How to Build a Nuclear Fallout Shelter in the U.S. for Maximum Safety - Ultimate Guide
The threat of nuclear war, intensified by rising global tensions such as the escalating Russia-Ukraine conflict, has led many to consider constructing nuclear fallout shelters. These shelters provide protection from radioactive fallout and increase the chances of survival in a nuclear event.
Learn more: The Safest Places/States in the U.S. to Seek Shelter in Case of Nuclear War
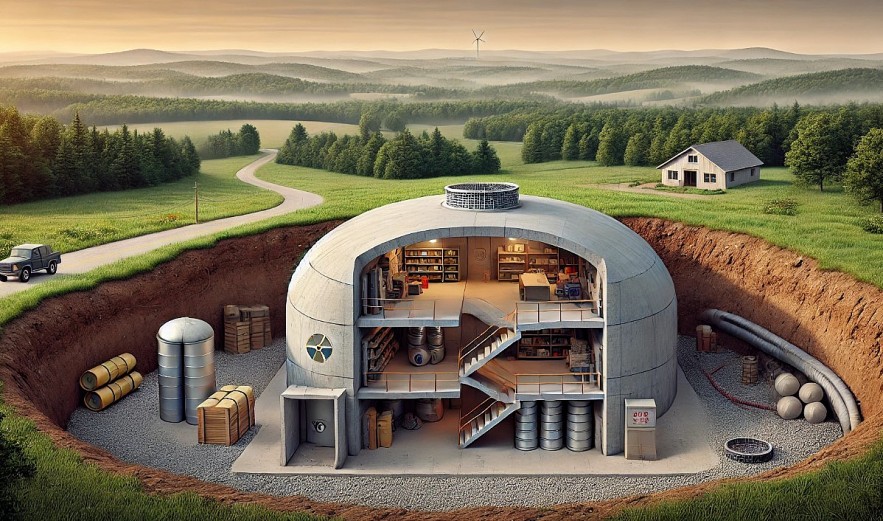 |
| A nuclear fallout shelter under construction in a rural area, showcasing its reinforced structure and stockpiled supplies. Image: KnowInsiders |
Why Build a Nuclear Fallout Shelter?
The Growing Threat
The ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict has highlighted the fragility of global stability, raising fears of potential nuclear escalation. According to international experts, the risk of miscalculations or deliberate nuclear attacks is a genuine concern. Fallout shelters offer safety during such emergencies by protecting individuals from:
• Blast Waves: The initial explosion causes destructive shockwaves.
• Radiation Exposure: Fallout particles can linger for weeks, posing long-term health risks.
• Contaminated Resources: Water and food supplies in affected areas may become unsafe.
Historical Precedent
The Cold War era saw an increase in fallout shelter construction across the U.S. These shelters became vital for civilian protection, a practice that remains relevant today amid renewed nuclear concerns.
The Safest Locations in the U.S. to Build a Fallout Shelter
When choosing where to build a shelter, consider locations far from potential nuclear targets. Targets include major cities, military bases, and industrial hubs. Here are some of the safest areas:
• Rural Midwest: States like Nebraska, South Dakota, and Kansas are far from high-risk zones and offer low population density.
• Rocky Mountains: Montana and Wyoming provide natural barriers like mountains, which shield against fallout and blast waves.
• Alaska: Remote and sparsely populated, Alaska is an unlikely target with abundant natural resources.
• Pacific Northwest: Northern Idaho and parts of Oregon are isolated with sustainable resources like fresh water and arable land.
• Appalachian Region: West Virginia’s mountainous terrain offers protection and access to fresh water.
Costs of Building a Fallout Shelter
 |
| A completed underground shelter, highlighting its safety features and preparedness measures. Image: KnowInsiders.com |
Building a fallout shelter can be a significant financial investment, but it ensures safety and long-term survival. The costs depend on the size, features, and location of the shelter:
• Basic Shelter: A simple underground bunker with reinforced concrete walls, ventilation, and basic supplies costs between $10,000 and $50,000.
• Advanced Shelters: Larger shelters with radiation shielding, air filtration systems, and multiple rooms can cost $100,000 to $500,000.
• Luxury Shelters: Fully equipped shelters with amenities like kitchens, bathrooms, and entertainment spaces may exceed $1 million.
Factors Influencing Cost
• Location: Remote areas with rocky terrain may increase excavation costs.
• Materials: High-density materials like lead and reinforced concrete add to expenses.
• Customization: Features such as blast doors, air filtration, and radiation shielding require specialized construction.
U.S. Government Guidelines on Nuclear Safety
The U.S. government provides extensive resources and recommendations for preparing for nuclear emergencies. Agencies like FEMA and Ready.gov outline steps for protection:
Sheltering Guidelines
• Immediate Actions: In the event of a nuclear explosion, move to a designated shelter or the nearest building. Basements and interior rooms without windows offer the best protection.
