What are the Limitations of ATACMS and Combat History
 The Threat of World War Three from Ukraine’s Use of Long-Range Missiles The Threat of World War Three from Ukraine’s Use of Long-Range Missiles |
 World War III in the Predictions of Prophets and Thinkers World War III in the Predictions of Prophets and Thinkers |
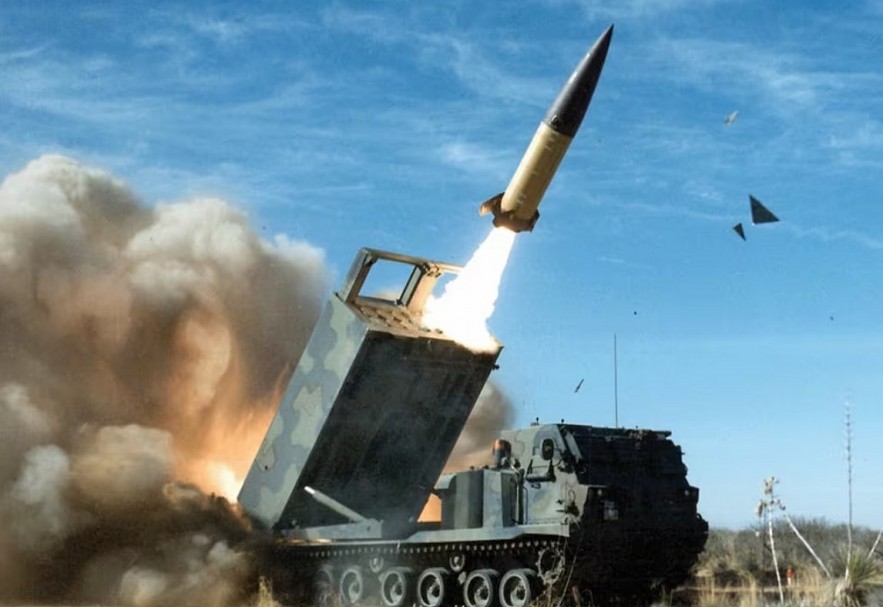
The Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) is one of the most powerful long-range tactical ballistic missile systems in the world, designed to deliver precise strikes deep into enemy territory. ATACMS, which Lockheed Martin created for the American military, has emerged as a crucial tool for precision warfare, particularly in situations where deep penetration of enemy defenses is necessary. With recent developments, such as its deployment in Ukraine, the global focus on ATACMS has intensified.
 |
| Challenges and Limitations of ATACMS |
I. The Power of the ATACMS
1. Key Specifications
ATACMS is renowned for its precision, speed, and flexibility. Below are its primary features:
Range: Depending on the variant, ATACMS can hit targets between 165 km (102 miles) and 300 km (190 miles). Future iterations may extend this range even further.
- Payload: ATACMS can carry different types of warheads:
- Unitary Warheads: Designed to deliver a single, high-impact explosive, capable of destroying bunkers, buildings, or command centers.
- Cluster Munitions: Some variants deploy submunitions over a wide area, targeting troop formations or light vehicles.
- Launch Platforms: The system can be launched from the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) or the M142 High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS).
- Speed: ATACMS travels at speeds exceeding Mach 3 (around 3,700 km/h or 2,300 mph), making it difficult for enemy defenses to intercept.
- Guidance: Equipped with GPS/INS (Inertial Navigation System), ATACMS achieves near-perfect accuracy, making it suitable for precision strikes.
2. Advantages of ATACMS
• Precision: The missile's advanced guidance system ensures minimal collateral damage, making it ideal for operations in urban or sensitive areas.
• Range: The long reach allows it to target deep into enemy territory, disrupting logistics, command structures, and supply chains.
• Versatility: ATACMS can be adapted for various missions, from neutralizing hardened structures to saturating enemy positions with cluster munitions.
• Survivability: Its speed and unpredictable trajectory make it difficult for enemy air defenses to intercept.
3. Strategic Importance
ATACMS serves as a force multiplier, enabling militaries to:
• Strike high-value targets like airfields, ammunition depots, and radars.
• Weaken enemy infrastructure far behind the frontlines.
• Disrupt command and control systems, forcing the enemy into disarray.
II. Combat History of ATACMS
ATACMS has a proven track record in U.S. military operations. While not as widely used as other artillery systems, its deployment in key conflicts underscores its strategic value.
1. The Gulf War (1991)
The ATACMS made its combat debut during Operation Desert Storm in 1991. It was used to:
• Destroy Iraqi surface-to-air missile (SAM) sites.
