectivization of agriculture, which produced devastating famines in 1930s, and the encouragement of Russian immigration.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Its political life was controlled by Moscow. Economically, Turkmenistan played its delegated role within the USSR. However, the country declared its sovereignty in 1990 but was barely ready for independence, therefore, opting to preserve the USSR.
On October 27, 1991, the country declared its independence from the Soviet Union which was recognized on December 26, 1991. Since the country's independence from the Soviet Union, Turkmenistan has maintained in a neutral position in regards to most international matters.
Following independence, strongmen have ruled these mountainous, energy-rich countries. Although economically dependent on Russia, the former republics permitted American and NATO forces to use their airspace and military facilities during the war in Afghanistan following the September 11, 2001, attacks.
5.Uzbekistan
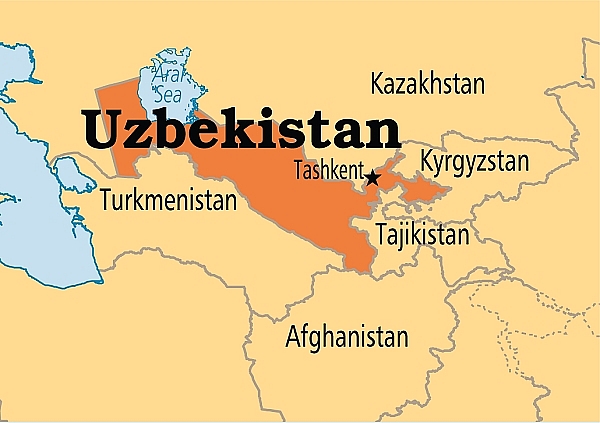 |
| Map of Uzbekistan |
The Republic of Uzbekistan is one of the world's doubly landlocked countries and is located in Central Asia. Soviet Uzbekistan was established on October 27, 1924. Between 1941 and 1945 about 1.5 million Uzbekistanis fought against Nazi Germany alongside the red army during World War II.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Uzbekistan proclaimed itself a sovereign state on June 20, 1990 and declared its independence on August 31, 1991. Following the country's independence, Uzbekistan held its first election. At present, Uzbekistan has the second highest rate of modern slavery in the world at 3.97%
In Uzbekistan, Communist Party leader Islam Karimov easily won the country’s first presidential election and ruled Central Asia’s most populous country for a quarter-century until his 2016 death. Karimov’s successor, Shavkat Mirziyoyev, has continued to consolidate power and limit political opposition—while deepening ties with Russia.
6. Belarus
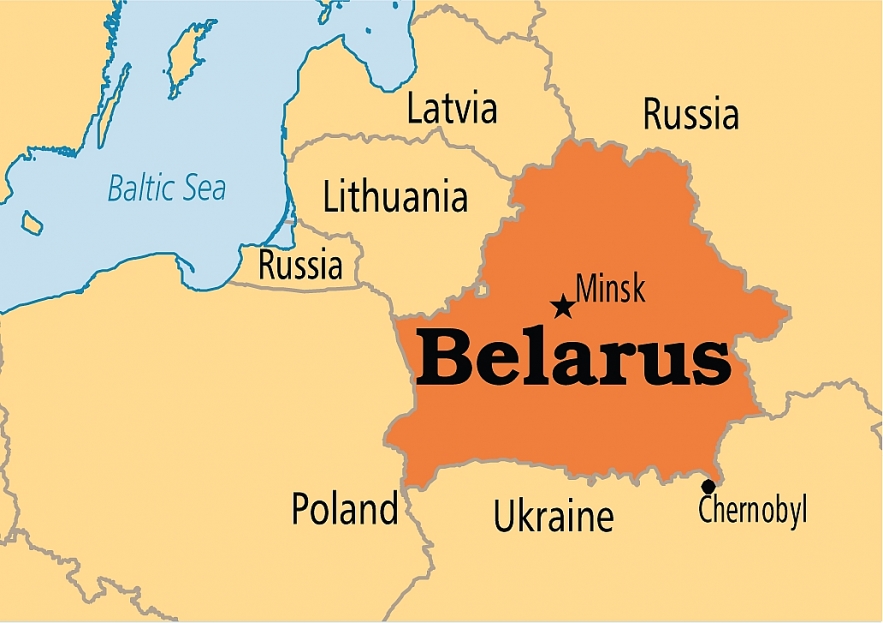 |
| Map of Belarus |
Soviet Belarus, Soviet Byelorussia, or BSSR was the name given to the area of Belarus that was ruled by Russia as of 1919. However, Lithuanian Byelorussia SSR soon became competitive with Poland and the Soviet Union. While the Belarusian SSR became a founding member of the USSR, the western portion of modern-day Belarus was still included in Poland before being annexed by the BSSR. The Soviet Union imposed economic and agricultural policies on the region between the 1920s and 1930s that led to political repression and famine. Near Minsk, a mass grave for those who were executed between 1937 and 1941 was found. The act was connected to the Soviet Union, which prompted Belarusian nationalists to declare their country's sovereignty on July 27, 1990.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Numerous disagreements with Russia that have arisen since the country's independence have harmed their relationship.