• Stay Indoors: Remain in the shelter for at least 24 hours, or until authorities provide further instructions.
• Seal the Shelter: Use duct tape and plastic sheeting to seal doors, windows, and vents to reduce exposure to radioactive dust.
Stockpile Essentials
• Water: Store at least one gallon per person per day for a minimum of two weeks.
• Food: Non-perishable items such as canned goods and freeze-dried meals.
• Medical Supplies: Include a first-aid kit, radiation sickness medications (e.g., potassium iodide), and prescription drugs.
Radiation Monitoring
• Geiger Counters: Measure radiation levels inside and outside the shelter.
• Potassium Iodide: These tablets help protect the thyroid gland from radioactive iodine.
Communication Tools
Use battery-operated radios to receive updates from local authorities. Ready.gov also provides printable emergency plans and lists of recommended supplies.
Steps to Build a Safe Nuclear Fallout Shelter
-
Choose a Safe Location
- Avoid areas near cities, military bases, or industrial centers.
- Select high ground or mountainous areas to reduce flood risks.
-
Plan the Design
- Underground Placement: Provides maximum protection from radiation.
- Reinforced Walls: Use concrete, lead, or steel for shielding.
- Ventilation System: Install air filters to prevent contamination.
-
Excavate and Construct
- Excavate deep enough to place the shelter underground.
- Install blast doors, airlocks, and drainage systems.
-
Equip the Shelter
- Stockpile essentials like food, water, and medical supplies.
- Include emergency lighting, power generators, and communication devices.
-
Regular Maintenance
- Inspect and test air filtration systems and radiation monitors regularly.
- Replace expired supplies and ensure structural integrity.
Conclusion
Building a nuclear fallout shelter in the U.S. is a proactive step in ensuring safety during uncertain times. With escalating global tensions, understanding where to build, how much it costs, and adhering to government guidelines are crucial for survival. By taking these measures, individuals and families can increase their resilience against one of the most devastating threats humanity may face.
FAQs About Building a Nuclear Fallout Shelter
1. Why should I consider building a nuclear fallout shelter?
With escalating global tensions, such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the risk of nuclear warfare, while low, remains a possibility. Fallout shelters provide protection from radiation, fallout, and contaminated resources, ensuring safety during such catastrophic events.
2. How much does it cost to build a nuclear fallout shelter?
The cost varies depending on the size, features, and materials:
-
Basic shelters: $10,000 to $50,000.
-
Advanced shelters with air filtration and radiation shielding: $100,000 to $500,000.
-
Luxury shelters with full amenities: Over $1 million.
3. Where is the safest location to build a fallout shelter in the U.S.?
Safe areas are far from major cities, military bases, and industrial hubs. Top locations include rural Midwest states (e.g., Nebraska, South Dakota), the Rocky Mountains, Alaska, and parts of the Pacific Northwest.
4. What are the key features of a good fallout shelter?
A proper fallout shelter should include:
-
Reinforced walls with materials like concrete or steel for radiation shielding.
-
An air filtration system with HEPA filters.
-
Stockpiled water, food, and medical supplies.
-
Emergency power sources and communication tools.
5. Are there official U.S. government guidelines for nuclear safety?
Yes, FEMA and Ready.gov provide detailed instructions on how to prepare for and survive nuclear events. These include:
-
Sheltering in place.
-
Sealing windows and doors.
-
Stockpiling essentials.
-
Using radiation monitors and following local authority updates.
 Does Ukraine Have Nuclear Weapon? Does Ukraine Have Nuclear Weapon? The global community is inquiring as to whether Ukraine possesses nuclear weapons. It was previously a nuclear power; however, it does not possess nuclear weapons ... |
 How Strong Is North Korean Army/Nukes – The World's 30th Powerful Militaries How Strong Is North Korean Army/Nukes – The World's 30th Powerful Militaries With its lengthy and intriguing history, nuclear weapons, and enormous strength and power, North Korea's military is ranked as the 30th strongest in the world. |
 Mystery of President Putin's Nuclear Briefcase (Cheget) and Russia’s Current Nuclear Arsenal Mystery of President Putin's Nuclear Briefcase (Cheget) and Russia’s Current Nuclear Arsenal The nuclear briefcase, often seen near Russian President Vladimir Putin, has long been a symbol of supreme power. Known as the "Cheget," this device is ... |
 What Makes an ICBM Deadly? Nuclear Warheads, and Catastrophic Impact What Makes an ICBM Deadly? Nuclear Warheads, and Catastrophic Impact The world is shocked by Ukraine's claim that Russia has used an Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) in combat for the first time. The devastating scope ... |























