Who Is Pepper - First Robot That Can Read Emotions
 |
| Photo Venture Beat |
Pepper was introduced in Tokyo on June 5, 2014 by Masayoshi Son, founder of SoftBank. Pepper was available in December 2015 at SoftBank Mobile stores. Pepper went on sale in June 2015 with the first batch of 1,000 units selling out in just 60 seconds. Pepper was launched in the UK in 2016.
Japanese-based Softbank Group recently announced it was pressing pause on “Pepper” after multiple “firings.”
Pepper has been axed by multiple companies around the world for various issues.
Nissei Eco Co., a plastics manufacturer with a sideline in the funeral business, hired Pepper to chant sutras or scriptures to mourners at funerals, but soon fired it after Pepper kept breaking down during practice runs.
“What if it refused to operate in the middle of a ceremony?” funeral-business manager Osamu Funaki told the Wall Street Journal. “It would be such a disaster.”
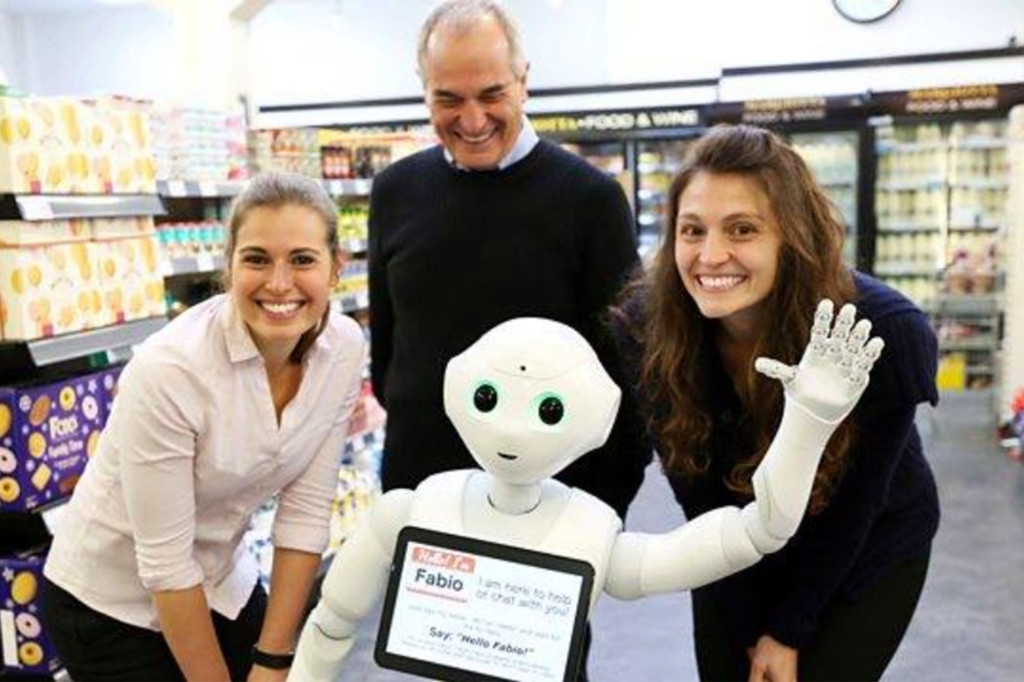 |
| Pepper the robot at work at Margiotta Food and Wine in Edinburgh.Photo Facebook |
Scottish grocery chain Margiotta installed a Pepper in their flagship Edinburgh store, but was fired after continually telling customers to look “in the alcohol section” when they asked where things were.
Robotics expert Professor Noel Sharkey told the BBC: “Pepper did a lot to harm genuine robotics research by giving an often false impression of a bright cognitive being that could hold conversations.”
“Because it has the shape of a person, people expect the intelligence of a human,” Takayuki Furuta, head of the Future Robotics Technology Center at Chiba Institute of Technology, told the Journal. “The level of the technology completely falls short of that. It’s like the difference between a toy car and an actual car.”
How does Pepper look?
