What are the First Aircraft Carrier of America - Top 10 Oldest
 |
| What are the First Aircraft Carrier of America - Top 10 Oldest |
| Table Content |
As airplanes became part of military forces, there was a need for aircraft carriers. In fact, America’s first aircraft carrier was the USS Langley, commissioned 100 years ago. At first, however, senior naval officers were highly skeptical about the use of carriers, believing they had little value “beyond scouting and observing the fall of shot for battleships,” as The Smithsonian explains.Aircraft carriers trace their history back to 1806 when a ship was used to carry out airborne operations via balloons. Today’s aircraft carriers have come a long way and are now able to haul tons of equipment, crew, and of course various aircraft vehicles. Currently, there are about 43 active aircraft carriers in the world operated by fourteen navies. Since the United States has the world’s largest navy, a majority of the active aircraft carriers are American. In fact, only two of the oldest active aircraft carriers belong to different countries.
But the previously all-important battleships have given way to aircraft carriers — at least in the world’s largest navies. Among other capabilities, their utility is that they can strike at targets hundreds of miles away because of the range of the planes they carry. America’s Nimitz-class aircraft carriers weigh over 100,000 tons, are over 1,000 feet long, and carry 90 fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters.
History of U.S. Aircraft Carriers
September 26, 1910 – The first recorded reference to a provision for aviation in the Navy Department.
November 14, 1910 – Eugene Ely, 24, a civilian pilot, took off in a 50hp Curtiss plane from a wooden platform built over the bow of the light cruiser USS Birmingham (CL-2).
November 29, 1910 – Glenn H. Curtiss wrote to Secretary of the Navy, George Meyer, offering flight instruction without charge for one Navy officer as one means of assisting “in developing the adaptability of the airplane to military purposes.”
April 12, 1911 – Lt. T. Gordon “Spuds” Ellyson completed his training at the Glenn Curtiss Aviation Camp and became Naval Aviator No. 1.
November 8, 1917 – Lieutenant Commander Earl W. Spencer Jr., U.S. Navy, became the commanding officer of the first permanent naval air station for training, today is known as Naval Air Station North Island in San Diego, CA.
July 11, 1919 – the Naval Appropriations Act for Fiscal Year 1920 provided for the conversion of the collier Jupiter into an aircraft carrier later to be named Langley.
March 20, 1922 – USS Langley (CV 1), converted from the collier USS Jupiter (AC 3), was commissioned as the U.S. Navy’s first aircraft carrier. Commodore Kenneth Whiting was in command.
October 17, 1922 – Lt. V.C. Griffin, in a Vought VE-7SF, took off from USS Langley at anchor in the York River, VA, making the first take-off from an aircraft carrier.
November 17, 1924 – USS Langley reported for duty, becoming the first operational aircraft carrier in the U.S. Navy.
November 16, 1927 – USS Saratoga (CV 3) was commissioned.
December 14, 1927 – USS Lexington (CV 2) was commissioned.
September 26, 1931 – The keel for the USS Ranger (CV 4), the first ship in the U.S. Navy to be designed and constructed as an aircraft carrier, was laid. The ship launched on February 25, 1933, and was commissioned on June 4, 1934.
May 12, 1938 – USS Enterprise (CV 6) was commissioned. It had launched on October 3, 1936.
December 7, 1941 – Carrier aircraft of the Japanese Imperial Army launched a devastating attack on Pearl Harbor. The three carriers of the Pacific Fleet – Saratoga, Lexington, and Enterprise – were not present. The Enterprise was at sea, about 200 miles west of the harbor, and launched her aircraft in a fruitless search for the Japanese striking force.
February 1, 1942 – the first U.S. carrier offensive occurred when Task Forces 8 and 17, with the Enterprise and Yorktown, attacked installations on various Japanese islands.
June 3-6, 1942 – The Battle of Midway. The Japanese attempted to occupy Midway Island but were met with a greatly outnumbered U.S. carrier force. In the battle, four large Japanese carriers were sunk, with 258 planes and a high percentage of Japan’s most trained and experienced carrier pilots.
1943 – The Navy commissioned a large number of aircraft and escort carriers
June 4, 1944 – the USS Guadalcanal (CVE 60) captured the German submarine U-505, the only submarine captured by the U.S. Navy in World War II.
March 19, 1945 – USS Franklin (CV 13), which had maneuvered closer to the Japanese homeland than any other U.S. carrier, was attacked by a single Japanese plane which dropped two bombs, devastating the hangar deck and setting off ammunition. The ship was enveloped by fire, killing 724 and wounding 265.
1945-1946 – The Navy commissioned numerous aircraft carriers.
February 7, 1950 – In a demonstration of carrier long-range attack capabilities, a pilot flew 5,060 miles in 25 hours and 59 minutes, the longest flight ever made from a carrier deck.
August 5, 1950 – USS Valley Forge (CV 45) and USS Philippine Sea (CV 47) began what would be almost three years of continuous carrier operation in Korea.
Fall 1950 – The first United States Navy advisors arrived in South Vietnam.
September 1, 1952 – The largest carrier raid of the Korean War occurred when 144 aircraft from USS Boxer (CV 21), USS Essex (CV 9), and USS Princeton (CV 37) struck an oil refinery in North Korea.
January 12, 1953 – Test operations began on USS Antietam (CV 36), America’s first angled-deck carrier.
October 1, 1955 – USS Forrestal (CV 59), the first of four ships in a class and the Navy’s first supercarrier, was commissioned.
May 17, 1959 – The end of the escort carrier as a combatant ship in the U.S. Navy.
May 5, 1961 – USS Lake Champlain (CVA 39) recovered Alan B. Shepard, the first American to go into space, as he completed his Freedom 7 flight.
July 21, 1961 – USS Randolph (CVA 15) recovered Virgil “Gus” Grissom, the second American in space.
