'Cow Killer' Velvet Ant - The Strangest Animal In The World
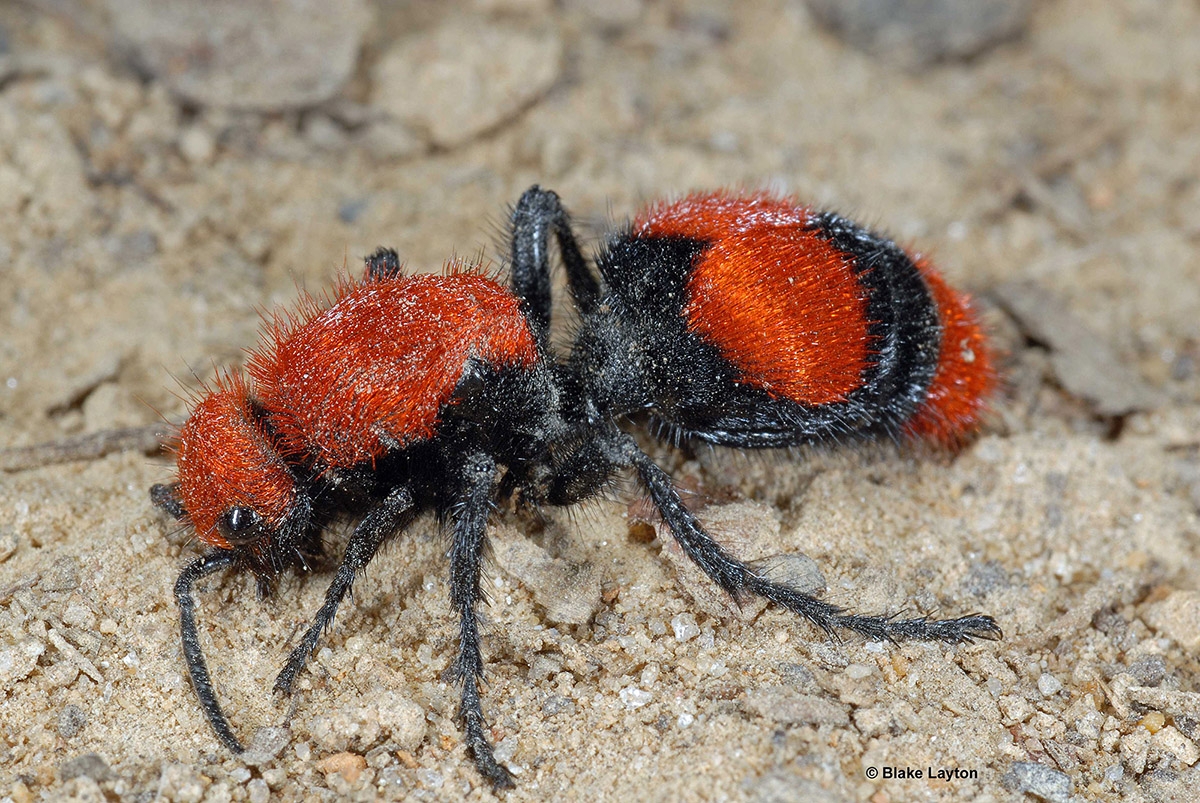 |
| A lady velvet ant. Photo: Mississippi State University Extention Service |
'Cow Killer' Velvet Ant: Family
The Mutillidae are a family of more than 7,000 species of wasps whose wingless females resemble large, hairy ants, Entomology cites. Their common name velvet ant refers to their dense pile of hair, which most often is bright scarlet or orange, but may also be black, white, silver, or gold. Moreover, their bright colors serve as aposematic signals.
'Cow Killer' Velvet Ant: Description
These insects are wasps, not ants. Females are wingless and covered with dense hair, superficially resembling ants. The red velvet-ant is the largest velvet-ant species, reaching about 3/4 inch in length. They are black overall with patches of dense orange-red hair on the thorax and abdomen. Males are similar but have wings and can not sting. Velvet ants usually run on the ground quite rapidly, as cited by the University of Florida.
