What is the Health Condition of Bruce Willis Right Now
 |
| Disorder has been ‘impacting’ Willis’ ‘cognitive abilities,’ |
What Happened to Bruce Willis - Diagnosed with Aphasia
Bruce Willis will be “stepping away” from his acting career after he was diagnosed with aphasia.
Willis' family said on social media that the actor was having "cognitive" issues due to his recent diagnosis.
"To Bruce's amazing supporters, as a family we wanted to share that our beloved Bruce has been experiencing some health issues and has recently been diagnosed with aphasia, which is impacting his cognitive abilities," his ex-wife and fellow actor Demi Moore said in a statement on Instagram. "As a result of this and with much consideration Bruce is stepping away from the career that has meant so much to him."
There are no reports on which type Willis, who turned 67 this year, has been diagnosed with nor whether he had a stroke that led to the aphasia.
Willis' daughter said the condition "is affecting his cognitive ability" in an Instagram post, although experts believe aphasia is more correctly classified as a language disorder than a cognitive sickness.
"This is a really challenging time for our family and we are so appreciative of your continued love, compassion and support," Willis' family said in a statement.
"We are moving through this as a strong family unit, and wanted to bring his fans in because we know how much he means to you, as you do to him."
| Aphasia is generally diagnosed in middle-age or later, though it can occur in young children. It affects some 2 million Americans, according to the National Aphasia Association, making it more common than Parkinson's Disease, cerebral palsy, or muscular dystrophy. A 2016 survey carried out by the same group found that fewer than 9 percent of people knew what was. There are over 100,000 Canadians living with aphasia today and one in three stroke survivors are diagnosed with aphasia. The number of people with this disorder is expected to increase significantly as the population ages. |
Viveo - the Medical Condition of Bruce Willis:
How to Treat Aphasia?
There is no cure for aphasia, but treatments such as speech therapy and active family intervention can go a long way in helping the person affected by aphasia to regain speech and language function over time.
"Recovery of language skills is usually a relatively slow process," Mayo Clinic says. "Although most people make significant progress, few people regain full pre-injury communication levels."
Treatment can include speech therapy as well training to use communication aids that enable a person to "speak" via pictures, gestures and even electronic devices, according to the NIDCD.
“Even when the aphasia is severe, many are capable of participating in decisions that pertain to them if the appropriate support is provided,” the Aphasia institute says. “Similar to giving a wheelchair or walker to someone who can’t walk.”
These issues are related to brain damage in the left side of the brain, which controls language, Johns Hopkins explains.
Someone who have experienced brain injuries that resulted in the disorder may see improvements within the first few months, even without treatment. However, once the cause of the disorder has been addressed, the main treatment for aphasia consists of speech and language therapy, which entails relearning and practicing language skills and other ways to communicate.
Following a brain injury, tremendous changes occur in the brain, which help it to recover. As a result, people with aphasia often see dramatic improvements in their language and communication abilities in the first few months, even without treatment. But in many cases, some aphasia remains following this initial recovery period. In these instances, speech-language therapy is used to help patients regain their ability to communicate.
Research has shown that language and communication abilities can continue to improve for many years and are sometimes accompanied by new activity in brain tissue near the damaged area. Some of the factors that may influence the amount of improvement include the cause of the brain injury, the area of the brain that was damaged and its extent, and the age and health of the individual.
Aphasia therapy aims to improve a person's ability to communicate by helping him or her to use remaining language abilities, restore language abilities as much as possible, and learn other ways of communicating, such as gestures, pictures, or use of electronic devices. Individual therapy focuses on the specific needs of the person, while group therapy offers the opportunity to use new communication skills in a small-group setting.
Recent technologies have provided new tools for people with aphasia. "Virtual" speech pathologists provide patients with the flexibility and convenience of getting therapy in their homes through a computer. The use of speech-generating applications on mobile devices like tablets can also provide an alternative way to communicate for people who have difficulty using spoken language.
Increasingly, patients with aphasia participate in activities, such as book clubs, technology groups, and art and drama clubs. Such experiences help patients regain their confidence and social self-esteem, in addition to improving their communication skills. Stroke clubs, regional support groups formed by people who have had a stroke, are available in most major cities. These clubs can help a person and his or her family adjust to the life changes that accompany stroke and aphasia.
Family involvement is often a crucial component of aphasia treatment because it enables family members to learn the best way to communicate with their loved one.
Family members are encouraged to:
-Participate in therapy sessions, if possible.
-Simplify language by using short, uncomplicated sentences.