October 24, 1962 – USS Enterprise (CVAN 65), USS Independence (CVA 62), USS Essex (CVS 9), and USS Randolph (CVS 15) took part in the Naval Quarantine of Cuba. This was imposed by order of President John F. Kennedy following the discovery of offensive nuclear missiles on Cuba, placed there by the Soviet Union (Russia).
August 1964 – The Navy’s air and surface bombardment in North Vietnam began. Aircraft carriers supported air campaigns by bombing facilities, power plants, bridges, and railroads. They also helped control the seas to support the land effort in Asia.
October 3, 1964 – USS Enterprise (CVAN 65), USS Long Beach, and USS Bainbridge complete Operation Sea Orbit, the world’s first task force composed of solely nuclear-powered ships. The ships circumnavigated the globe in 65 days without stopping for fuel or provisions.
May 3, 1975 – USS Nimitz (CVN 68) deployed, activating the Nimitz-class of carriers.
August 2, 1990 – The Gulf War began.
October 7, 2001 – Operation Enduring Freedom began in response to the attacks on September 11, 2001.
Read More: Top 10 Largest Warships in the World of All Time
List of Top 10 Oldest Aircraft Carrier In American History
1. USS Langley (CV-1)
2. CV-2 Lexington
3. CV-3 Saratoga
4. CV-4 Ranger
5. CV-5 Yorktown
6. CV-6 Enterprise
7. CV-7 Wasp
8. CV-8 Hornet
9. CV-9 Essex
10. CV-10 Yorktown
********
What are the First Aircraft Carrier of America?
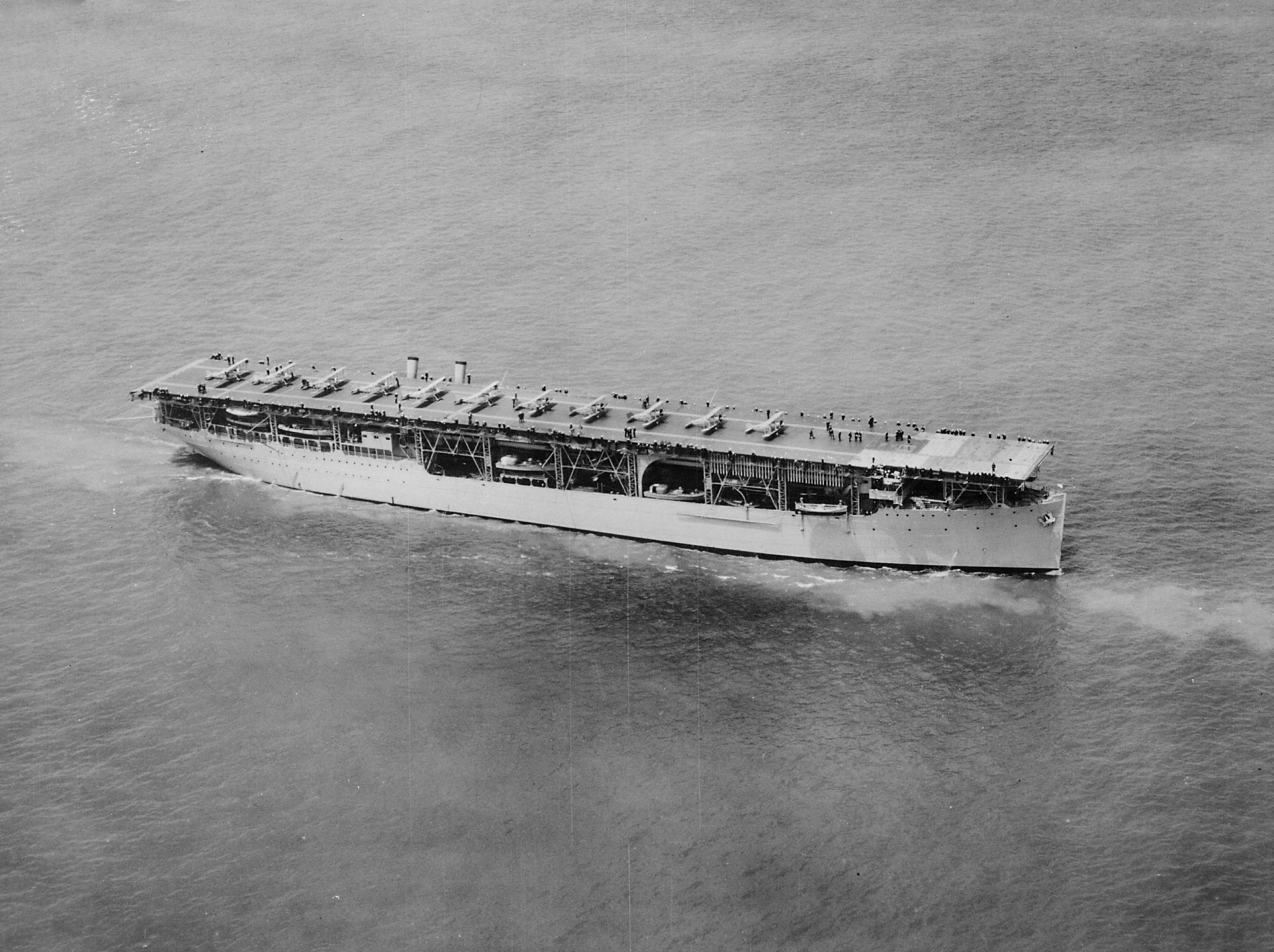
1. USS Langley (CV-1)
 |
| Photo: wikipedia |
Commissioned: March 20, 1922
The first U.S. carrier, a converted collier renamed the USS Langley, joined the fleet in March 1922. A Japanese carrier, the Hosyo, which entered service in December 1922, was the first carrier designed as such from the keel up.