Alexander Lukashenko, the only post-Soviet president of the nation, established nearly absolute power through a repressive regime that is accused of rigging elections, imprisoning political opponents, and stifling the press. Belarus, a founding member of the USSR, has resisted privatization and keeps a close relationship with Russia.
7.Kyrgyzstan
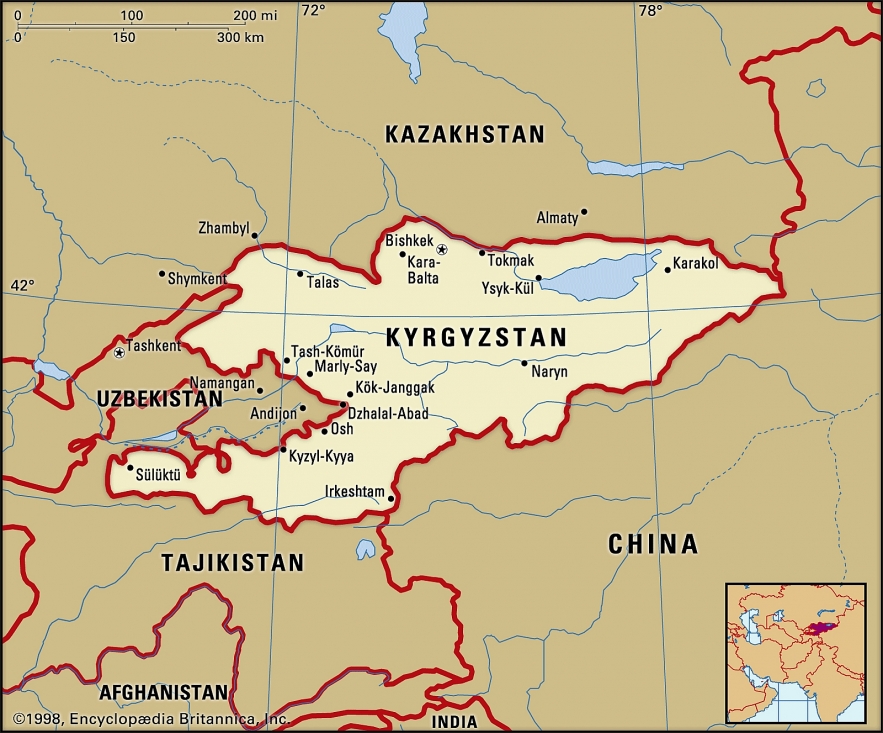 |
| Map of Kyrgyzstan |
With 77,000 square miles, Kyrgyzstan is a mountainous and landlocked country. Initially, the Soviet Union had established its power in the region in 1919. However, Soviet Kyrgyzstan was established on December 5, 1936.
After the USSR’s disintegration
The name of the region was changed to the Republic of Kyrgyzstan in December 1990 following a vote by the Supreme Soviet. Kyrgyzstan achieved complete independence on December 25, 1991, and the name was changed to the Kyrgyz Republic on May 5, 1993. Following its declaration of independence, the nation ascended to membership in both the OSCE and the UN. The majority of the new millennium has seen significant political instability in the nation.
