What is Panama Canal: Everything you need to know
 Major US Visa Changes in 2025: What You Must Know Now! Major US Visa Changes in 2025: What You Must Know Now! |
 Retiring in 2025? Essential Tips for Financial Security, Housing, and Healthcare Retiring in 2025? Essential Tips for Financial Security, Housing, and Healthcare |
 Where in the US Has White Christmas 2024? Where in the US Has White Christmas 2024? |
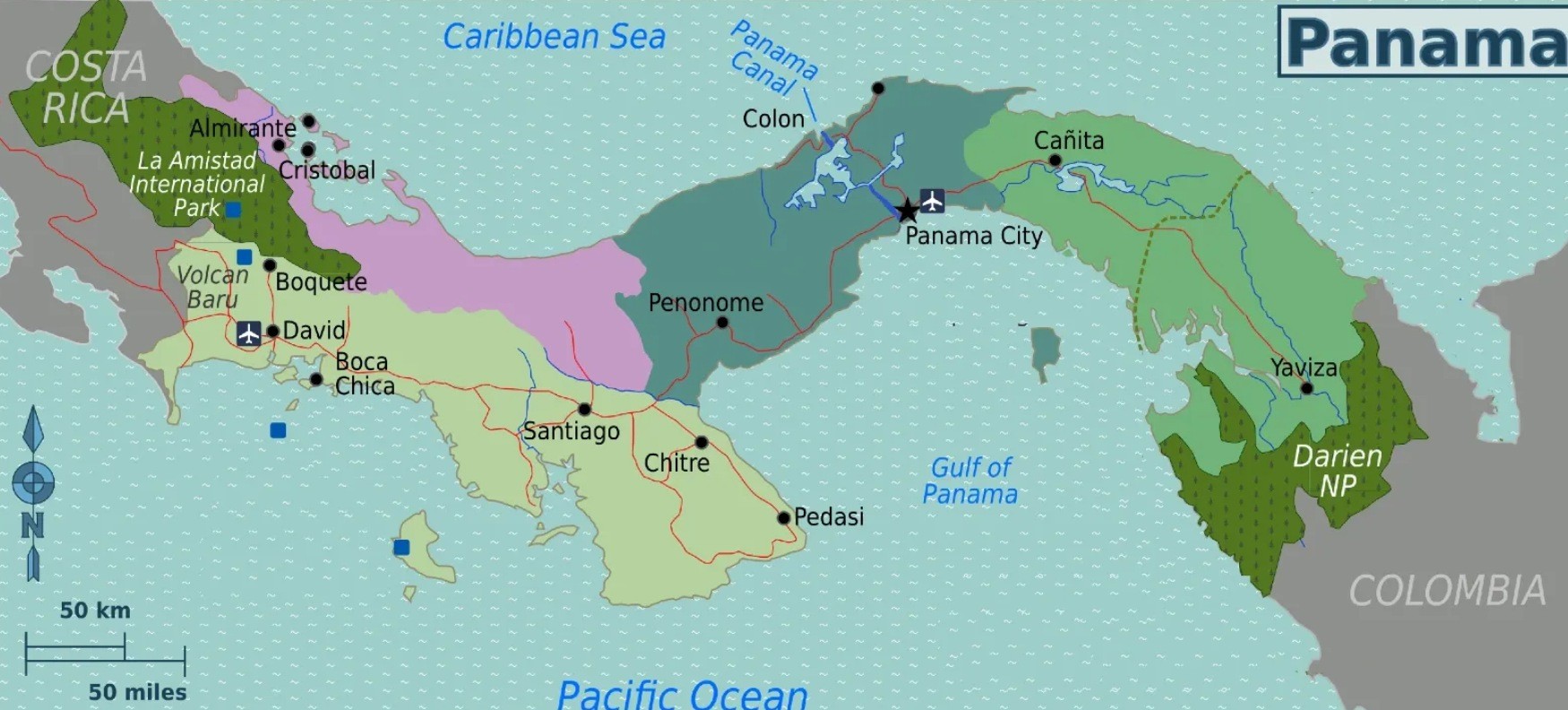
The Panama Canal is one of the most significant engineering achievements in human history, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans through the Isthmus of Panama. Opened in 1914, this 51-mile-long canal revolutionized global trade by drastically reducing the time and distance required for maritime shipping. Instead of navigating around South America’s Cape Horn, vessels can take this shortcut, saving thousands of miles and weeks of travel time.