They’ve been called “Cities at Sea.” Crewed by as many as 5,000 sailors and measuring more than 1,000 feet long, an aircraft carrier is a floating air base able to project power almost anywhere in the world, carrying as many as 90 aircraft. This year, the carrier celebrates its 100th birthday, born in the form of the USS Langley, a plodding little flattop commissioned in 1922. The Langley was an experiment to see if aircraft could operate effectively off ships. Langley showed it could be done, and then trained the U.S. Navy’s first generation of carrier aviators.
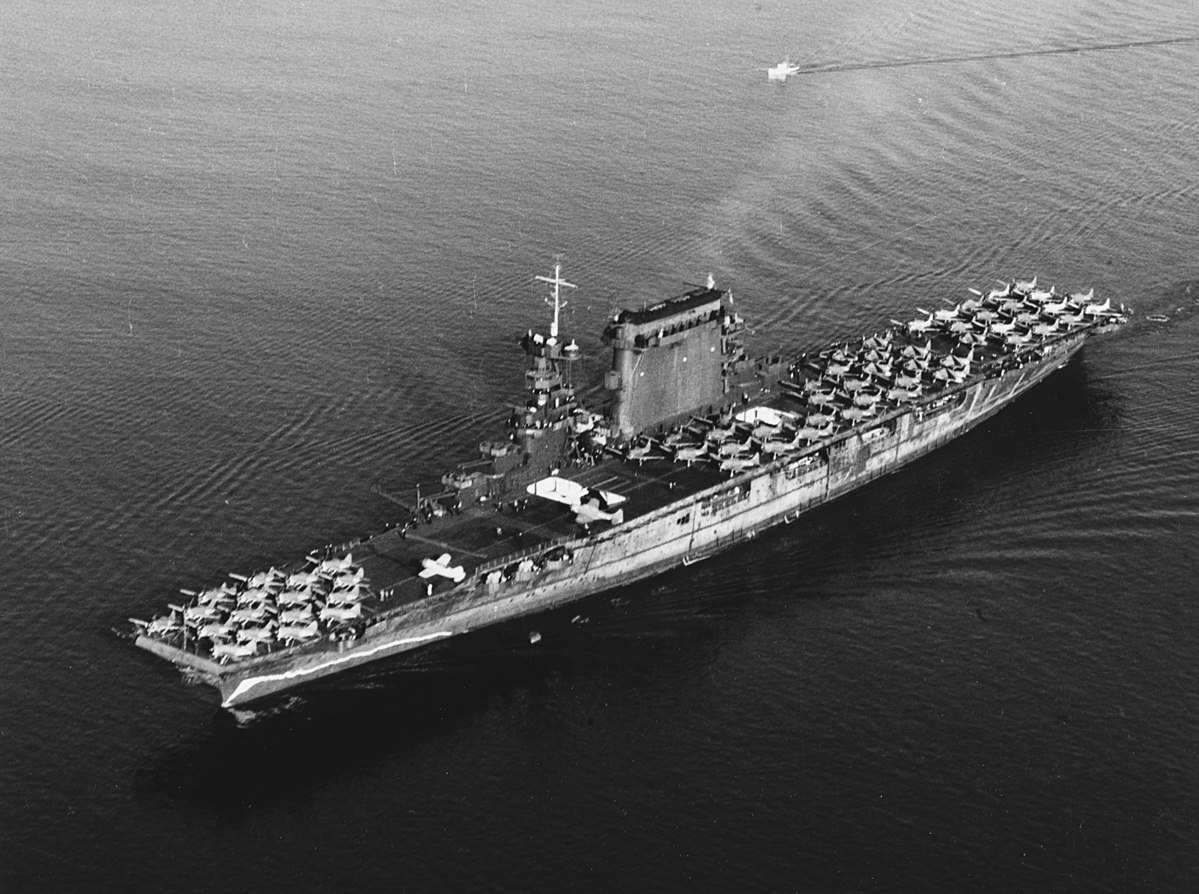
2. CV-2 Lexington
 |
| Photo: wikipedia |
Commissioned: December 14, 1927
USS Lexington (CV-2), one of the U.S. Navy's first two aircraft carriers, was commissioned in December 1927 at Quincy, Massachusetts. Operating mainly in the Pacific, she took part in fleet maneuvers in the Hawaiian Islands, the Caribbean, and Panama Canal. When the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, Lexington was transporting aircraft to Midway Island. During the December 11 attempt to relieve Wake Island, which was aborted, she was sent to attack Japanese installations in the Marshall Islands as a diversion. In January and February 1942, her aircraft raided Japanese positions in the southwestern Pacific.