After the 1991 presidential election of Asakar Akayev, who advocated liberal policies, Kyrgyzstan initially stood out as one of central Asia's most democratically oriented nations. Akayev, however, became more and more authoritarian as the economy of the nation deteriorated, and he was eventually forced from power in the 2005 Tulip Revolution by anti-corruption and pro-democracy protests. Similar protests prompted the resignation of Akayev's successor in 2010.
8. Tajikistan
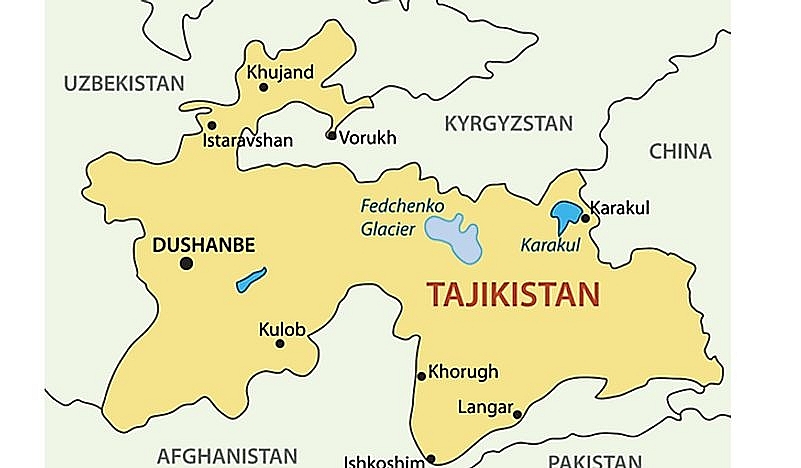 |
| Map of Tajikistan |
In Central Asia, there is a landlocked, mountainous nation known as the Republic of Tajikistan. Formerly known as Tajikistan or the Tajik SSR. Tajikistan was a Soviet republic from 1929 until 1991. Particularly in the southern part of the territory, collective farming and the rapid expansion of cotton production occurred between 1927 and 1934. The infrastructure for irrigation was improved over time as a result of additional small-scale developments.
After the USSR’s disintegration
On August 31, 1991, the region adopted the name Republic of Tajikistan, and on September 9, 1991, it proclaimed its independence. The Soviet Union officially recognized Tajikistan's independence on December 26, 1991. Following its declaration of independence, the nation became embroiled in a Civil War involving various factions. As a result of the increased poverty and persecution, more than 500,000 citizens left the nation.
Following independence, a five-year civil war between communists and a coalition of pro-Western democratic reformers and Islamists broke out in Tajikistan in 1992. Emomali Rahmon, the current president, came to power in November 1992 with the support of Russian troops. Since then, he has tightened control by repressing the press and political opponents. The authoritarian regime, which is plagued by pervasive corruption, is heavily reliant on Russian financial assistance.
9.Azerbaijan
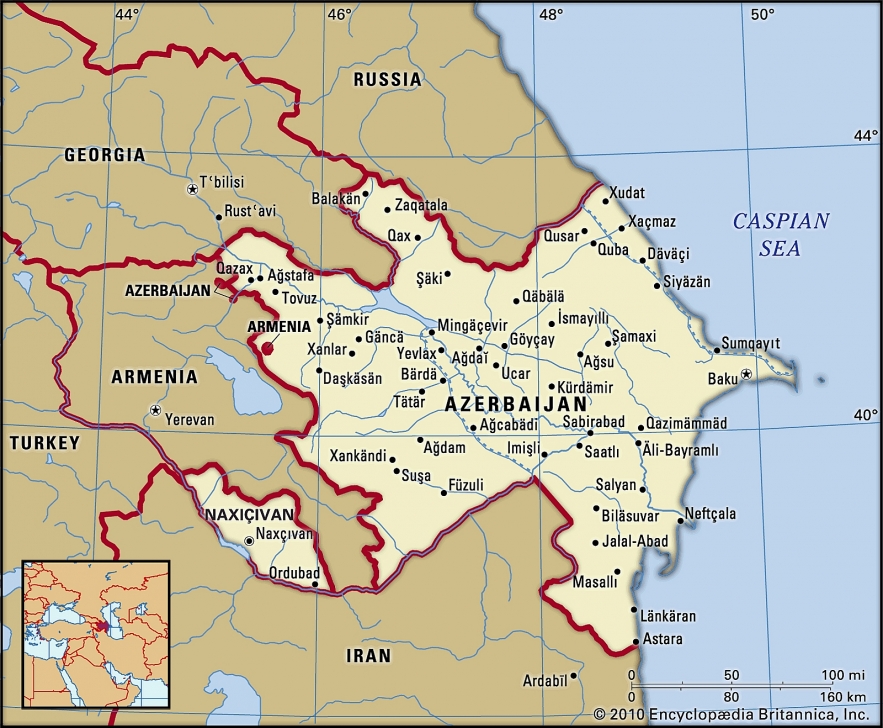 |
| Map of Azerbaijan |
The Republic of Azerbaijan is a country located at the crossroads of Southeastern Europe and Southwest Asia. The country was formerly known as Soviet Azerbaijan or Azerbaijan SSR.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Azerbaijan SSR was renamed on November 19, 1990, as the Republic of Azerbaijan and remained in the Soviet Union until its full independence in 1991. Following the adoption of the country's new constitution in 1995, the Azerbaijan SSR Constitution ceased to exist. Following its independence, Azerbaijan became a member state of the Non-Aligned Movement and was elected by the United Nations General Assembly to become a member of the Human Rights Council on May 9, 2006.