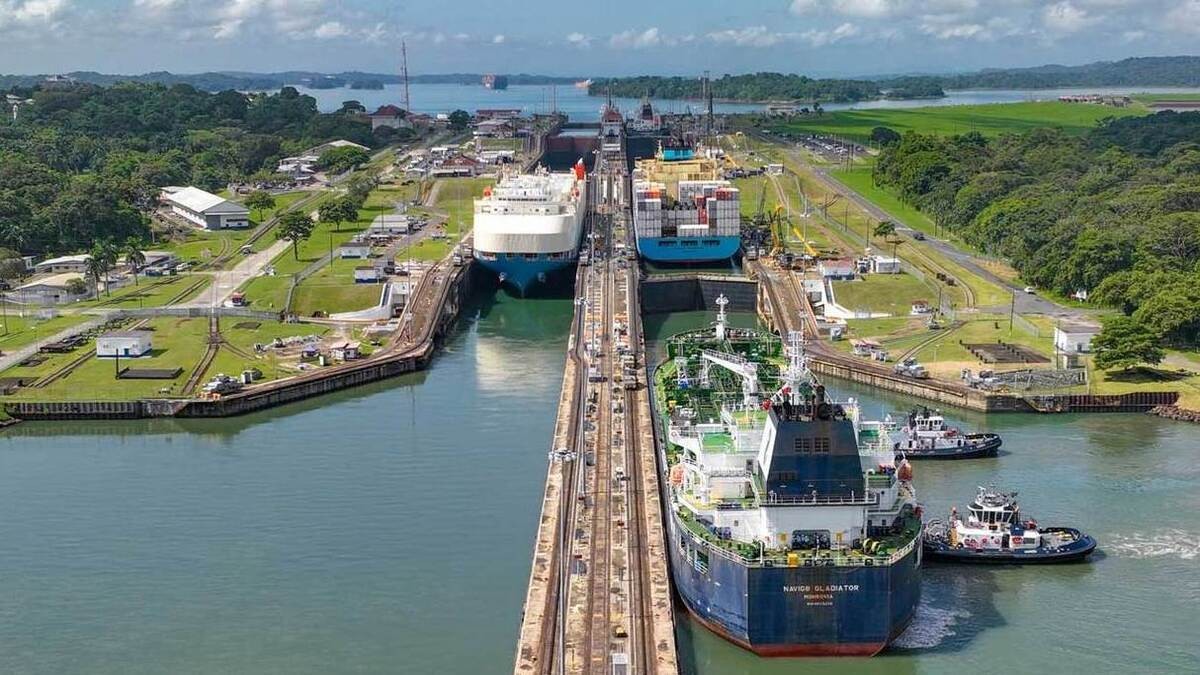 |
The canal has been a critical asset not only for global commerce but also for the geopolitical strategies of nations, particularly the United States. Its history reflects a complex interplay of engineering brilliance, international politics, and evolving ownership.