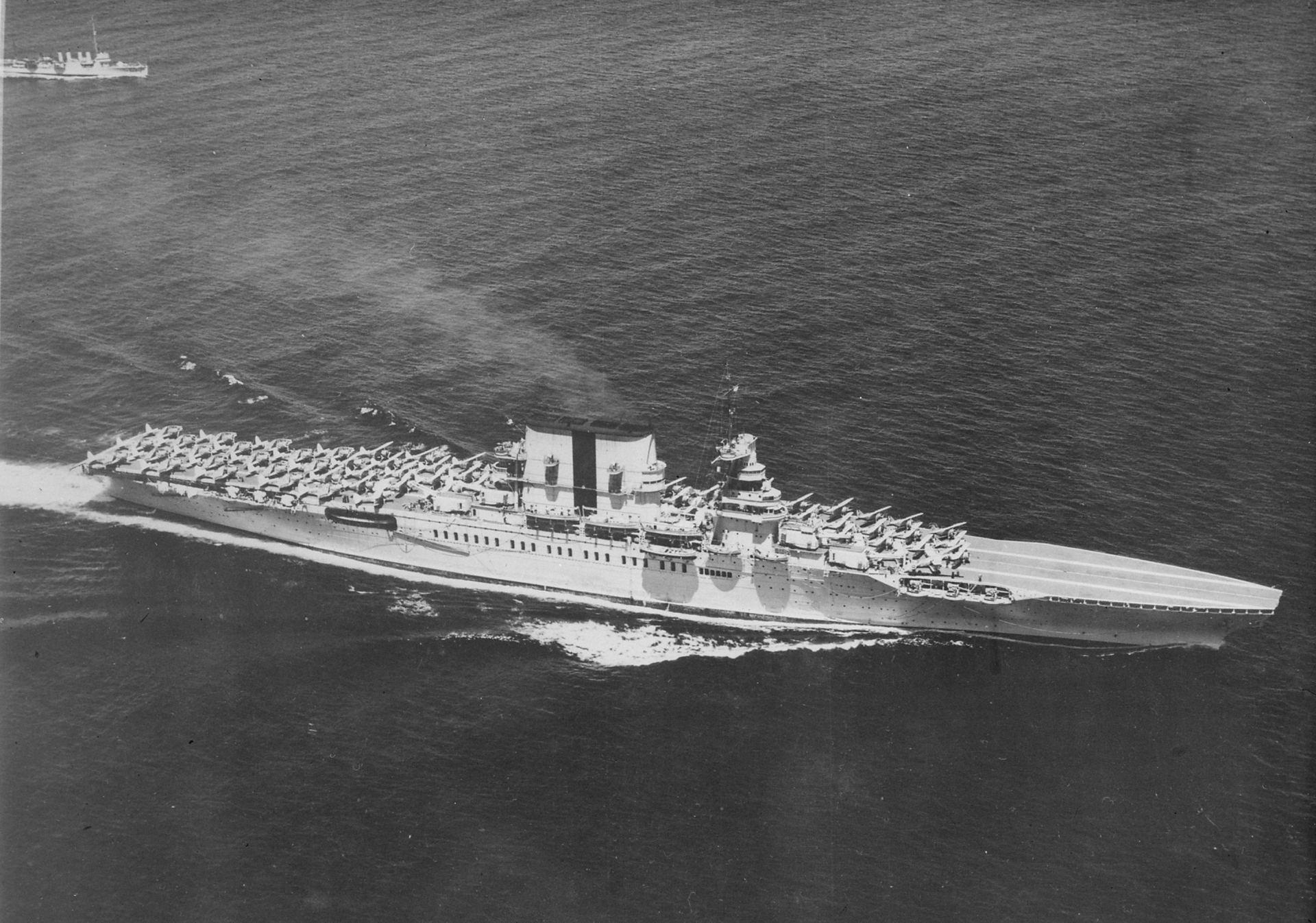
3. CV-3 Saratoga
 |
| Photo: wikiwand |
Commissioned: November 16, 1927
USS Saratoga (CV-3) was commissioned on 16 November 1927 with Captain Harry E. Yarnell in command. The ship was originally to be built as a battle cruiser, but was later authorized to be completed as an aircraft carrier. Saratoga was the U.S. Navy’s first fast carrier. She sailed from Philadelphia, on 6 January 1928, on shakedown and on 11 January, Saratoga’s air officer, Marc A. Mitscher, landed the first aircraft on her flight deck. On 27 January, during an experiment, rigid airship Los Angeles (ZR-3) moored to Saratoga's stern and took on fuel and stores. Later that day, she sailed for the Pacific where she joined the Battle Fleet at San Pedro, California. For the remainder of the decade and throughout the 1930s, Saratoga maintained readiness by participating in multiple fleet exercises in the Pacific, Atlantic, and the Mediterranean.
Related: What Are The First War Ships of US Navy - Top 10 Oldest
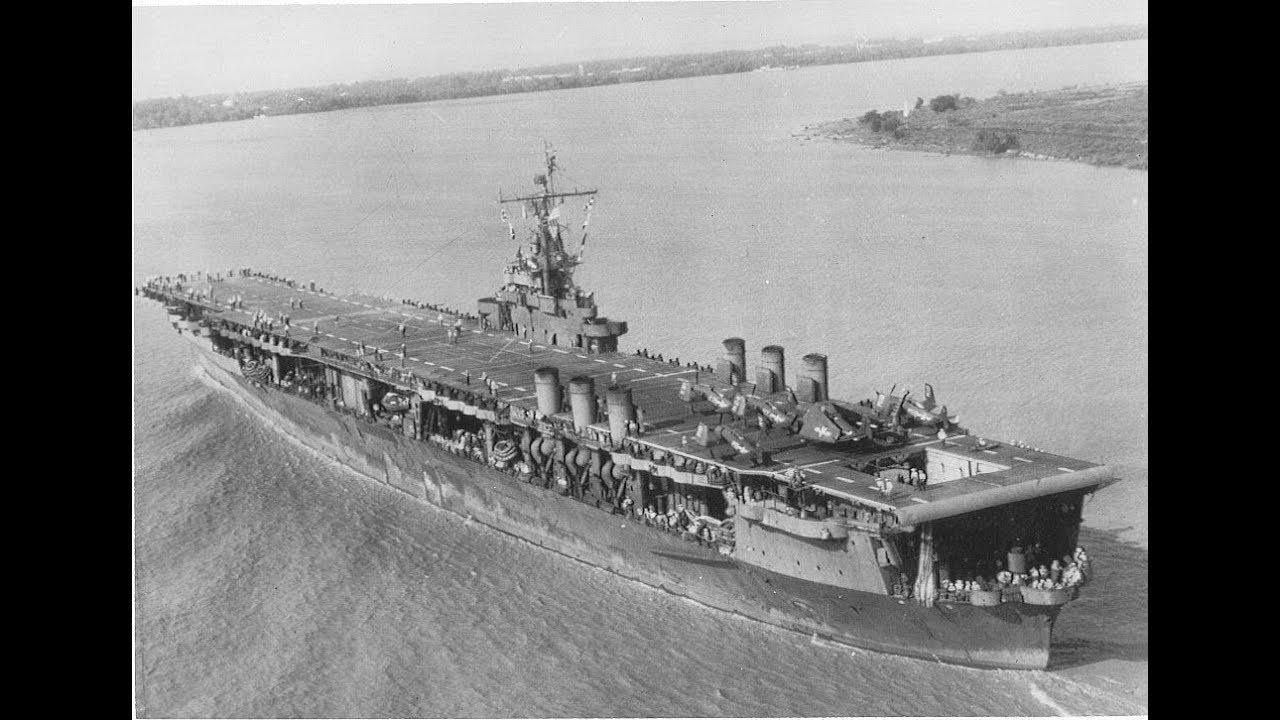
4. CV-4 Ranger
 |
| Photo: Youtube |
Commissioned: June 4, 1934
USS Ranger (CV-4) was the first USN aircraft carrier designed as such and remained unique. She was a relatively light Treaty ship, with a displacement of only 15,000 long tons (15,000 t), and an island superstructure that was added after completion. Her small size and low speed eliminated her from the Pacific Fleet and instead spent most of the war in the Atlantic, providing air support for Operation Torch, and Operation Leader off Norway among others. She was too small to deploy an efficient air group, which was taken into account for the Yorktown class.
