Which Countries Possess Nuclear Weapons in 2026? List of 9 Nations Are Nuclear-Ready
Global Nuclear Weapons Landscape in 2026: What Has Changed?
As of early 2026, the global nuclear weapons landscape remains numerically stable but strategically tense. According to the latest assessments, only nine countries officially possess nuclear weapons, unchanged from 2025: the United States, Russia, China, France, United Kingdom, India, Pakistan, Israel, and North Korea. Together, they control an estimated 12,000+ nuclear warheads worldwide, with more than 3,900 currently deployed and ready for use. Importantly, no new country has officially joined the nuclear club entering 2026.
However, geopolitical risks are rising. One major concern is the future of the New START treaty, the last remaining nuclear arms control agreement between the United States and Russia. Set to expire in early 2026, the treaty’s uncertain extension or replacement raises fears of a renewed arms race, potentially leading to expanded nuclear stockpiles and reduced transparency.
Meanwhile, North Korea has intensified its military testing, conducting multiple ballistic and hypersonic missile launches toward surrounding seas in early 2026. These actions signal an effort to strengthen deterrence capabilities rather than a change in nuclear ownership status.
Another focal point is Iran, which still does not officially possess nuclear weapons. Nonetheless, its advanced enrichment capacity and technical expertise have fueled international concern that Iran could rapidly become a nuclear-armed state if its political stance shifts.
In short, while the number of nuclear-armed nations remains unchanged in 2026, escalating tests, expiring treaties, and latent nuclear capabilities are making the global security environment more fragile than ever.
How Many Nuclear-Weapon Countries Are There In The World?
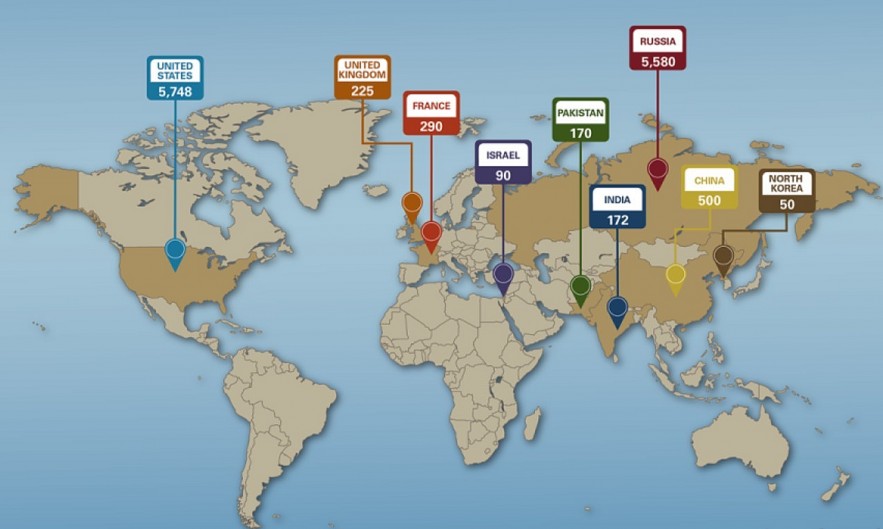
At present there are 9 countries in the world that possess nuclear weapons. They are:
1. Russia
2. United States
3. China
4. France
5. United Kingdom
6. Pakistan
7. India
8. Israel
9. North Korea
The 2024 State of the Worlds Nuclear Forces report by the Federation of Atomic Scientists estimates that these states possess about 12,100 nuclear warheads, of which over 9,500 are in active military stockpiles.
Learn more: Top 10 Countries Have the Most Nuclear Reactors in the World
 |
| List of Countries That Possess Nuclear Weapons |
Number of Nuclear Warheads in the World 2026
Even though this is a significant decrease from the roughly 70,000 warheads that the nuclear-armed states possessed during the Cold War, today's forces are far more capable and nuclear arsenals are predicted to grow over the next ten years.