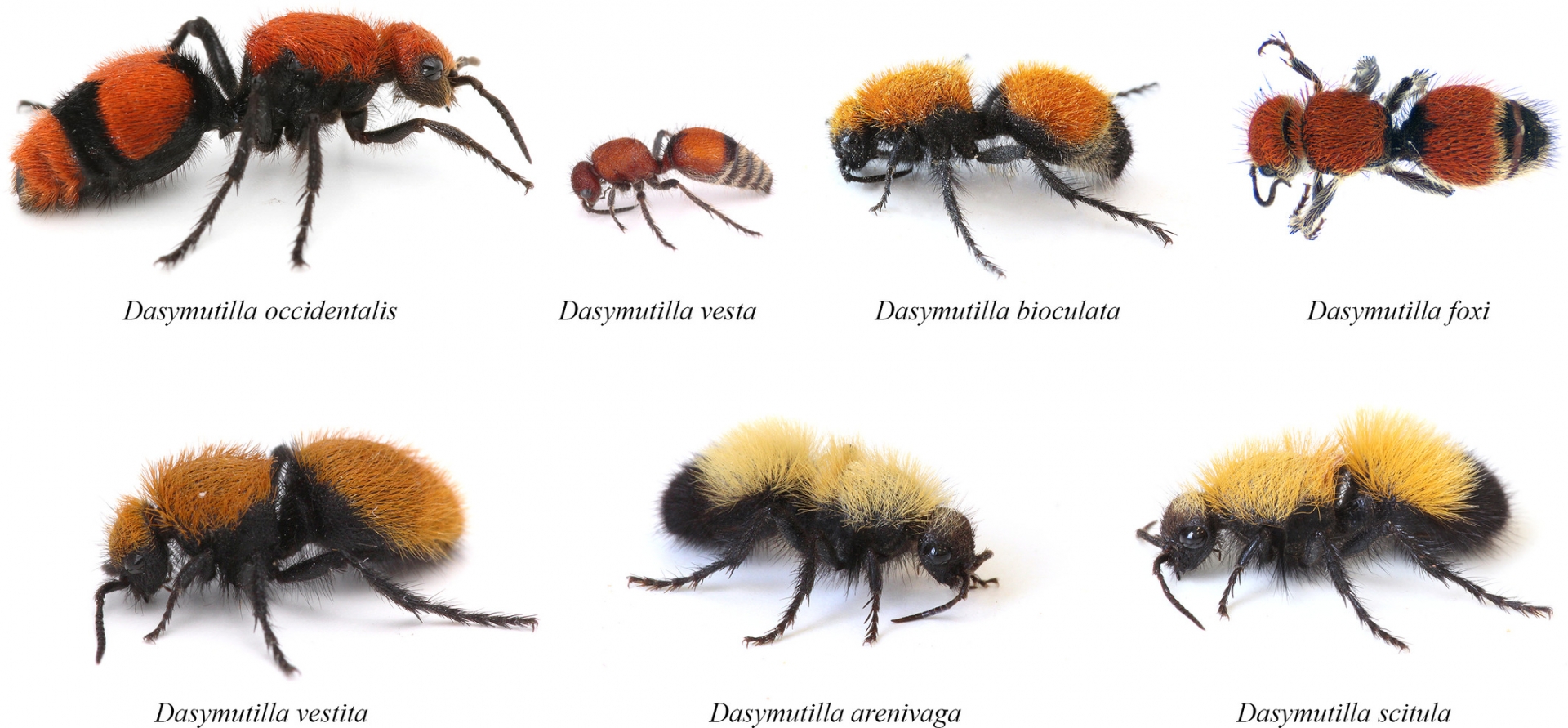 |
| Some appearances of velvet ants. Photo: Wiley Online Library |
Several other species of velvet ants are common in Texas, including the grey velvet ant or thistledown mutillid, Dasymutilla beutenmulleri, and D. fulvohirta. Most are solitary parasites of immature wasps (Vespidae and Sphecidae), solitary bees and some other insects such as beetles and flies. Winged males can be confused with other Hymenoptera. Adults of the tiphiid wasp, Myzinum sp. (Hymenoptera: Tiphiidae) are black and yellow, 3/4 inch long. They can occur in large numbers, sometimes on flowers of landscape plants. Larvae are parasites of white grubs (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae).
'Cow Killer' Velvet Ant: Distribution
The Mutillidae family contains approximately 230 genera/subgenera and about 8,000 species worldwide (Manley and Pitts 2002). Approximately 435 species occur in most arid areas of the southern and western parts of North America. Fifty species in seven genera are found in Florida.
'Cow Killer' Velvet Ant: Life cycle
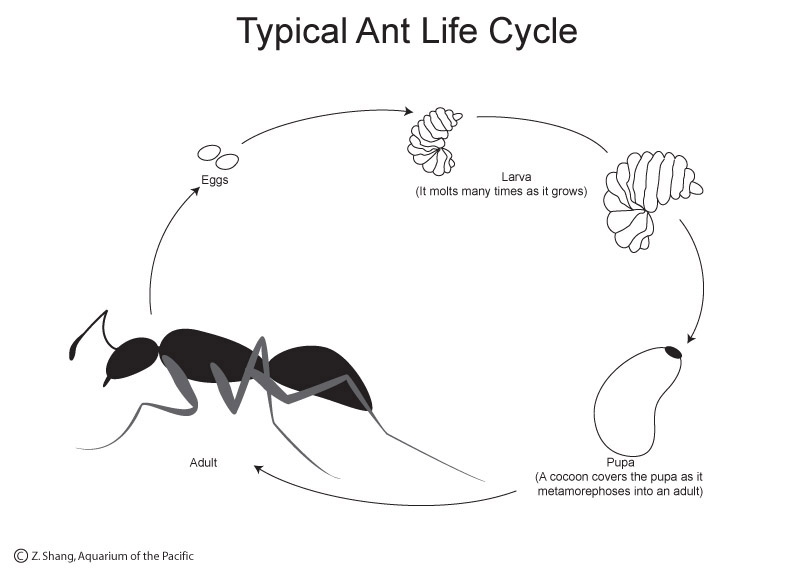 |
| Life cycle of a velvet ant. Photo: Aquarium of the Pacific |
Females seek the immature stages of ground-nesting bees, digging to the nesting chambers and eating a hole through the cocoon. She deposits an egg on the host larva, which soon hatches into a white legless grub. According to Texas Insects, the immature velvet-ant eats the host larva, developing through several larval stages before forming a pupa.