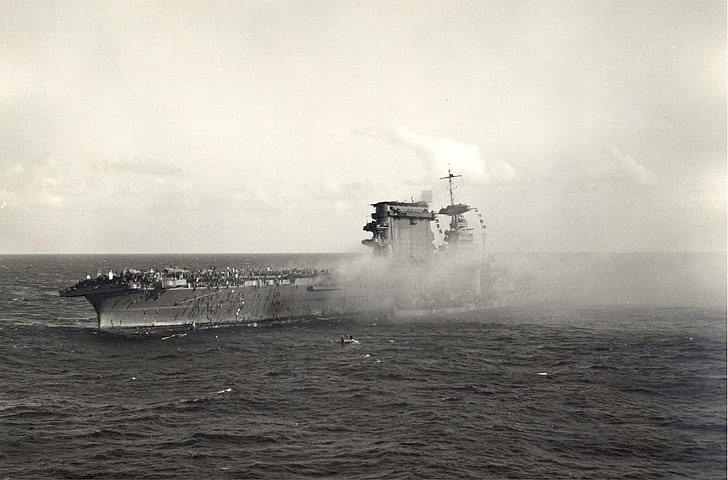
5. CV-5 Yorktown
 |
| Photo: wallpaperflare |
Commissioned: September 30, 1937
USS Yorktown, a 19,800-ton aircraft carrier built at Newport News, Virginia, was commissioned on 30 September 1937. Operating in the Atlantic and Caribbean areas until April 1939, she then spent the next two years in the Pacific. In May 1941 Yorktown returned to the Atlantic, patrolling actively during the troubled months preceding the outbreak of war between the United States and the Axis powers.
Following the attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941, YORKTOWN became the flagship of aircraft carrier Task Force 17, targeting Imperial Japanese Navy garrisons in the Marshall and Gilbert Islands in February 1942, and engaging IJN shipping in the Coral Sea in May 1942.
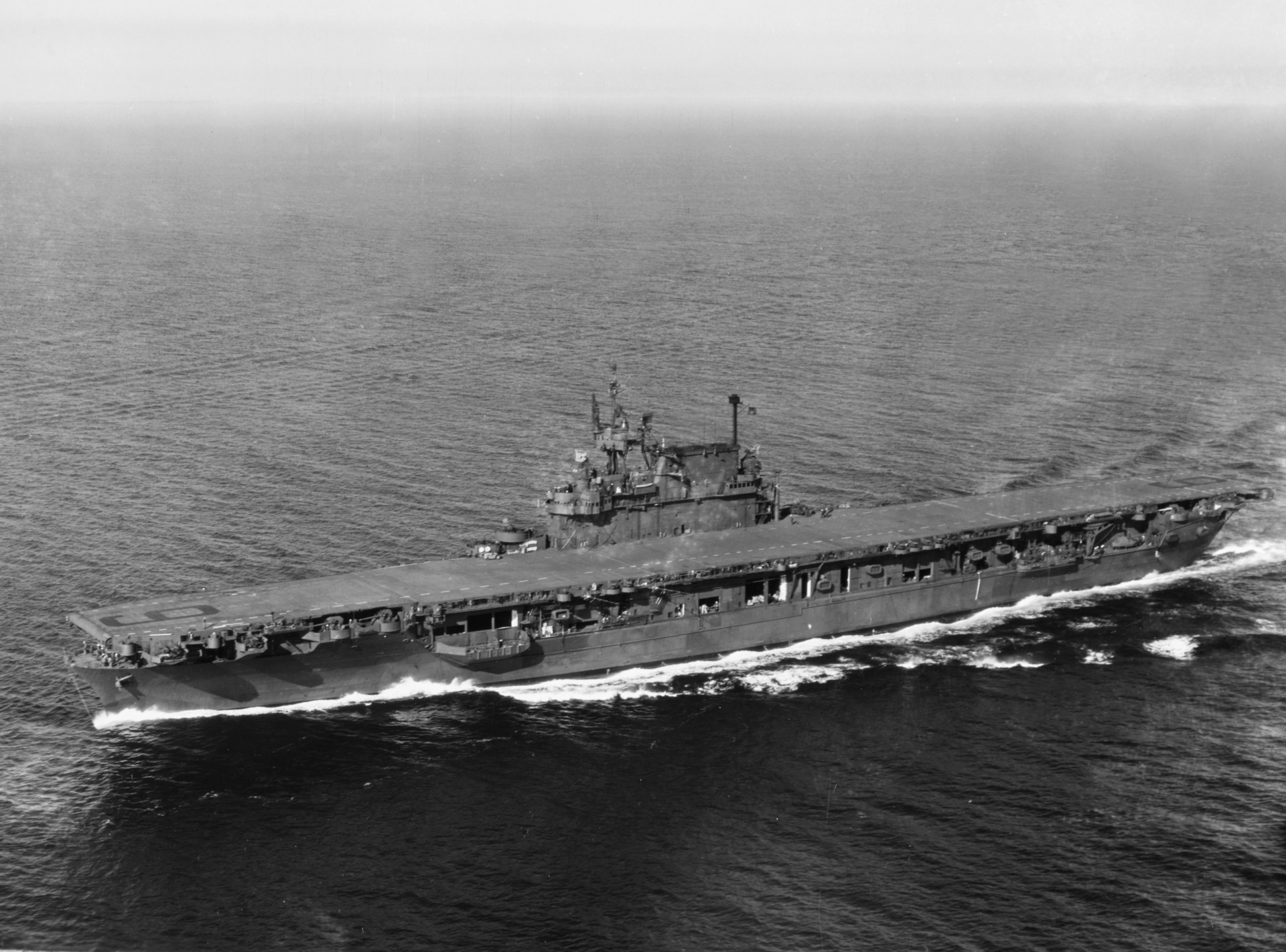
6. CV-6 Enterprise
 |
| Photo: wikipedia |
Commissioned: May 12, 1938
The Yorktown class aircraft carrier, USS Enterprise (CV-6) was commissioned at Newport News, Virginia, on May 12, 1938. Relocating to the Pacific, she was at sea during the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. Three days after, she became the first U.S. Navy