-Repeat the content words or write down key words to clarify meaning as needed.
-Maintain a natural conversational manner appropriate for an adult.
-Minimize distractions, such as a loud radio or TV, whenever possible.
-Include the person with aphasia in conversations.
-Ask for and value the opinion of the person with aphasia, especially regarding family matters.
-Encourage any type of communication, whether it is speech, gesture, pointing, or drawing.
-Avoid correcting the person's speech.
-Allow the person plenty of time to talk.
-Help the person become involved outside the home. Seek out support groups, such as stroke clubs.
What Is Aphasia - the Brain Disorder Bruce Willis Has Been Diagnosed With?
 |
| Bruce Willis with his wife Emma Heming Willis |
Aphasia is a condition that leaves an individual unable to communicate, as it can impact the ability to “speak, write and understand language, both verbal and written”.
"Aphasia just means that someone has a problem with language that they weren't born with," Hugo Botha, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Minnesota explained.
Aphasia typically “occurs suddenly” after an individual has experienced brain damage as a result of a stroke or a head injury, but that it can also come on gradually if the person has a “slow-growing brain tumour” or a degenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease. Sometimes temporary episodes of aphasia can occur as a result of migraines, seizures, or a transient ischemic attack, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is temporarily blocked.
The most common cause is stroke or head injury – and experts stress that while it can affect the production and comprehension of both speech and written words, it normally doesn't impact intelligence.
While it's normally caused by a specific one-time event such as stroke, "there are other possibilities, such as from a neurodegenerative disease," explained Brenda Rapp, a cognition scientist at Johns Hopkins University.
In such cases the damage is progressive and therapy focuses on preventing further loss of function.
What Causes Aphasia of Bruce Willis?
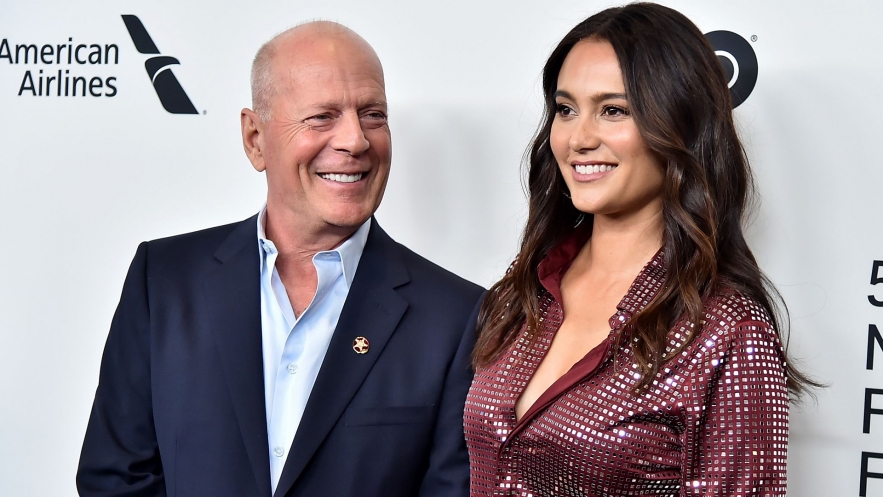
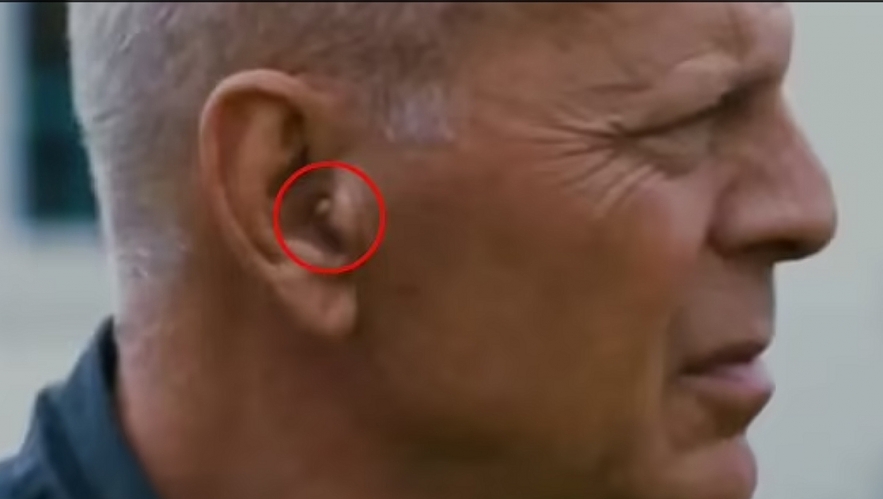 |
| Bruce Willis has been having trouble on the sets of his recent movies, and was even pictured wearing an earpiece to feed him lines on the set of American Siege in 2020 |
Bruce Willis' family did not share the cause of his diagnosis in their statement.