10. Georgia
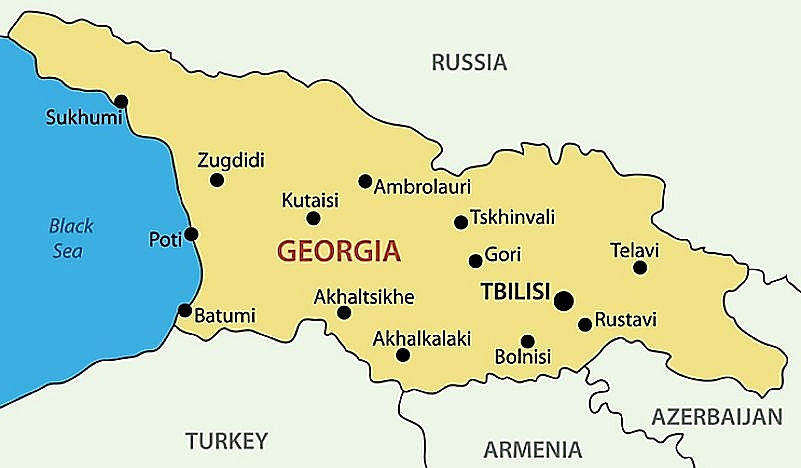 |
| Map of Georgia |
The Republic of Georgia is at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Formerly known as Soviet Georgia or Georgian SSR, the region covers an area of 27,000 square miles. Soviet Georgia was one of the Soviet Union's constituent republics admitted to the USSR on December 30, 1922.
After the USSR’s disintegration
The territory proclaimed its independence from the Soviet Union on November 18, 1989, and on November 14, 1990, it adopted the name Republic of Georgia. The nation struggled with the economic and civil crisis for the majority of the 1990s after gaining independence.
When Zviad Gamsakhurdia won the presidency in 1991, Georgia became the first Soviet republic to hold a democratic election. However, he only held office for a short time before a military coup installed former Soviet foreign minister Eduard Shevardnadze as president in 1992. The peaceful Rose Revolution of 2003, which removed Shevardnadze from office, was sparked by pervasive corruption and economic instability.
Relations with Russia are tense as a result of secessionist movements in the ethnic Russian enclaves of South Ossetia and Abkhazia. Georgia leaned more toward the West and signed an association agreement with the EU in 2014 after Russian forces crossed the border to join separatist fighters in South Ossetia in a brief war in August 2008.