warship to sink a Japanese warship, submarine I-70, and later that month participated in the Wake Island expedition. In April, Enterprise covered the Doolittle Raid on Japan and participated in the Battle of Midway that June, where her planes helped sink three Japanese aircraft carriers and a cruiser.
During the Guadalcanal Campaign, she covered the landings and participated in the battles of Eastern Solomons and the Santa Cruz Islands. Despite being damaged in both battles, she launched aircraft to assist the ships involved in the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal.
How Strong Is The American Army - No.1 Militaries In The World and Fact-Check
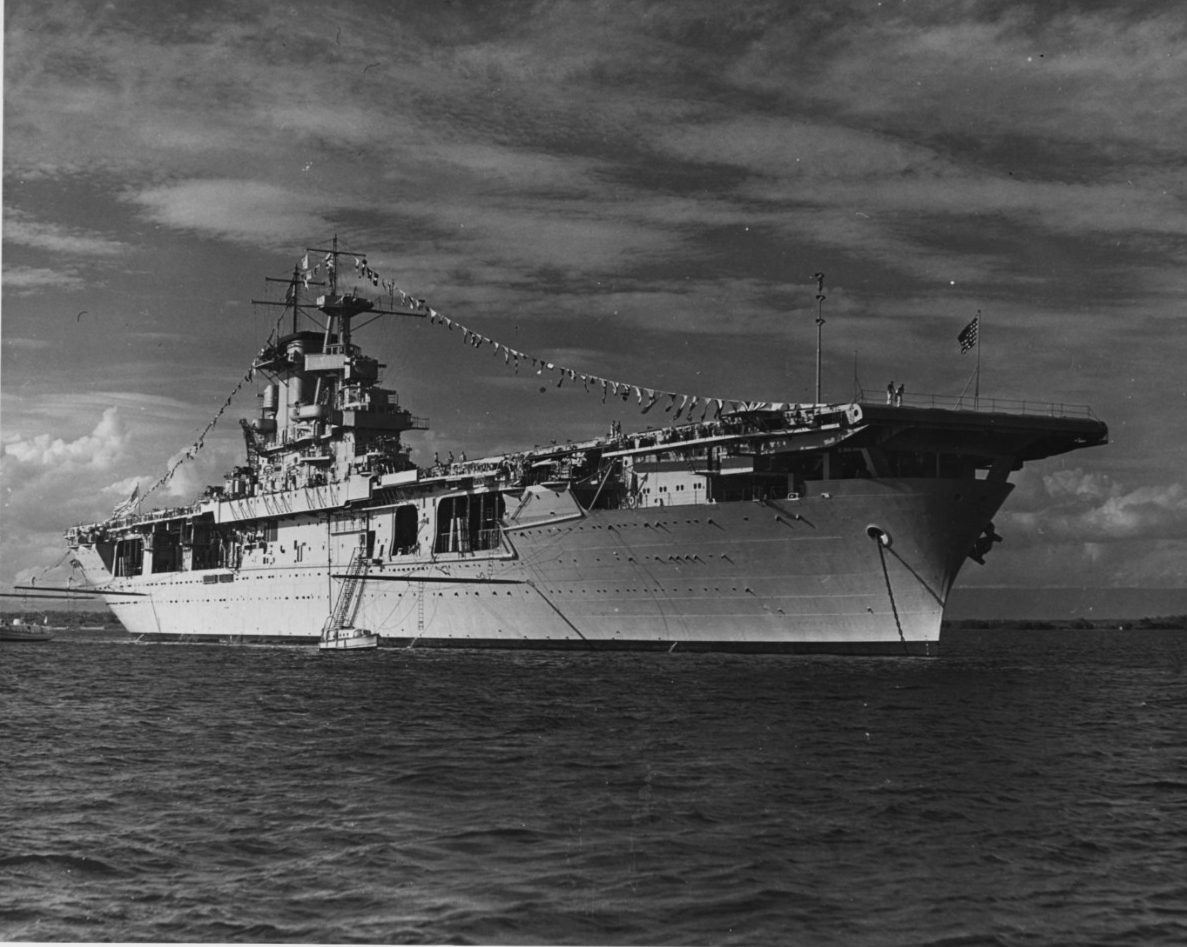
7. CV-7 Wasp
 |
| Photo: history.navy.mil |
Commissioned: April 25, 1940
The USS Wasp is a multipurpose amphibious assault ship and landing helicopter dock (LHD) and is the lead ship of its class. Wasp and her sister ships are the first specifically designed to accommodate new Landing Craft Air Cushion (LCAC) for fast troop movement over the beach, and Harrier II (AV-8B) Vertical/Short Take-Off and Landing (V/STOL) jets which provide close air support for the assault force.