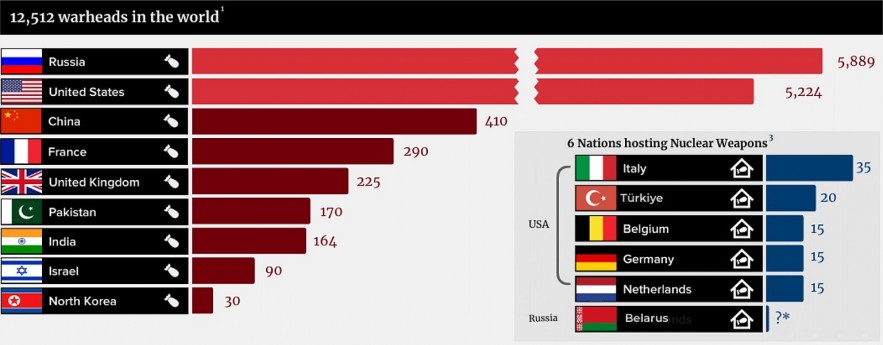
Some nations in the world have nuclear warheads in their defense stockpile, considering them to be weapons of mass destruction. As of January 2026, there were about 12,100 nuclear warheads in the world.
Which Country Has the Most Nuclear Weapons?
With more than 5,500 nuclear warheads, Russia has the most nuclear weapons that have been verified. With 5,044 nuclear weapons stationed in the US and five other countries—Turkey, Italy, Belgium, Germany, and the Netherlands—the US trails behind. Almost 90% of all nuclear weapons worldwide are held by these two nations alone in terms of total nuclear warheads.
It is unknown how many warheads Israel and North Korea have in total. Though Israel has enough material for up to 200 weapons and an estimated 90 warheads currently in operation, North Korea is thought to have enough fissile material to develop between 40 and 50 individual weapons.
The same two nations still hold the bulk of the nuclear weapons in the world, despite the fact that their number has decreased since the end of the Cold War.
The US, Russia, and China all have smaller numbers of non-strategic (or tactical) nuclear warheads. These are weapons with shorter ranges and lower yields that are not limited by any treaties.
China, India, and Pakistan are all working on making new cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, and nuclear delivery systems that can be used at sea. North Korea is still working on getting nuclear weapons, even though it has promised to stop doing so.
Learn more: Top 9 Worst Nuclear Disasters In the World of All Time
 |
| Nuclear Warheads in the World |
What Does These Countries Having Nuclear Weapons Mean?
A single nuclear bomb could kill hundreds of thousands of people, and the long-term effects would be terrible for the environment and people in need. About 583,160 people would have died if a single nuclear bomb had been dropped over New York.
There are more than 12,000 nuclear weapons in the hands of the US, Russia, the UK, France, China, India, Pakistan, Israel, North Korea, and the US. Most of these weapons are much stronger than the one that was dropped on Hiroshima. There are 32 more states that are affected by the problem, including 6 that have nuclear weapons and 28 that support their use.
5 Nuclear-Weapon States
Five states—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—are officially acknowledged as possessing nuclear weapons by the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT). These states are referred to as nuclear-weapon states (NWS). The treaty acknowledges the nuclear arsenals of these states; however, they are prohibited from constructing and maintaining such weapons in perpetuity pursuant to Article VI of the NPT.
Russia
The New START declaration from September 2022 says that Russia has 1,549 strategic warheads on 540 strategic delivery systems, such as heavy bombers, intercontinental ballistic missiles, and submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Because Russia pulled out of the New START Treaty in February 2022, it did not provide the latest data as required by the treaty. But both Russia and the US have promised to follow the limits set by the treaty until 2026.
According to the U.S. intelligence community, Russia also has an arsenal of 1,000 to 2,000 non-strategic nuclear warheads that is not limited by the New START Treaty as of December 2022.
The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) says that as of March 2024, Russia's military stockpile has about 4,380 nuclear warheads and another 1,200 retired warheads that need to be taken apart.
United States
According to the March 2023 New START declaration, the US has 1,419 strategic nuclear warheads on 662 delivery systems, including heavy bombers, intercontinental ballistic missiles, and submarine-launched missiles.
About 100 B-61 nuclear gravity bombs have been sent to six NATO bases in Italy, Germany, Turkey, Belgium, and the Netherlands: Aviano and Ghedi, Büchel, Incirlik, Kleine Brogel, and Volkel.
A July 19, 2024 Energy Department declassification notice stated that there were 3,748 "active" and "inactive" U.S. warheads as of September 2023. The department says the stockpile doesn't include the 2,000 retired or awaiting disassembly warheads. In May 2024, FAS estimated that the military had 5,044 warheads, 3,708 active and 1,336 retired, ready to be disassembled. Former warheads are being disassembled slower than expected, causing the difference in numbers.