• Target key command and control centers.
• Neutralize logistics hubs, effectively crippling Iraqi operations.
The system’s ability to deliver precise, long-range strikes gave coalition forces a critical edge, allowing air superiority and paving the way for a swift ground offensive.
2. The Iraq War (2003–2011)
During the U.S. invasion of Iraq, ATACMS was again deployed to:
• Strike critical Iraqi military installations and airfields.
• Target underground bunkers and command facilities.
• Support advancing U.S. troops by eliminating enemy reinforcements and supply lines.
The missile system’s accuracy and range enabled coalition forces to operate effectively in a vast and complex battlefield.
3. Afghanistan Conflict
While not heavily utilized in Afghanistan due to the nature of the conflict (focused more on counter-insurgency than large-scale military engagements), ATACMS was occasionally employed to destroy fortified enemy positions and training camps in remote areas.
4. The War Against ISIS (2014–2019)
ATACMS was deployed in operations against ISIS in Iraq and Syria. It played a crucial role in targeting:
• Hardened enemy positions.
• Weapons caches and ammunition depots.
• Key logistical nodes, disrupting ISIS’s operational capabilities.
The precision of ATACMS ensured minimal civilian casualties in densely populated areas where ISIS fighters were often embedded.
III. The Role of ATACMS in Modern Conflicts
1. Ukraine - Russia War
Ukrainian forces reportedly used the ATACMS to devastating effect in October 2023. Ukraine targeted Russian airfields, destroying helicopters, ammunition depots, and logistical hubs. This marked the first known use of ATACMS in a conflict involving a major power since the Cold War.
• Impact: The strikes disrupted Russian operations in occupied territories and showcased the missile’s capability to shape the battlefield.
• Significance: The deployment of ATACMS in Ukraine underscores its relevance in modern warfare, particularly in conflicts involving large-scale military forces.
2. Deterrence in the Asia-Pacific
The U.S. has stationed ATACMS-capable systems in the Asia-Pacific region to counter potential threats from China and North Korea. These missiles play a critical role in:
• Defending allied territories, such as South Korea and Japan.
• Deterring aggressive moves in hotspots like the South China Sea and the Taiwan Strait.
3. Potential Future Deployments
As global tensions rise, ATACMS may see further use in:
• The Middle East, in response to Iranian missile and drone threats.
• The Indo-Pacific, where its range and precision could counter Chinese anti-access/area-denial (A2/AD) strategies.
IV. Top 8 Challenges and Limitations
Despite its reputation as a powerful and versatile weapon, ATACMS is not without its challenges and limitations. These factors can influence its effectiveness and deployment in various combat scenarios:
1. High Cost of Production and Use
Expense per Missile: Each ATACMS missile costs between $750,000 and $1.5 million, depending on the variant. This makes it an expensive choice for prolonged or widespread use in high-intensity conflicts.
Budget Constraints: High costs may limit the number of missiles procured by militaries, requiring judicious use during operations.
2. Limited Stockpile
Finite Inventory: The U.S. and its allies maintain a limited stockpile of ATACMS missiles. Prolonged conflicts or simultaneous engagements in multiple theaters can quickly deplete available reserves.
Slow Replenishment: The production of new missiles takes time, and manufacturing capacity may not meet demand during extended conflicts.
3. Restricted Range
Range Limitations: ATACMS has a maximum range of 300 km (190 miles), which, while significant, is insufficient compared to intermediate-range or intercontinental ballistic missiles (IRBMs or ICBMs).
Vulnerability in Large-Scale Theaters: In conflicts requiring strikes beyond this range, ATACMS may fall short, necessitating reliance on other missile systems.
4. Susceptibility to Advanced Air Defenses
Modern Countermeasures: Advanced air defense systems, such as Russia’s S-400 and China’s HQ-9, are designed to detect and intercept ballistic missiles, including ATACMS.
Electronic Countermeasures: Sophisticated jamming technologies or GPS spoofing could potentially disrupt ATACMS’s guidance systems, affecting accuracy.
Risk of Saturation: ATACMS’s effectiveness may diminish against well-fortified and layered defense systems unless deployed in large numbers.
5. Environmental and Weather Constraints
Operational Dependency on Weather: Harsh weather conditions, such as heavy rain, fog, or sandstorms, can affect the missile's precision and the effectiveness of its targeting systems.
Terrain Challenges: Dense urban environments, mountainous terrain, or areas with heavy vegetation can complicate target identification and missile trajectory planning.