11.Lithuania
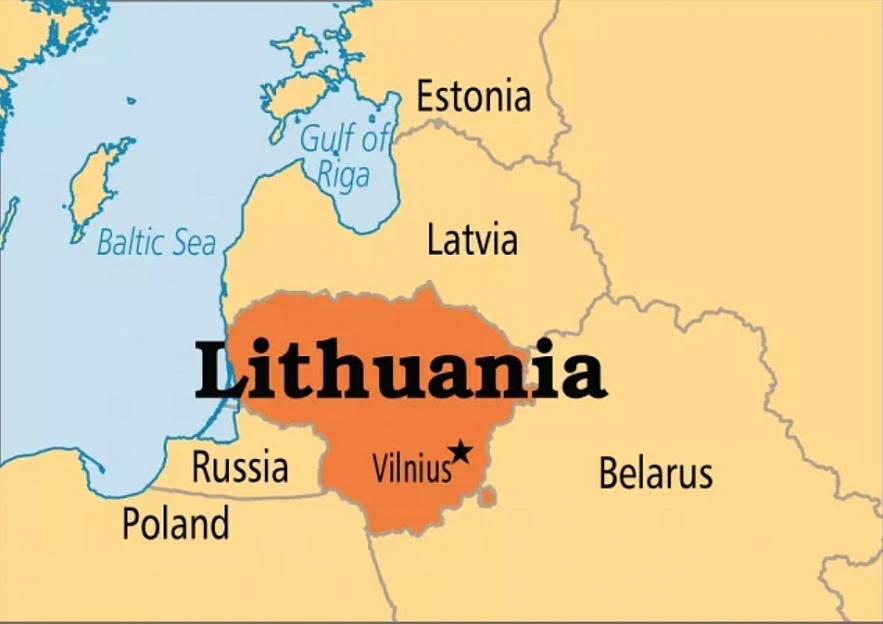 |
| Map of Lithuania |
One of the three Baltic States, the Republic of Lithuania is a landlocked country in Northern Europe with a total area of about 25,000 square miles. From 1940 to 1990, the nation was a republic within the Soviet Union known as Soviet Lithuania or the Lithuanian SSR. On July 21, 1940, Soviet Lithuania was officially founded. Between 1941 and 1944, the German Nazis occupied the region, and for the following 50 years, the Soviet Union reoccupied the area. The US, along with the majority of European countries, continued to recognize Lithuania as a sovereign independent state.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Soviet On May 18, 1989, Lithuania proclaimed itself a sovereign state, and even though Soviet authorities deemed the move illegal, the country was reestablished and recognized as an independent country. On September 6, 1991, the USSR recognized Lithuania as an independent nation under the name Republic of Lithuania. Following its independence, Lithuania joined the United Nations on September 17, 1991, as well as NATO and the European Union in 2004.
12. Latvia
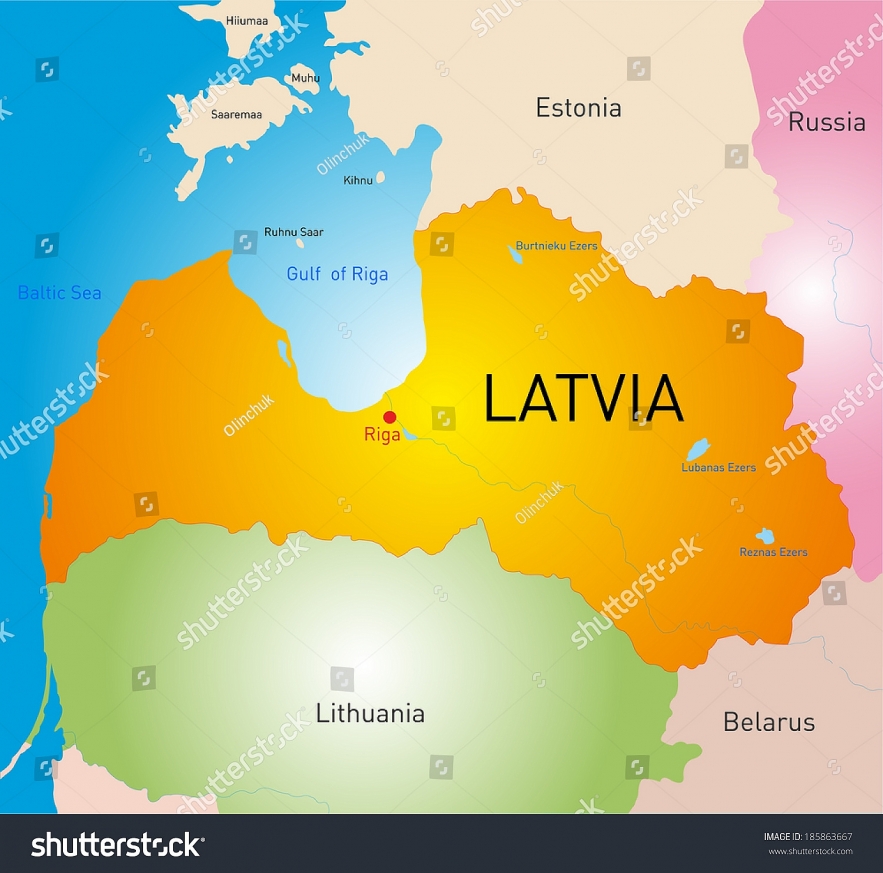 |
| Map of Latvia |
The Republic of Latvia is another Baltic State located in Northern Europe. The country is one of former Soviet Union's constituent republics also known as Soviet Latvia or Latvia SSR. Soviet Latvia was established during World War II on July 21, 1940 as a puppet state of the Soviet Union. Both the European community and the US refused to acknowledge the annexation of Latvia into the USSR on August 5, 1940.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Following the demise of the Soviet Union, the country restored its official name as the Republic of Latvia attaining its full independence on August 21, 1991. It was fully recognized as an independent state on September 6, 1991 by the Soviet Union. The country's primary goals in the post Soviet era were joining the European Union and NATO in 2004.