China
Outside researchers estimate that China has 440 nuclear warheads for bombers, land-based and sea-based ballistic missiles. They estimate that China has 310 warheads on 206 strategic launchers, including intercontinental and submarine-launched ballistic missiles. At least 60 warheads were made to arm more road-mobile and silo-based missiles and bombers.
China has modernized its nuclear forces since the 1990s. Recently, its weapon arsenal has grown in number and type. The Defense Department estimated 500 nuclear weapons in China in October 2023. If current trends continue, China could have 1,000 nuclear warheads by 2030.
France
When January 2022 rolls around, France will have 290 operational warheads stored and ready to go on 98 strategic delivery systems. There are 48 ballistic missiles that can be launched from submarines and 50 cruise missiles that can be launched from aircraft in the air that can be used by fighter jets that can land and fly from carriers.
France will not be adding to its nuclear arsenal, but it has pledged to modernize its nuclear forces over the long term.
United Kingdom
There are 225 warheads in the UK military inventory as of January 2022. Roughly 120 of these are ready to be deployed on 48 ballistic missiles launched from submarines, while the remaining 105 are stored.
The United Kingdom's sole nuclear deterrent is its fleet of four nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines, the Vanguard-class Trident.
Non-NPT Nuclear Weapons Possessors
Israel, India, and Pakistan are known to have nuclear weapons but they have never ratified the NPT. In 1974, India conducted its first nuclear explosive device test. Pakistan increased the pace of work on its covert nuclear weapons program as a result of that test. Both India and Pakistan publicly displayed their nuclear weaponry in May 1998 with a series of tit-for-tat tests. Although Israel has not publicly carried out a nuclear test, it is widely assumed that it possesses nuclear weapons.
India
India is estimated to possess up to 172 nuclear warheads.
Pakistan
Pakistan is estimated to possess approximately 170 nuclear warheads.
Israel
Israel is thought to possess 90 nuclear warheads and enough fissile material in its stockpiles to make 200 more.
Israel declares that it will not be the first country in the Middle East to introduce nuclear weapons, but it does neither acknowledge nor deny possessing them. However, it is widely accepted that Israel has nuclear weapons that are kept in a partially disassembled state, though the precise quantity is unknown.
Countries that Declared Their Withdrawal from the NPT
Although North Korea declared its intention to leave the NPT in 2003, the other NPT members have not formally acknowledged this decision. North Korea entered the NPT as a non-nuclear weapon state. North Korea has conducted nuclear weapons and ballistic missile tests. The number of nuclear weapons North Korea has amassed is still unknown.
North Korea
There is a lot of uncertainty around these estimates, but North Korea is thought to have about 30 nuclear warheads and probably has more fissile material that isn't weaponized.
North Korea is currently extracting plutonium for its nuclear warheads using a 5-megawatt heavy-water graphite-moderated reactor. North Korea is known to possess uranium enrichment technology and to have a facility at Yongbyon. It probably runs other clandestine uranium enrichment facilities somewhere else.
Apart from developing nuclear-capable missiles with a range of up to 500 meters, North Korea also asserts that it has produced tactical nuclear warheads.
 How Strong Is North Korean Army – The World's 30th Powerful Militaries How Strong Is North Korean Army – The World's 30th Powerful Militaries |
Countries of Immediate Proliferation Concern
Iran has achieved the status of a threshold state since it has acquired the technology to produce nuclear weapons. If Tehran's security concerns change, it has threatened to pursue a nuclear deterrent and withdraw from the NPT.
Iran
Iran ratified the NPT in 1970 but continued illicit nuclear activities, including an organized nuclear weapons program, through 2003, according to the IAEA and US intelligence community.
In 2006, Tehran refused to cooperate with the IAEA's nuclear program investigation, alerting the Security Council. From 2006-2010, six Security Council resolutions targeted Iran's nuclear program.
Unclassified 2007 US intelligence estimates said "Iran has the scientific, technical and industrial capacity eventually to produce nuclear weapons if it decides to do so."
In July 2015, Iran and six world powers agreed to limit Iran's nuclear program and improve transparency in exchange for NPT sanctions relief. The US left the JCPOA and reimposed sanctions on Iran in May 2018. Iran broke JCPOA nuclear restrictions the following year. Tehran says its actions are a response to the U.S. nuclear deal withdrawal and sanctions reimposition and do not involve nuclear weapons. (Arms Control Today, P4+1, and Iran Nuclear Deal Alert cover JCPOA.)