Sources say acclaimed actor Bruce Willis, 67, has been having trouble on the sets of his recent movies, and was even pictured wearing an earpiece to feed him lines on the set of American Siege in 2020.
Aphasia is caused by damage to one or more of the language areas of the brain. Most often, the cause of the brain injury is a stroke. A stroke occurs when a blood clot or a leaking or burst vessel cuts off blood flow to part of the brain. Brain cells die when they do not receive their normal supply of blood, which carries oxygen and important nutrients.
Other causes of brain injury are severe blows to the head, brain tumors, gunshot wounds, brain infections, and progressive neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease.
Although the cause of Willis’ aphasia is unclear, Mayo Clinic says that aphasia can be caused by a stroke, head injury, a brain tumor or a disease.
While potential drug therapies are being tested, the current treatment options are limited. Most patients are advised to undergo language and speech rehabilitation, that focus on restoring as much language as possible and finding alternative methods to communicate.
| Gossip magazine OK! first published rumours in January 2021 that Willis had been battling memory loss, and was spending more time with his family. That came after Willis was booted from a Los Angeles chemist for not wearing a mask during Covid-19. He later apologised, saying in a statement that it was “an error in judgement”. But an “insider” told OK! that Willis “simply forgot” to bring the bandana hanging around his neck up to his face. “Those close to Bruce have been helping him out, and trying to maintain the secret,” they said. |
What Types of Aphasia are There?
 |
| What types of aphasia are there? |
The brain system governing language is a "very complex machine" that involves selecting the right words, moving the mouth appropriately to vocalize them, and on the other end hearing and decoding their meaning.
Doctors sometimes split aphasia into broad clinical categories which correlate to where in the brain injury occurred. A person with this type of aphasia might use simple sentences like "want food" to be understood.
There are two broad categories of aphasia: fluent and nonfluent, and there are several types within these groups.
Damage to the temporal lobe of the brain may result in Wernicke's aphasia the most common type of fluent aphasia. People with Wernicke's aphasia may speak in long, complete sentences that have no meaning, adding unnecessary words and even creating made-up words.
The most common type of nonfluent aphasia is Broca's aphasia. People with Broca's aphasia have damage that primarily affects the frontal lobe of the brain. They often have right-sided weakness or paralysis of the arm and leg because the frontal lobe is also important for motor movements. People with Broca's aphasia may understand speech and know what they want to say, but they frequently speak in short phrases that are produced with great effort. They often omit small words, such as "is," "and" and "the."
Another type of aphasia, global aphasia, results from damage to extensive portions of the language areas of the brain. Individuals with global aphasia have severe communication difficulties and may be extremely limited in their ability to speak or comprehend language. They may be unable to say even a few words or may repeat the same words or phrases over and over again. They may have trouble understanding even simple words and sentences.
There are other types of aphasia, each of which results from damage to different language areas in the brain. Some people may have difficulty repeating words and sentences even though they understand them and can speak fluently (conduction aphasia). Others may have difficulty naming objects even though they know what the object is and what it may be used for (anomic aphasia).
What are the symptoms of aphasia?
According to The Mayo Clinic, aphasia is often a symptom of another medical condition, such as a stroke, but a person with aphasia can display the following characteristics:
-Speak in short or incomplete sentences
-Speak in sentences that don’t make sense
-Substitute one word for another or one sound for another
-Speak unrecognizable words
-Not understand other conversations
-Write sentences that don’t make sense
Bruce Willis CareerBruce Willis is best known for his starring role as John McClane in the "Die Hard" action franchise. As of 2022, films featuring Willis have grossed over US$5 billion worldwide, making him one of the highest-grossing actors in the world. Willis came to national attention alongside Cybill Shepherd in the 1980s TV hit Moonlighting. His first big film role was as John McClane in the smash hit Die Hard in 1988. He went on to star in Pulp Fiction, 12 Monkeys and The Sixth Sense. Over four decades he has starred in more than 100 films, which have amassed more than $5 billion (£3.8 billion) at the box office worldwide. He has won one Golden Globe award and two Emmys. Willis has several films in post-production, including Vendetta, Fortress: Sniper's Eye and White Elephant. Fortress 3 is in pre-production. |