'Cow Killer' Velvet Ant: Habitat
Mouthparts are for chewing. Lone females can be found crawling on the ground, particularly in open sandy areas. Adults are most common during the warm summer months. Larvae are solitary, external parasites of developing bumble bees.
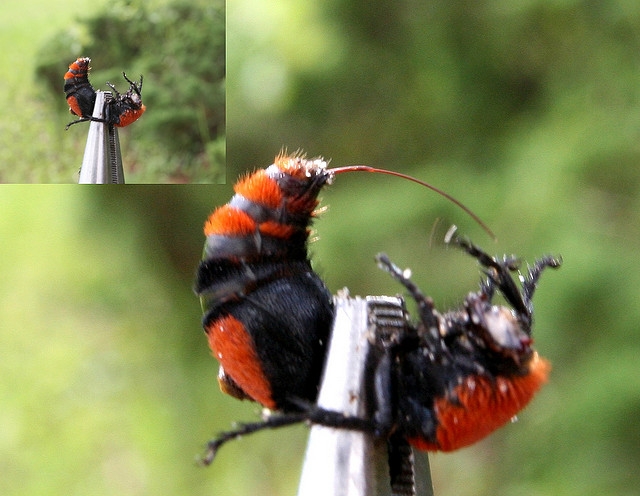 |
| Photo: Reddit |
Pest Status: The common name, “cow killer,” is thought to describe the painful sting these insects can inflict to man and animals, although it is doubtful that many cows are actually stung.
'Cow Killer' Velvet Ant: Biology
All Mutillidae are solitary parasitoid wasps that mostly attack mature larvae or pupae of other solitary Hymenoptera. However, velvet ants have been observed targeting non-feeding stages of Diptera, Coleoptera, Lepidoptera, Blattodea, and even some eusocial Hymenoptera.
Finding a matching reproductive pair can be difficult, if not impossible for some species, because of the extreme sexual dimorphism displayed within this family. Colour patterns and the relative body size of the two sexes of the same species can be very different, making it very difficult to relate one sex with the other.
In Florida, male Mutillidae are frequently larger (heavier) than the females. One study in south-central Florida found that in seven out of 13 species, the males were heavier than the females. The remaining six species either showed comparable sizes between the male and female or the female was larger than the male.
Females have the difficult job of locating potential hosts. Suitable hosts may be difficult to find for several reasons including concealment, low population densities when solitary and lastly if the hosts are eusocial, they will be heavily defended. Once a host is located, female velvet ants parasitize the "hard" life stages (i.e., hardened pre-pupae, pupae, ootheca, eusocial cells, and cocoons) of the hosts and the emerging velvet ant larvae are essentially ectoparasites of those life stages. Once development is completed, adults leave the nest and seek a mate.
 |
| The brightly coloured cow killer velvet ant is common in late summer. |
| One unusual insect that is occasionally seen running around open areas in the yard during July, August and September is the velvet ant. These solitary wasps, as the name implies, are densely covered with short hair. Because velvet ants are uncommon and do not cause any damage, no chemical control is recommended. |
 Top 15 Weirdest Animals in the World You Probably Didn't Know Exist Top 15 Weirdest Animals in the World You Probably Didn't Know Exist With more than 8 million species of living things on Earth, no wonder that nobody knows or has seen them all. That's why we've chosen ... |
 Aye-aye - World's Strangest Animal Aye-aye - World's Strangest Animal The aye-aye (Daubentonia madagascariensis) is a long-fingered lemur listed as the world's largest nocturnal primate. It is native to Madagascar with rodent-like teeth that perpetually ... |
 Top 7 Insanely Appetizers around the Globe Top 7 Insanely Appetizers around the Globe If you plan to travel around the world, eating foods in these countries you arrive is indispensable. Let's look at this piece of information to ... |


