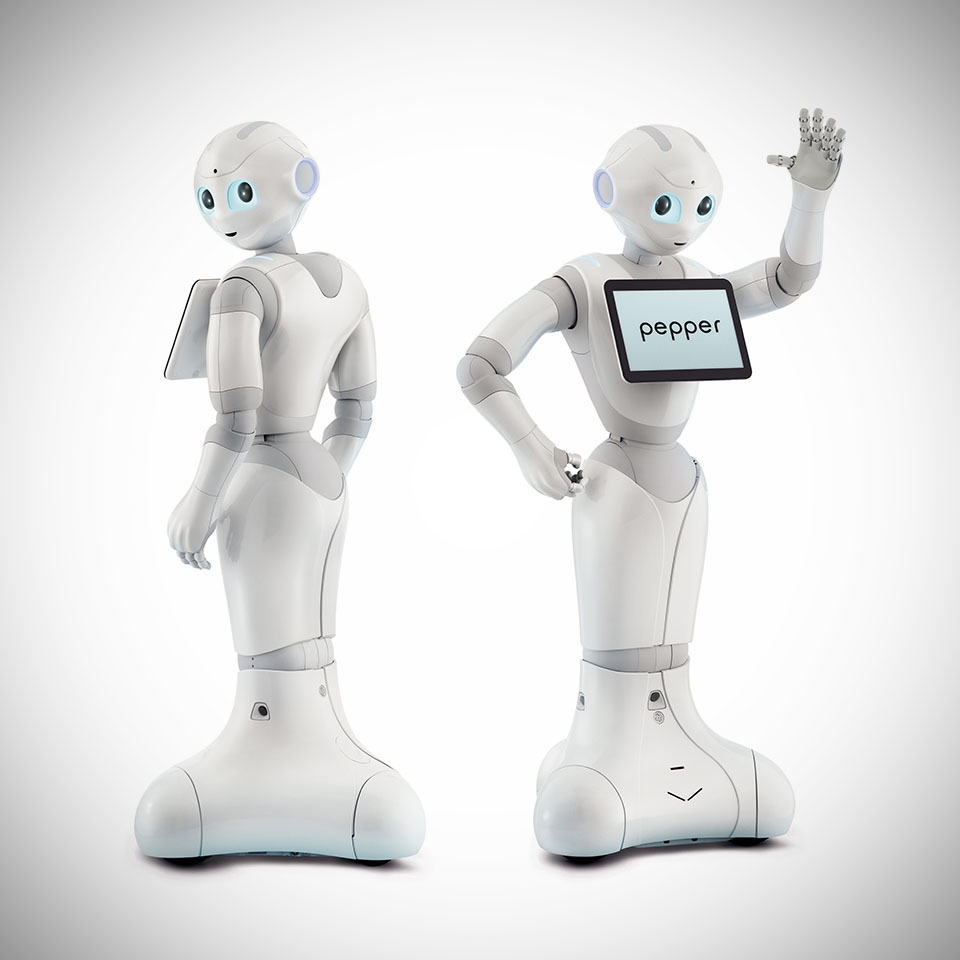 |
| Photo MikeShouts |
Pepper, who stands 4 feet tall and weighs about 62 pounds, is equipped with facial-recognition technology and a number of cameras, audio recorders and sensors. That technology allows the robot to learn how to behave over time, instead of being programmed for specific tasks, Softbank said.
Pepper is about four feet tall, gets around on wheels, and has a tablet in the center of its chest. The humanoid robot made its debut in 2015 and was designed to interact with people. Cameras and microphones are used to help Pepper recognize human emotions, like hostility or joy, and respond appropriately with a smile or indications of sadness.
This type of intelligence likely comes in handy for the environments where Pepper operates, like banks, hotels, and Pizza Huts in some parts of Asia.
| Dimensions: 1210mm × 480mm × 425mm Weight: 29kg Battery: Lithium-ion battery Capacity: 30.0Ah/795Wh Operation time: approx. over 12 hours |
What can Pepper do?
Pepper has also been programmed to dance, take selfies, make a credit card pitch, or perform Buddhist burial rites.
Affectiva’s emotion recognition AI is able to identify things like laughter in your voice or facial expressions of joy, disgust, surprise, fear, and contempt, as well as specific characteristics about a person, such as age, gender, and ethnicity.
