How Strong Is The Ukrainian Army - 22nd Strongest Militaries in The World
 |
| How Ukraine Has The World's 22nd Strongest Militaries? |
Russia has amassed an estimated 127,000 troops near the borders of Ukraine. Ukraine's military would be greatly outnumbered, and some Western experts believe Kyiv's forces could be quickly overwhelmed.
Most military analysts expect Russia to opt for crushing air strikes and/or limited land grabs rather than all-out war including battles for major cities.
Ukraine's Army
The Armed Forces of Ukraine are the principal deterrent force against any aggression that could be shown against the sovereign state of Ukraine. All military and security forces, including the Armed Forces, are under the command of the President of Ukraine, and subject to oversight by a permanent Verkhovna Rada parliamentary commission.
The Armed Forces of Ukraine are composed of the Ukrainian Ground Forces, the Ukrainian Navy, the Ukrainian Air Force, and the Ukrainian Airmobile Forces. Ukraine's naval forces maintain their own small Ukrainian Naval Infantry force as well as their own Ukrainian Naval Aviation force. The Ukrainian Sea Guard is the coast guard service of Ukraine, however, it is part of the State Border Guard Service of Ukraine and is not subordinate to the Navy. As a result of the Russian military intervention in Ukraine from 2014, the president commissioned governors of oblasts of Ukraine to create volunteer units under the government program "Territorial Defense". Initially these units received minimal funding coming from regional budgets and mostly relied on donations. In November 2014 most of the territorial battalions were integrated into Ukraine's Ground forces.
Read More: Top 15 Most Beautiful & Hottest Ukrainian Women That Mesmerize World
Here are the history, power and reasons why Ukraine has the world’s 22nd strongest militaries.
How Strong is Ukraine Military - Ukraine's Military Power Today
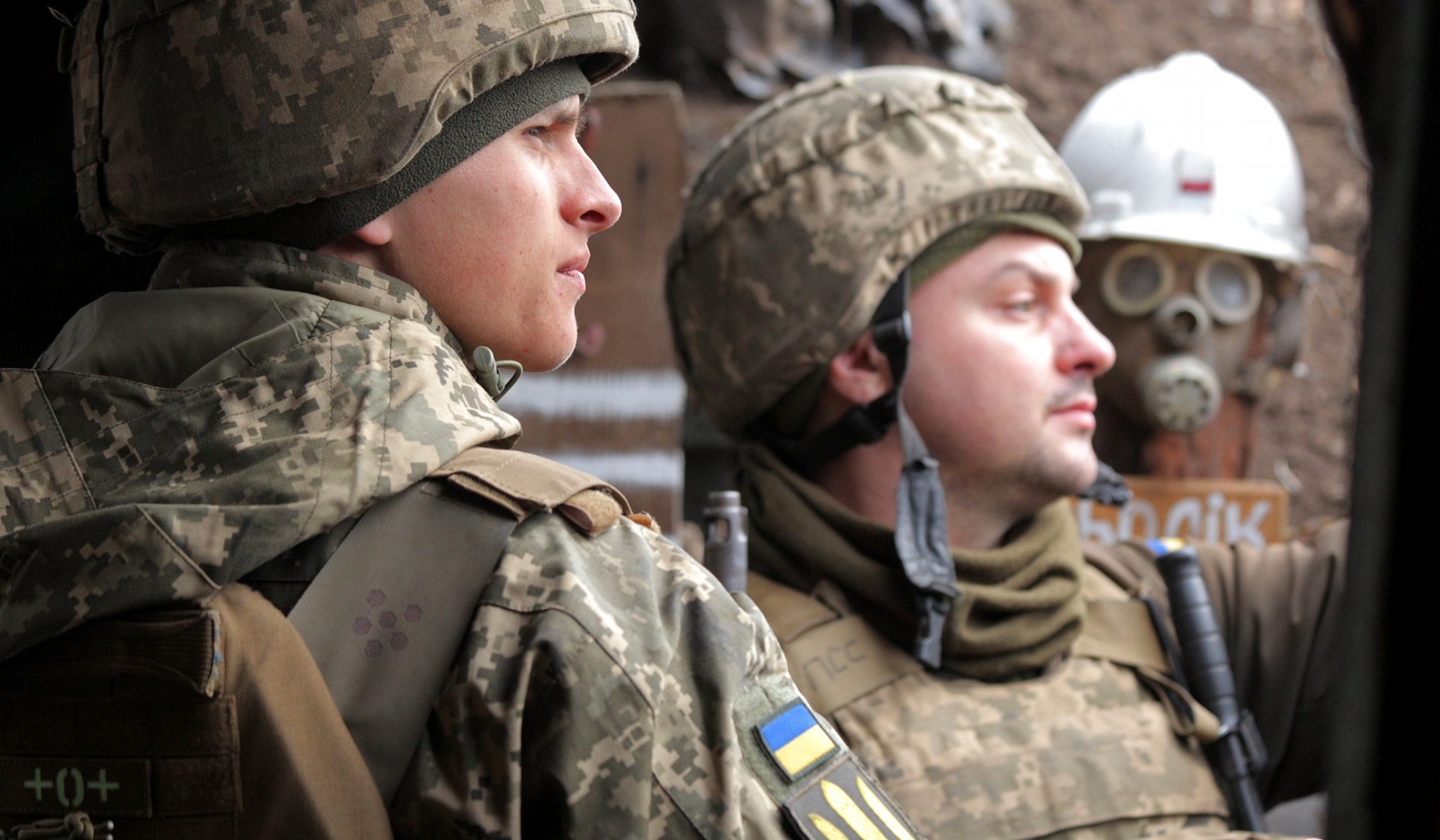 |
| Photo: National Review |
Despite being armed by Western nations since 2014, when pro-Russian rebels took control of eastern Ukraine from the central government forces, Kiev cannot do much to change military capability. However, it does not mean that Ukrainians do not have military capability.