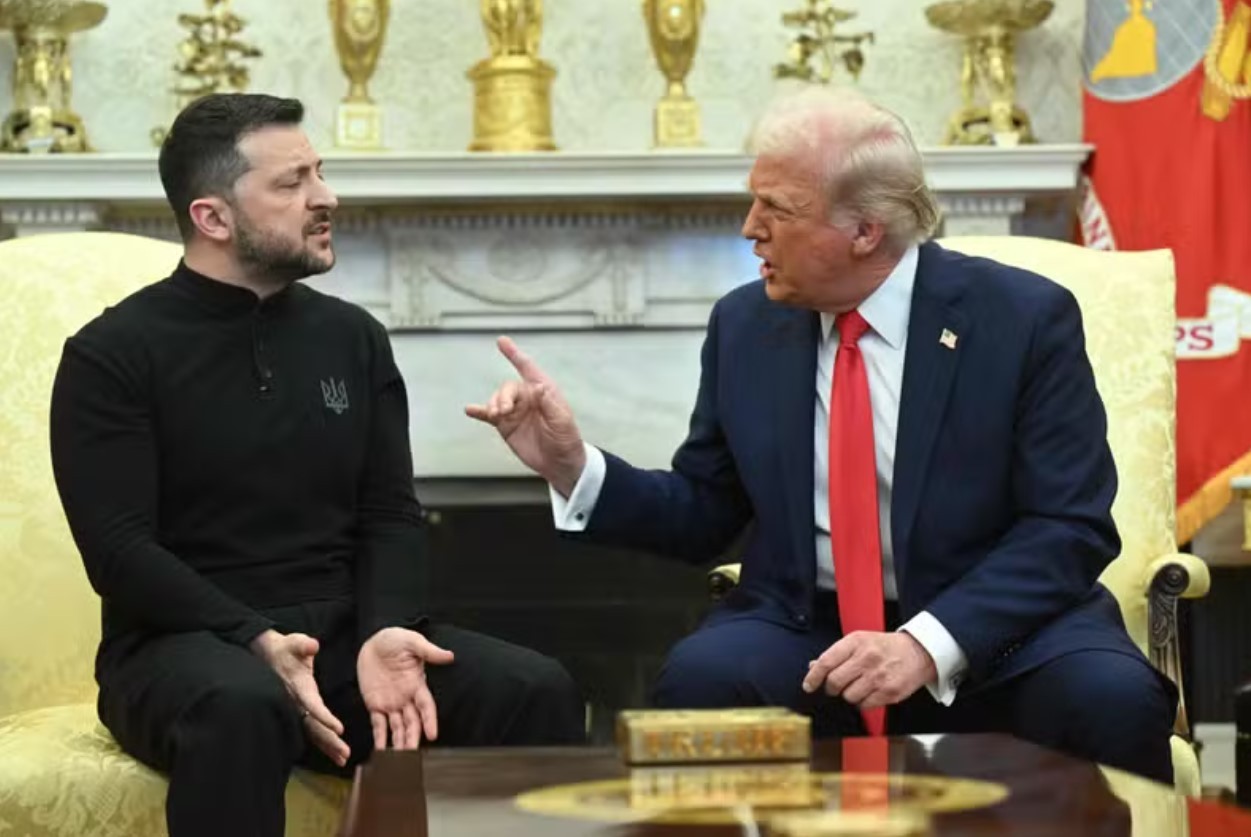
| President-elect Donald Trump has threatened to retake the Panama Canal in a lengthy post on Truth Social. Trump accused Panama of “ripping off” American vessels by charging “exorbitant prices” to use the vital waterway that acts as a shortcut linking the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. |
History of the Panama Canal
Pre-Colonial and Early Efforts
- Pre-Columbian Trade Routes: Indigenous peoples of Panama recognized the isthmus’s strategic importance for trade.
- First European Interest: In the 16th century, Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa was the first European to realize Panama’s potential as a shortcut between the oceans.
19th Century: French Attempt
- In the 1880s, the French, led by Ferdinand de Lesseps (the engineer behind the Suez Canal), attempted to build the canal. However, the project failed due to:
- Poor planning.
- Tropical diseases like malaria and yellow fever.
- Engineering challenges related to Panama's mountainous terrain.
- The French project collapsed after spending millions and losing thousands of workers to disease and accidents.
 |
The American Era (1904–1999)
- After the French failure, the United States took over the project in 1904.
- Engineering Feats:
- The U.S. introduced lock systems to lift ships over the terrain instead of cutting through it entirely.
- Thousands of workers and engineers worked tirelessly, with major advancements in disease control under Dr. William C. Gorgas.
- Completion and Opening:
- The canal was officially opened on August 15, 1914, just as World War I began.
Ownership and the Panama Canal Treaty
- For decades, the canal was controlled by the U.S., creating tensions with Panama.