In the 2024 Worldwide Threat Assessment, the US intelligence community found that Iran has not resumed key nuclear weapons-related activities, but its nuclear advances allow it to develop nuclear weapons if needed.
Iran has enough 60 percent-enriched uranium to build nuclear weapons, but the warhead would be bulky and inconsistent with its pre-2003 weapons work.
IAEA is investigating evidence that Iran did not declare uranium activities under safeguards in 2003.
Iran denies developing nuclear weapons, but after an April 2024 attack on Israel, officials suggested the country may reconsider its nuclear doctrine if security conditions change or its nuclear facilities are attacked.
Learn more: Does Ukraine Have Nuclear Weapon?
List of Countries That Had Nuclear Weapons or Nuclear Weapons Programs at One Time
After receiving nuclear weapons from the Soviet Union, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine turned them back to Russia and became non-nuclear weapon states, joining the NPT.
Separation of race A limited number of nuclear weapons were clandestinely developed by the South African government. Prior to its 1994 transition to a multi-racial democracy, South Africa dismantled its entire nuclear weapons program and joined the NPT in 1991.
Iraq had a nuclear weapons program that was active before the Persian Gulf War of 1991, but it was verified dismantled by UN inspectors. The Bush administration's justification for invading Iraq in 2003 was to stop the country from acquiring WMD. In contrast, Iraq did not possess chemical or biological weapon stockpiles, and its nuclear program had been dormant since its dismantlement in the 1990s.
After months of clandestine nuclear weapon development, Libya voluntarily ended those efforts in December 2003.
Syria is being asked by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to clarify its nuclear program. At Al Kibar, a reactor was bombed in 2007 while it was being built. Syria may have been building the reactor for its illicit nuclear weapons program, according to the available evidence.
A number of countries, including Argentina, Brazil, South Korea, Sweden, Australia, and Taiwan, have done nuclear weapons research in the past.
FAQs
Does Ukraine have nuclear weapons?
There are no nuclear weapons in Ukraine's arsenal. In exchange for security guarantees, Ukraine signed the Budapest Memorandum in 1994 and relinquished its nuclear arsenal, which was the third-largest in the world at the time.
Following the removal of the last warhead from the country on June 2, 1996, Ukraine lost its nuclear status. Since then, the country has faithfully adhered to its non-nuclear-weapons-state obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty.
Does Iran have nuclear weapons?
With the 2015 nuclear agreement with major powers deteriorating over time, Iran has ramped up its nuclear program, shortening the time it would take to construct a nuclear weapon—something it denies wanting—though it insists it has no such intention.
Does Taiwan have nuclear weapons?
At present, there is no indication that Taiwan possesses any chemical, biological, or nuclear weapons. Nevertheless, the United States deployed nuclear weapons to Taiwan during a period of elevated regional tensions with China that commenced with the First Taiwan Strait Crisis and concluded in the 1970s.
What are Nuclear Warheads?
Nuclear bombs are extremely hazardous weapons that have the potential to decimate entire cities and kill millions of individuals. The environment and future generations are adversely affected by the radioactive fallout from these explosions for an extended period of time. The United States employed them only once, in 1945, in Hiroshima and Nagasaki, near the conclusion of World War II. Despite the high level of danger associated with nuclear weapons, certain nations have been conducting routine nuclear tests.
What are the Tactical nuclear weapons in the world?
Any nuclear weapon not considered "strategic" under US-Russia arms control agreements is this type. The Federation of American Scientists reports that Russia has 1,912 non-strategic nuclear warheads and the US has 100 in five European countries. These are often called "smaller" or "low yield" nuclear weapons, which implies less damage. However, their warheads can yield 300 kilotons, 20 times the Hiroshima bomb.