13.Estonia
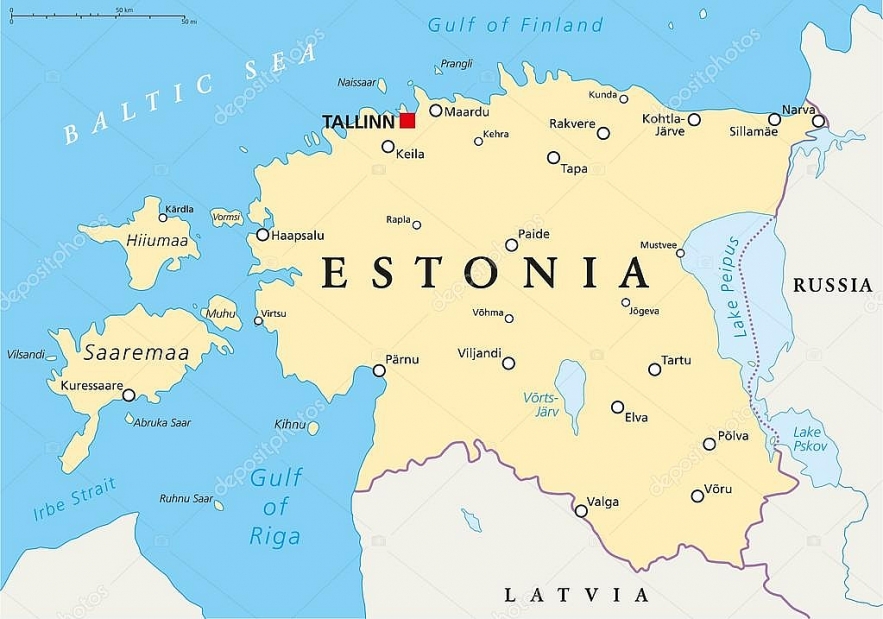 |
| Map of Estonia |
One of the three Baltic States in northern Europe is Estonia. The area was a member republic of the Soviet Union and was formerly known as the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic, or ESSR. As a result of the Soviet troops' invasion on June 17, 1940, the ESSR was initially established on the territory of the Republic of Estonia on July 21, 1940. Additionally, a puppet administration supported by the Soviet Union gave the go-ahead for the establishment of the nation. ESSR was eventually absorbed into the Soviet Union on August 9, 1940. The region was occupied by Nazi Germany from 1941 to 1944.
After the USSR’s disintegration
The Republic of Estonia was renamed ESSR on May 8, 1990, and the USSR officially recognized its independence on September 6, 1991. Russian troops left the country in August 1994, and after Estonia seized control of its nuclear reactor facilities in Paldiski, its military presence left in September 1995.