The Ukrainian military has improved since 2014. In every area from the number of tanks to the strength of air force and active military personnel numbers.
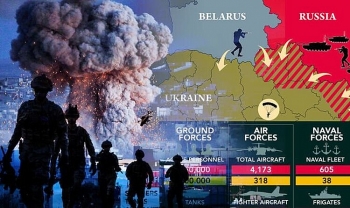 Military Strengths of Russia and Ukraine in Latest Comparison Military Strengths of Russia and Ukraine in Latest Comparison Russia is mobilizing a massive combat force near its border with Ukraine that includes tanks, artillery, rockets, and other heavy weaponry. How does Russia’s military ... |
How experienced are Ukraine's Army
When war between government troops and Russian-backed separatists erupted in eastern Ukraine 8 years ago, Ukrainian soldiers fought in tattered sneakers and donated flak jackets while their inexperienced commanders often waffled —sometimes with deadly consequences.
Ukraine's forces have gained combat experience in the Donbass region in the east of the country, where they have been fighting Russia-backed separatists since 2014, and are highly motivated.
In 2019, Kiev acquired Turkish drones, which have shown its military prowess in different battlefields from Libya to Syria and most recently Azerbaijan’s Karabakh region disputed between Baku and Yerevan.
Ukraine spent 3.4 percent of its GDP on defense in 2019, up from 2.2 percent in 2014, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Russia spent 3.9 percent in 2019. However, the raw numbers are very different. In constant U.S. dollars, Ukraine is spending $5.2 billion, while Russia spends $65 billion.
Ukraine's forces have short-range air defences and anti-tank weaponry, including U.S.-supplied Javelin missiles, which would help to slow any Russian advance.
Beyond the regular army, Ukraine has volunteer territorial defence units and around 900,000 reservists. Most adult males have at least basic military training, so Russia could find itself facing stubborn and protracted resistance if it tried to capture and hold on to territory.
The military challenge would be incomparably higher than in previous wars Russia has fought since the Soviet Union's collapse, including in breakaway Chechnya in the 1990s and against Georgia in 2008.
President Volodymyr Zelenskiy has signed a decree on increasing the size of Ukraine's armed forces by about 100,000 troops over three years and raising soldiers' pay. Ukraine's prime minister said the decree signed by Zelenskiy - on priority measures to strengthen the state's defence capabilities, increase the attractiveness of military service and the gradual transition to a professional army - would eventually bring Ukraine's armed forces to 361,000 personnel.
Military Personnel of Ukraine
The current size of Ukraine's armed forces, which consists of 250,000 (215,000 military personnel), alongside 900,000 reservists, is the largest in Europe, and second in the region after the Russian Armed Forces. This is a high number for a country the size of Ukraine (just over 44 million people).
In 2022, President Zelensky ordered to increase the size of the forces by 100,000 by 2025, while ending conscription in 2024.
Ukrainian Ground Forces: As of 2016, there were a reported 169,000 personnel in the Ukrainian Ground Forces. The Ukrainian Ground Forces are divided into Armoured and Mechanized Forces, Army Aviation, Army Air Defence and Rocket and Artillery Troops. There are 13 mechanized brigades and two mountain warfare brigades in the Mechanized Forces. Ukraine also has two armoured brigades. There are also seven rocket and artillery brigades. Until 2013, the Ground Forces were divided into three army corps. These were disbanded in 2013 and reorganized as Operation Command West, Operation Command North and Operation Command South. Operation Command East was formed in 2015 to coordinate forces in the war in Donbas.
Ukrainian Air Force: In 2016, the Ukrainian Air Force was reported to have included 36,300 personnel.
Ukrainian Navy: According to an August 2015 Kyiv Post report, the Ukrainian Navy consisted of 6,500 personnel.