Additionally, the USS Wasp can accommodate the full range of Navy and Marine Corps helicopters, conventional landing craft, and amphibious vehicles.
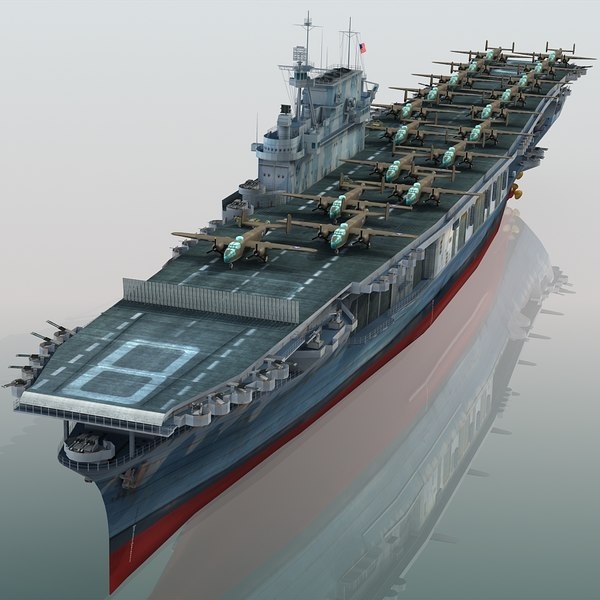
8. CV-8 Hornet
 |
| Photo: turbosquid |
Commissioned: October 20, 1941
The seventh U.S. Navy ship named Hornet was an early aircraft carrier commissioned in October 1941. USS Hornet (CV-8) was the third and final member of the Yorktown-class, commissioned just weeks before the attack on Pearl Harbor. As a pre-World War II vessel, her size was limited in accordance with international naval treaties from the 1930s.
Her first mission was the transport of the famous Doolittle Raid in April 1942., the first U.S. air raid to strike the Japanese home islands after the attack on Pearl Harbor. The raid demonstrated the vulnerability of the Japanese home islands to air attack and the Raid significantly boosted American morale.
CV-8 would continue to fight in the Pacific Theater, participating in the historic Battle of Midway and others before she was ultimately dealt a mortal blow at the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands in October 1942.
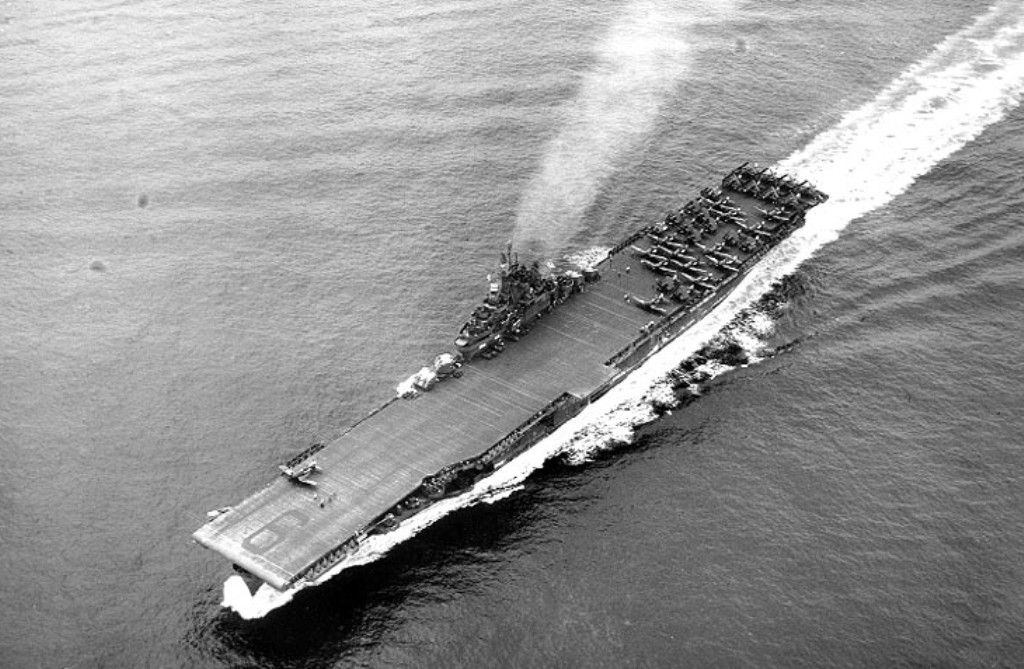
9. CV-9 Essex
 |
| Photo: greelane |
Commissioned: December 31, 1942
The USS Essex is the second oldest Wasp-class amphibious assault ship and is the fifth ship in the U.S. Navy named after Essex County, Massachusetts. Commissioned in 1992, the USS Essex made its maiden deployment in 1994 to prepare for the complex task of covering the withdrawal of United Nations multinational force from Somalia in Operation United Shield. Essex served as the command ship for Expeditionary Strike Group Seven until replaced by USS Bonhomme Richard on April 23, 2012. Most recently, in 2018, the USS Essex was deployed to the United States Central Command area of operations.