14. Moldova
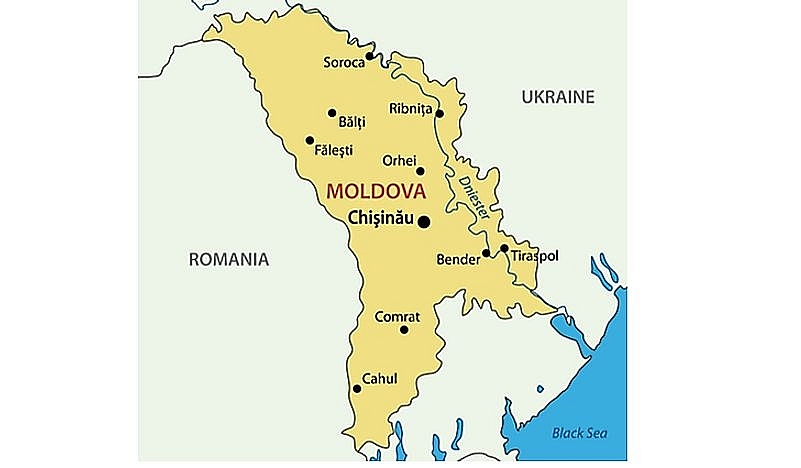 |
| Map of Moldova |
Officially known as Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic or MSSR, Moldova was among the Soviet Union's 15 republics from 1940 to 1991. Soviet Moldova was created on August 2, 1940 from a region that was annexed from Romania known as Bessarabia and parts of an autonomous state within the Ukrainian SSR.
After the USSR’s disintegration
Moldova became a sovereign state on June 23, 1990, but up until May 23, 1991, it was referred to as the Soviet Socialist Republic of Moldova. The nation was renamed the Republic of Moldova even though it continued to be a republic that made up the USSR. Civil war impacted Moldova after it gained independence.
Following independence, politicians supporting the EU and Russia have fought for power in Moldova. Moldova has been one of the poorest nations in Europe due to political unrest and widespread corruption, but it has cautiously moved toward market capitalism and full EU membership.
15. Armenia
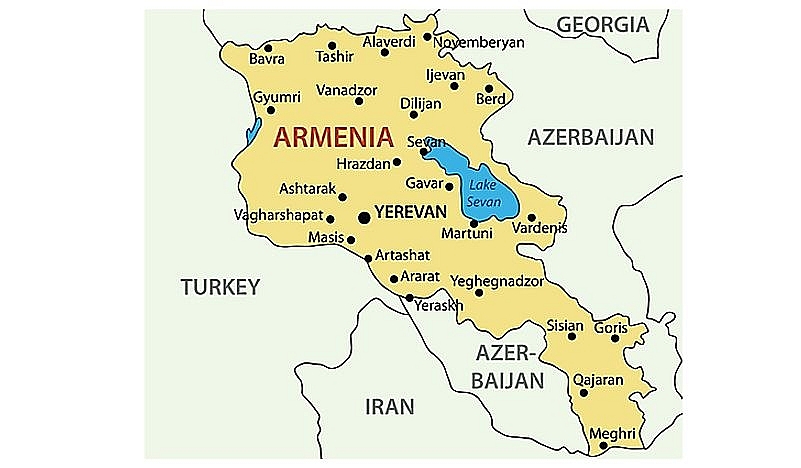 |
| Map of Armenia |
The Republic of Armenia, which covers an area of 11,500 square miles, was formerly known as Soviet Armenia. In December 1922, the nation was one of the Soviet Union's constituent republics. The First Republic of Armenia was taken over by the Soviets in 1920, at which point Soviet Armenia was born. The Second Republic of Armenia is another name for the nation, as the first was only briefly recognized.
After the USSR’s disintegration
On August 23, 1990, the nation formally proclaimed its independence and changed its name to the Republic of Armenia. But up until its official declaration of independence on September 21, 1991, Armenia was still a part of the Soviet Union. Armenia has advanced significantly since gaining its independence.
 Only in Ukraine: Top 50+ Weirdest Things, Unique Facts Only in Ukraine: Top 50+ Weirdest Things, Unique Facts Discover the weirdest and most interesting things about Ukraine that is being torn apart by the Russian attack. |
 Ukraine’s First Lady Olena Zelenska: Biography, Family and Career Ukraine’s First Lady Olena Zelenska: Biography, Family and Career Who is Ukraine’s First Lady? Biography, personal file of Olena Zelenska, the wife of President Zelensky. |


