Air Assault and Airborne Forces: The Ukrainian Airborne and Air Assault Forces are composed of 8 air landing, air assault and air-mobile brigades and support units.
 How Russia Has The World's 2nd Strongest Militaries How Russia Has The World's 2nd Strongest Militaries Russia is ranked 2 of 140 out of the countries considered for the annual The Global Firepower Index (GFP) review. We will learn about the ... |
Ukraine Weapon Power - Atomic Weapons
Ukraine has a lot of tanks and is ranked 13th across the globe with 2,430. In terms of armored vehicles, Kiev also ranks high, occupying the seventh spot globally with 11,435. Kiev’s artillery power is also formidable at 2,040 batteries. But compared to Russia, which has the world’s largest tank repertoire, and being the third largest artillery power, it’s not much.
Military analysts say Ukraine's anti-aircraft and anti-missile defences are weak, leaving it highly vulnerable to Russian strikes on its critical infrastructure. They say Russia would also seek to use its superiority in electronic warfare to paralyse its adversary's command and control and cut off communications with units in the field.
When the USSR collapsed in 1991 and a dozen former Soviet republics declared their independence, the Soviet Union's atomic arsenal was divided up, too. Overnight, Ukraine became the world's third-strongest atomic power, right after the US and Russia, although the authority to fire the weapons remained in Moscow's hands.
However, the fledgling country didn't have enough money to maintain the warheads, and, under Russian and Western pressure, it gave up its nuclear weapons. Missiles that threatened the West during the Cold War, such as the SS-18 (aka "Satan"), were destroyed. Supersonic bombers like the Tupolev-160 were scrapped or handed over to Russia.
Military History of Ukraine
 |
| Photo: Bigstock |
The modern military in Ukraine was completely inherited from the Soviet Union, in which Ukraine was a member state. Like other Soviet republics, it did not possess its own separate military command, as all military formations were uniformly subordinated to the central command of the Armed Forces of the USSR. Administratively the Ukrainian SSR was divided into three military districts (the Carpathian Military District, Kiev Military District, and Odessa Military District) and most of the Black Sea Fleet naval bases were located on the coast of Ukraine.
As the collapse of the Soviet Union took place before 1992 (see Novo-Ogoryovo process), Ukraine inherited one of the most powerful force grouping in Europe. According to an associate of the Conflict Studies Research Centre, James Sherr: "This grouping, its inventory of equipment and its officer corps were designed for one purpose: to wage combined arms, coalition, offensive (and nuclear) warfare against NATO on an external front". At that time, the former Soviet armed forces in the Ukrainian SSR included a rocket army (43rd Rocket Army), four air force armies, an air defense army (8th Air Defence Army), three regular armies, two tank armies, one army corps and the Black Sea Fleet. Altogether the Armed Forces of Ukraine included about 780,000 personnel, 6,500 tanks, about 7,000 combat armored vehicles, 1,500 combat aircraft, more than 350 ships, 1,272 strategic nuclear warheads and 2,500 tactical nuclear missiles.
On 26 February 1991 a parliamentary Standing Commission for Questions of Security and Defence was established. On August 24, 1991, the Ukrainian parliament (the Verkhovna Rada), in adapting the Declaration of Independence of Ukraine, also enacted a short resolution "About military formations in Ukraine". This took jurisdiction over all formations of the armed forces of the Soviet Union stationed on Ukrainian soil, and established one of the key agencies, the Ukrainian Ministry of Defence. On 3 September 1991 the Ministry of Defence commenced its duties. On 22 October 1991 units and formations of the Soviet Armed Forces on Ukrainian soil were nationalised. This was followed by two Laws of Ukraine that were adopted by the Supreme Council of Ukraine on December 6, 1991 and Presidential Ukase #4 "About Armed Forces of Ukraine" on December 12, 1991. The government of Ukraine surrendered any rights of succession of the Soviet Strategic Deterrence Forces (see Strategic Missile Troops) that were staged on the territory of Ukraine. Recognizing the complications of a smooth transition and seeking a consensus with other former members of the Soviet Union in dividing up their Soviet military inheritance, Ukraine joined ongoing talks that started in December 1991 regarding a joint military command of the Commonwealth of Independent States.
 |
| Photo: Business Insider |
Inherent in the process of creating a domestic military were political decisions by the Ukrainian leadership regarding the country's non-nuclear and international status. Among these was the definition, agreement and ratification of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE) which not only established the maximum level of armament for each republic of the former USSR, but also a special ceiling for the so-called CFE "Flank Region". Included in this region were Ukraine's Mykolaiv, Kherson, Zaporizhia Oblasts, and the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. Another key event in the creation of the Ukrainian military was the 1992 Tashkent Treaty, which laid out aspirations for a Commonwealth of Independent States military that would prove impossible to develop because the former republics of the USSR all wished to go their own way, ripping the intricate Soviet military machine into pieces.