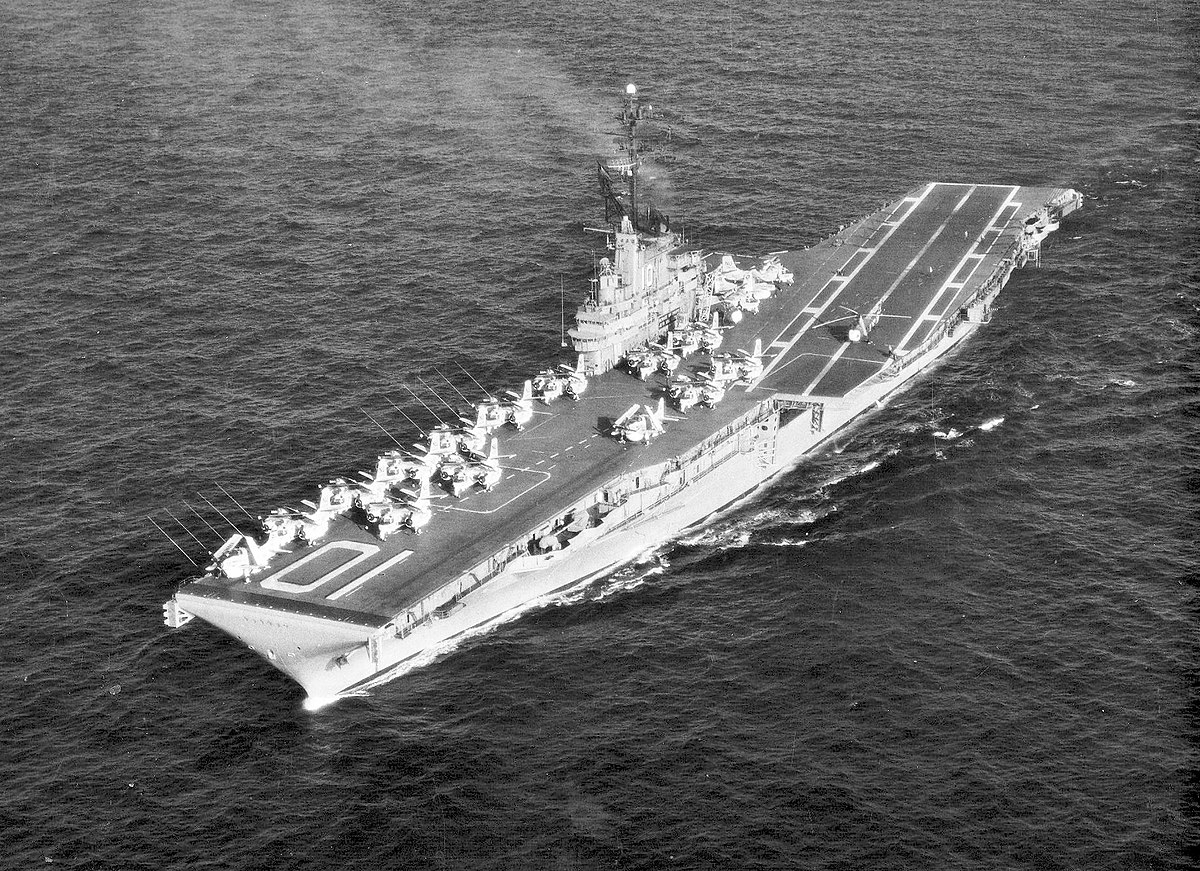
10. CV-10 Yorktown
 |
| Photo: wikipedia |
Commissioned: April 15, 1943
CV-10 was initially named Bon Homme Richard after Captain John Paul Jones's Bonhomme Richard (note different spelling), in turn named to honor Benjamin Franklin. Renamed, 26 September 1942, in tribute to USS Yorktown (CV-5), lost three months earlier at the Battle of Midway. The name Bon Homme Richard was subsequently assigned to CV-31.
The Siege of Yorktown or Battle of Yorktown (28 September–19 October 1781) was a decisive victory by a combined assault of French forces led by General Comte de Rochambeau and American forces led by General George Washington, over a British Army commanded by General Lord Cornwallis. It proved to be the last major battle of the American Revolutionary War, as the surrender of Cornwallis's army (NS020538) prompted the British government to eventually negotiate an end to the conflict.
What is a supercarrier?Supercarrier is an unofficial descriptive term for the largest type of aircraft carrier, usually displacing over 65,000 long tons. The U.S. Navy currently has 10 such ships. In comparison, a few countries operate what are, by today's standards, medium carriers (fleet carrier) of around 42,000 tons, such as the French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle (R91). The size and configuration of the Charles de Gaulle corresponds closely with the 45,000-ton Midway class the United States built at the end of World War II as a successor class to the much more numerous 27,000-ton Essex-class aircraft carrier, mainstay vessels of WWII after 1943 when they entered service. Internationally, light carriers closer to 20,000 tons (such as HMS Illustrious) are more typical. The United Kingdom has two Queen Elizabeth class aircraft carriers currently under construction, the first of which is expected to be delivered in 2016. They will displace 70,600 metric tons (up from an original estimate of 65,000) and, when built, will be the third largest Supercarrier class in service. Supercarriers are the largest warships ever built, eclipsing even the largest battleship class laid down by any country. |
 What Are The First War Ships of US Navy - Top 10 Oldest What Are The First War Ships of US Navy - Top 10 Oldest This article profiled 10 of the oldest consequential warships of the US Navy in American history. |
 Top 10 Oldest Beers In America You Should Drink Top 10 Oldest Beers In America You Should Drink Beer is a famous drink all around the world, and it's easy to find the best beer brands everywhere you go. We will introduce you ... |
 Which States Are The Richest And Wealthiest in The US? Which States Are The Richest And Wealthiest in The US? What are the richest states in the USA? Find out the country’s richest states with the top 10 in this article! |