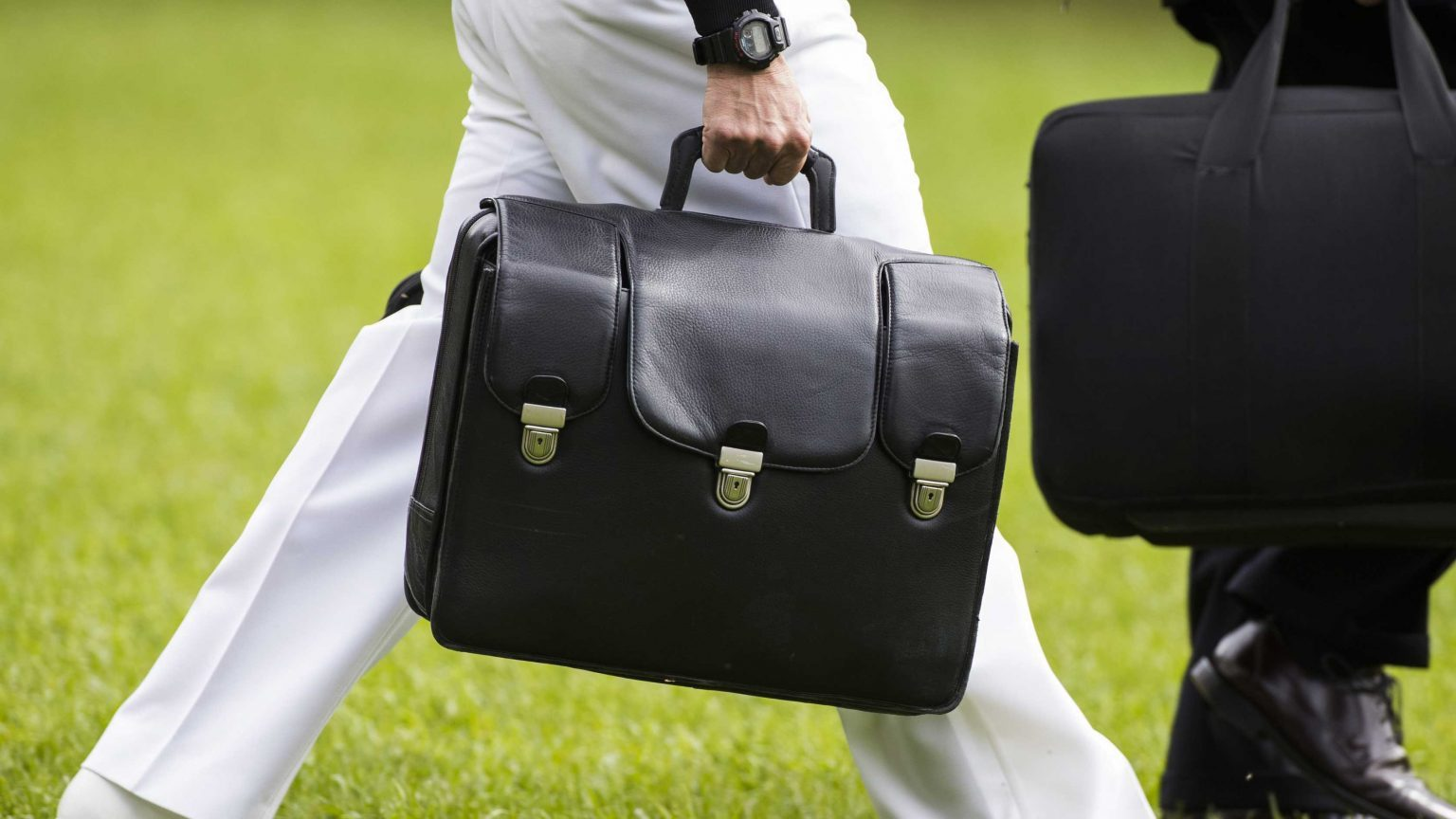 Facts About 'Nuclear Football' Briefcase of the U.S President: History, Inside and Red Button Facts About 'Nuclear Football' Briefcase of the U.S President: History, Inside and Red Button Nuclear Football, the powerful and mysterious briefcase that always follows the U.S President everywhere can be able to launch a nuclear attack. So, what is ... |
 TOS-1: Russia's Most Powerful Non-Nuclear Weapon in Ukraine Battlefield TOS-1: Russia's Most Powerful Non-Nuclear Weapon in Ukraine Battlefield The TOS-1 thermobaric rocket system is said to be one of the "unique" weapons that the Russian military uses on the Ukrainian battlefield. |
 Zaporizhzhia - Ukraine’s Largest Nuclear Plant with 6 Reactors Zaporizhzhia - Ukraine’s Largest Nuclear Plant with 6 Reactors A fire breaks out at the Zaporizhzhia nuclear plant, which is home to six of the fifteen nuclear energy reactors in Ukraine. |