All military and security forces, including the Armed Forces of Ukraine and a number of independent "militarized institutions" (paramilitary forces) are under the command of the President of Ukraine, and subject to oversight by a permanent Verkhovna Rada parliamentary commission. Ukrainian military tactics and organization are heavily dependent on Cold War tactics and former Soviet Armed Forces organization. Under former President Yushchenko Ukraine pursued a policy of independence from Russian dominance, and thus tried to fully integrate with the West, specifically NATO.
However, Ukraine retains tight military relations with Russia, inherited from their common Soviet history. Common use of naval bases in Crimea and joint air defense efforts are the most intense branches of such cooperation. This cooperation is a permanent irritant in bilateral relations, but the country is unable to break such ties quickly, being economically dependent on Moscow. Furthermore, following the election of current President Victor Yanukovych, ties between Moscow and Kiev have warmed, and those between Kiev and NATO have cooled relative to the Yushchenko years.
 |
| Photo: Kyiv Post |
Plagued at times by hostile relations with Russia following the breakup of the Soviet Union, Ukraine has been steadfastly trying to develop its own independent military industry. Notable results of this effort are the Ukrainian-built T-84 main battle tank, currently in service, and the aircraft manufacturer Antonov. Ukraine received about 30% of the Soviet military industry, which included between 50 and 60 percent of all Ukrainian enterprises, employing 40% of its working population. Ukraine was, and still remains, a leader in missile-related technology, navigation electronics for combat vessels and submarines, guidance systems, and radar for military jets. Tough competition in the world's weapons market obliged Ukraine to consider exporting arms to politically unstable or even aggressive regimes. Ukraine built its own connections in arms exporting. The first contracts on weapons deliveries to Iran, signed in the middle of 1992, caused negative reactions in the West, particularly from the United States federal government.
Several unfortunate accidents involving the Armed Forces have occurred since 1992, including the crash of an Air Force Su-27 in the Sknyliv airshow disaster of 2002.
 Top 15 Most Beautiful & Hottest Ukrainian Women Top 15 Most Beautiful & Hottest Ukrainian Women Ukraine is the birthplace of the most beautiful and sexiest women in the world of all time. Check out the list of Top 15 Most ... |
Organization
The Ukrainian armed forces are largely made up of conscripts. The total personnel (including 41,000 civilian workers) at the end of 2010 will be 200,000. The branch structure is as follows:
Ukrainian Ground Forces: 73,300 personnel
Ukrainian Air Force: 46,000 personnel
Ukrainian Navy: 15,000 personnel
With the adoption on December 26, 1996, of a new "State Programme for the Building and Development of the Armed Forces of Ukraine", a new type of military district was established in northeast Ukraine, centered in the city of Chernihiv and designated as the Northern Operational/Territorial Command, later renamed the Northern Operational Command. The State Programme also provided that two military districts, Carpathian and Odessa, [would] be renamed the Western and Southern Operational Commands respectively.
Ukraine maintains a number of Guards units, tracing their traditions to the Soviet Armed Forces. A list can be seen at List of guards units of Ukraine. Women comprise almost 13% of the armed forces (18,000 personnel) but few females hold high rank (2.9% or 1,202 women). Contractual military service accounts for almost 44% of women. However, this is closely linked to the low salary of such positions: men refuse to serve in these conditions while women accept them.
A number of universities have specialised military institutes, such as the Faculty of Military Legal Studies at Kharkiv's National Yaroslav Mudryi Law Academy of Ukraine. The primary Ukrainian military academies are:
Petro Sahaidachny Ground Forces Academy, Lviv
Nakhimov Naval Academy, Sevastopol
Ivan Kozhedub Air Force University, Kharkiv (ru:Харьковский университет Воздушных Сил имени Ивана Кожедуба)
In addition the National Defense University of Ukraine (uk:Національний університет оборони України) is in Kiev.
The Chief Military Clinic Hospital is located in Kiev.
 What Is The First Military Airplane In The World? What Is The First Military Airplane In The World? The 1909 Wright Military Flyer is the world's first military airplane. Read on to know its history. |
 Top 10 Oldest Military Aircrafts In Service Top 10 Oldest Military Aircrafts In Service Check out a list of 10 oldest military aircrafts that have been in service for over half a century. |
 Top 9 Most Powerful Militaries In The World - Updated Top 9 Most Powerful Militaries In The World - Updated What are the most powerful militaries in the world? It’s an outwardly simple question that hides a remarkable degree of complexity. We have a ... |
 Which Country Is The Most Powerful In The World? Which Country Is The Most Powerful In The World? Defining the world’s most powerful countries is not always clear-cut and can be subjective. The most powerful nations are the ones that shape global ... |