- Torrijos–Carter Treaties (1977):
- U.S. President Jimmy Carter and Panamanian leader Omar Torrijos signed agreements to gradually transfer control of the canal to Panama.
- On December 31, 1999, Panama officially gained sovereignty over the canal.
The Panama Canal Today
Current Operations
- Managed by the Panama Canal Authority (ACP), the canal remains a vital artery of global trade.
- It handles over 14,000 vessels annually, contributing significantly to Panama’s economy.
- Expansion Project (2016):
- The Panama Canal was expanded to accommodate larger ships, known as "New Panamax" vessels.
- This project doubled the canal’s capacity, allowing it to compete with alternative shipping routes.
Challenges
- Climate Change: Reduced rainfall in Panama has led to lower water levels in the canal’s reservoirs, impacting its operations.
- Competition: The Suez Canal and Arctic shipping routes challenge the Panama Canal’s dominance.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The canal remains a strategic asset in global politics, with nations like the U.S. and China showing significant interest.
 |
| Donald Trump accused Panama of charging American vessels ‘exorbitant prices’ to use the vital waterway |
The United States and the Panama Canal
Strategic Importance
The canal has been a cornerstone of U.S. naval and commercial strategy. By controlling the canal for most of the 20th century, the U.S. secured its dominance in the Western Hemisphere.
U.S.–Panama Relations
- The canal has been a source of pride and contention between the two nations.
- Military Presence: The U.S. maintained military bases near the canal until the handover in 1999.
China’s Growing Influence
In recent years, China has invested heavily in Panama, raising concerns in Washington. Chinese companies have signed contracts to manage ports near the canal, sparking debates about the canal’s strategic vulnerability.
Donald Trump’s Comments on the Panama Canal
Former U.S. President Donald Trump has recently made remarks suggesting that the U.S. should reconsider its role in the Panama Canal. While he didn’t call for outright control, his statements focused on:
- Strategic Value: Trump highlighted the canal’s importance for U.S. trade and military logistics.
- Criticism of Past Decisions: He criticized the 1977 treaties that transferred control to Panama, calling it a loss for American interests.
- Future Policies: Trump hinted at increasing U.S. involvement in Panama through economic and security partnerships.
Trump’s comments have sparked mixed reactions, with some viewing them as a nostalgic nod to American dominance and others as a potential strain on U.S.–Panama relations.
FAQs About the Panama Canal
1. What is the Panama Canal?
The Panama Canal is a 51-mile-long artificial waterway connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, allowing ships to bypass the lengthy route around South America.
2. When was the Panama Canal built?
The canal was built between 1904 and 1914, though earlier efforts by the French in the 1880s failed.
3. Why is the Panama Canal important?
It significantly reduces travel time and costs for global maritime trade and holds strategic military importance.
4. Who controls the Panama Canal?
Since December 31, 1999, the Panama Canal has been managed by Panama’s government through the Panama Canal Authority (ACP).
5. How many ships pass through the Panama Canal each year?
Approximately 14,000 vessels transit the canal annually.
6. What is the significance of the canal’s expansion?
The 2016 expansion allows larger ships (New Panamax vessels) to pass through, doubling the canal’s capacity.
7. How much does it cost to use the Panama Canal?
Transit fees vary depending on ship size and cargo. Some large vessels pay over $500,000 for a single crossing.
8. What challenges does the Panama Canal face?
Climate change, competition from other trade routes, and political tensions are major challenges for the canal.
9. What role did the U.S. play in the canal’s history?
The U.S. built and operated the canal from 1904 to 1999, viewing it as a critical asset for trade and defense.
10. What has Donald Trump said about the Panama Canal?
Trump has criticized the 1977 treaties that transferred control to Panama and suggested increasing U.S. involvement in the region.
| The Panama Canal remains an engineering marvel and a vital component of global trade. Its history reflects the interplay of innovation, politics, and international cooperation. While the U.S. no longer controls the canal, its strategic importance continues to shape geopolitics, with nations vying for influence in the region. As the world grapples with climate change, evolving trade dynamics, and shifting power structures, the Panama Canal will undoubtedly remain at the center of global discussions—whether about commerce, diplomacy, or history. |