6. Ethical and Political Concerns
Cluster Munitions Controversy: Some variants of ATACMS carry cluster munitions, which have been criticized for their potential to cause civilian casualties and leave unexploded ordnance behind, leading to long-term hazards.
Escalation Risks: The use of ATACMS, particularly in politically sensitive regions, can escalate tensions, prompting adversaries to retaliate with advanced weaponry or asymmetric tactics.
7. Logistical Challenges
Complex Deployment: ATACMS requires compatible platforms such as HIMARS or M270 MLRS for launching. These systems must be strategically positioned and protected, adding logistical complexity to operations.
Supply Chain Dependencies: The reliance on specialized components, such as advanced guidance systems and propulsion units, makes ATACMS production vulnerable to supply chain disruptions.
8. Potential Obsolescence
Emerging Threats: The rapid development of next-generation missile defense systems, hypersonic missiles, and counter-strike technologies could reduce ATACMS's battlefield relevance.
Competition from New Systems: The planned replacement of ATACMS with the Precision Strike Missile (PrSM) reflects the need to address these challenges and enhance performance in future conflicts.
V. Future of the ATACMS System
1. Modernization and Upgrades
Lockheed Martin is actively working on enhancements to ensure ATACMS remains relevant:
• Increased Range: Future versions may extend the missile’s range beyond 300 km, potentially reaching 500 km.
• Improved Guidance Systems: Enhanced GPS and autonomous targeting technologies will increase precision.
• Multi-Domain Integration: Newer models are expected to integrate with space-based sensors, enabling real-time targeting.
2. Replacement: Precision Strike Missile (PrSM)
The PrSM is set to replace ATACMS in the coming years. It offers:
Longer range (500+ km).
Greater payload flexibility.
Smaller size, allowing more missiles to be loaded onto launch platforms.
3. Global Proliferation
As the U.S. considers exporting ATACMS to allied nations, its role in global military strategy could expand. Countries like South Korea and Australia are potential buyers, further strengthening their deterrence capabilities.
VI. Strategic Implications
The ATACMS exemplifies the evolution of modern warfare. Its long-range precision capabilities have shifted the way militaries conduct operations, emphasizing the importance of deep strikes in degrading enemy capabilities.
Key Impacts
• Force Multiplier: By neutralizing high-value targets, ATACMS reduces the need for large-scale ground operations.
• Deterrence: The threat of ATACMS deployment serves as a powerful deterrent against adversaries.
• Allied Security: As a shared asset, it strengthens the collective defense capabilities of NATO and other alliances.
Conclusion
The ATACMS is a formidable weapon that has proven its value in multiple conflicts, from the Gulf War to the Ukraine-Russia war. Its combination of precision, range, and adaptability makes it a critical asset in modern military arsenals. While challenges such as cost and countermeasures exist, ongoing upgrades and replacements like the PrSM ensure that the legacy of ATACMS will endure.
As global tensions continue to rise, the importance of weapons like ATACMS in shaping the future of warfare cannot be understated. Its power is not only a testament to technological advancement but also a reminder of the responsibility required in wielding such devastating capabilities.
 Top 10 Best Assault Rifles In The World of All Time Top 10 Best Assault Rifles In The World of All Time We are going to define what an assault rifle is, talk about the origin of the term, and then we’ll even delve in the top ... |
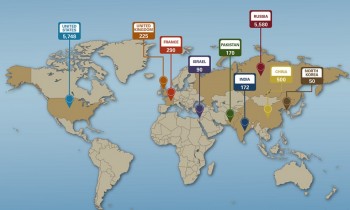 How Many Countries Are Armed with Nuclear Weapons in 2024/2025? How Many Countries Are Armed with Nuclear Weapons in 2024/2025? After Ukraine eliminated this kind of devastating weapon, nine nations made their nuclear weapons publicly known by the end of 2024 or the beginning of ... |
 Does Ukraine Have Nuclear Weapon? Does Ukraine Have Nuclear Weapon? The global community is inquiring as to whether Ukraine possesses nuclear weapons. It was previously a nuclear power; however, it does not possess nuclear weapons ... |
 How Strong Is North Korean Army/Nukes – The World's 30th Powerful Militaries How Strong Is North Korean Army/Nukes – The World's 30th Powerful Militaries With its lengthy and intriguing history, nuclear weapons, and enormous strength and power, North Korea's military is ranked as the 30th strongest in the world. |