Though the robot is already equipped to recognize some human emotions, Affectiva is being used to give Pepper the ability to understand more nuanced states of human feelings, such as the difference between a smile and a smirk.
 |
| Photo MikeShouts |
“Understanding these complex states will enable Pepper to have more meaningful interactions with people and adapt its behavior to better reflect the way people interact with one another,” the company said in a statement about the partnership shared with VentureBeat.
| Affectiva CEO Rana el Kaliouby believes emotion recognition or affective computing is essential in a variety of human-machine encounters, including interactions with home robots, AI assistants like Google Assistant and Alexa, and even autonomous vehicles. |
In March, Affectiva launched emotion tracking for cameras in modern cars or semi-autonomous vehicle systems to recognize if people are angry or happy, or to assign drivers distraction scores.
| Recognition of a person’s emotional or cognitive state could also be used by AI assistants or other forms of tech to help people lead happier, healthier, more productive lives, and could even assist in mental health treatment, el Kaliouby said. Emotion detection from cameras and detection drawn from voices and sounds are effective together, but each can be used for different purposes. |
Pepper will not only be able to read emotions—Pepper has evolved to have emotions. Pepper’s emotions use functions developed by cocoro SB Corp. that enable robots to artificially generate their own emotions. These emotion functions in Pepper are modeled on the human release of hormones in response to stimuli absorbed by the five senses, which in turn generate emotions. In addition to Pepper’s emotion recognition functions, Pepper has capabilities to generate emotions autonomously by processing information from his cameras, touch sensors, accelerometer, and other sensors within his “endocrine-type multi-layer neural network.”
With this emotion function, Pepper’s emotions are influenced by people’s facial expressions and words, as well as his surroundings, which in turn affects Pepper’s words and actions. For example, Pepper is at ease when he is around people he knows, happy when he is praised, and gets scared when the lights go down.
Depending on the emotion at the time, Pepper raises his voice or sighs, for example. Pepper’s emotions can be seen on the heart display, which shows different colors and movements. Furthermore, a number of robot apps have been developed to make life fun with an emotional robot. “Pepper's Diary,” for example, links Pepper’s emotions with daily family events that are recorded with pictures and photos.
| Robots are getting more emotive in general. Jibo, a tabletop digital helper---think of a more charming Amazon Echo---understands colloquial speech, expresses a range of emotions, and even develops its own opinions. The Parorobot substitutes for puppies and kittens in animal therapy sessions in extended care facilities where live animals would pose logistical difficulties, and some elementary schools are testing robots to help teach kids with special needs. |
Programming Pepper
Pepper isn't a butler. It can't vacuum or fold fitted sheets (though be honest: Neither can you, right?). Its humanoid shape is supposed to make it easier to express emotions to. “We designed Pepper’s form to incentivize engagement," says Steve Carlin, vice president of SoftBank Robotics America. "Its height, shape, the fact that it has arms that can gesticulate---are all designed to show empathy."
Exactly how to turn all that physicality into empathy isn't clear from the SDK alone; SoftBank engineers say they'll have forums for would-be Pepper-programmers to ask what kind of gesture or language conveys the right tone for, say, assisting someone in a car dealership or a grocery store. Right now, the SDK lets coders plan out moves and language and watch the robot execute in an animated sandbox. So at least it gets to practice.
And it'll need to. Roboticists expect that US homes are going to be more skeptical of having robots around the house than Japanese society has been. Maybe because Americans worry that no matter how much they teach the robots, the robots are going to teach them, too.
| How much does Pepper cost? Base price: 198,000 yen (approximately $1,600 U.S.) Pepper Basic Plan: 14,800 yen ($120 U.S.) × 36 months (payment installments) Pepper Insurance Pack: 9,800 yen ($80 U.S.) × 36 months (payment installments) *A separate robot charge (9,800 yen) is required. Basic Plan, Pepper Insurance Pack can be paid with a 36 installment contract or at once. *Standalone purchases can only be applied for at shops. |
 What is PAPR device - new Covid-19 Mask What is PAPR device - new Covid-19 Mask Researchers from the US have found “a more perfect mask” that could protect against Covid-19 25 times longer than cloth masks. What are the Powered ... |
 The first washing machine ever made in history The first washing machine ever made in history Do you know when washing machine, one of the most common and useful home appliance that we could see everyday in every houses, was invented? ... |
 What is the first television in the world and who invented it? What is the first television in the world and who invented it? Evidently, television is one of the historic inventions in the world that allows us to get access to the information easily and conveniently. It takes ... |
























