Colon Infection: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
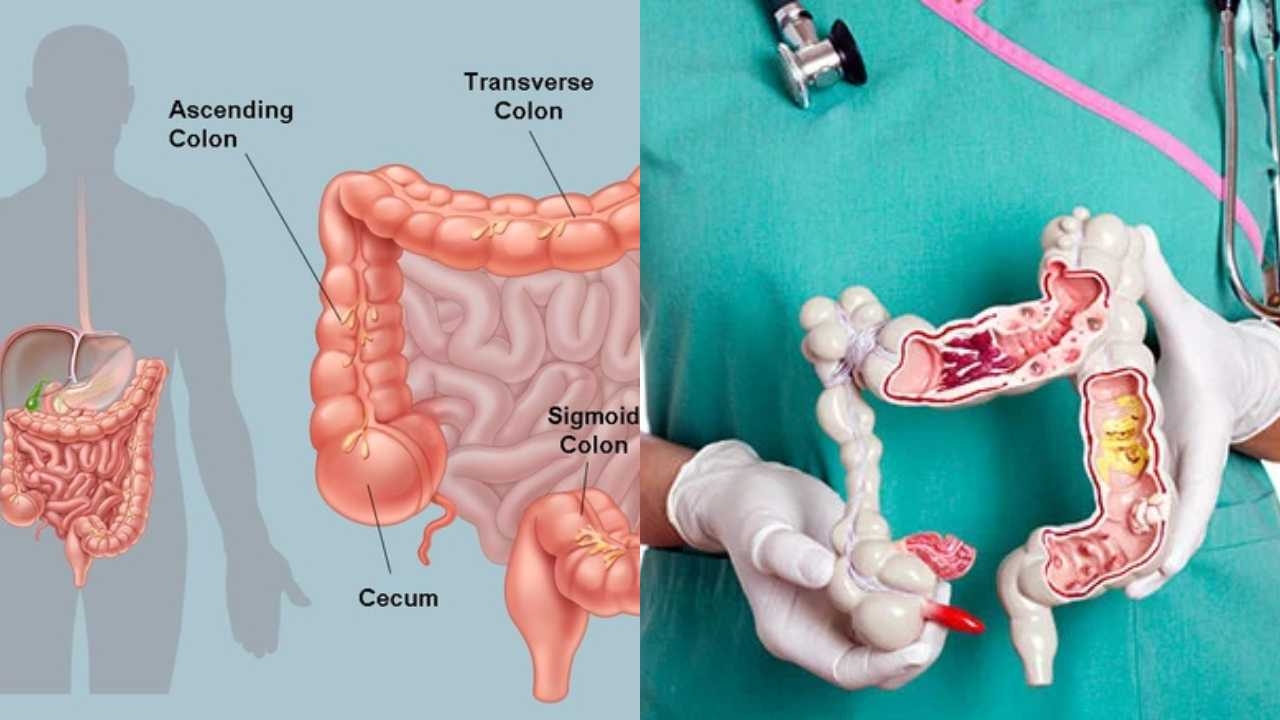 |
| Colon Infection. Photo: Newsd.in |
What is a colon infection?
Colitis is a general term for the inflammation of the inner lining of the colon, which is your large intestine. According to the Health line, there are different types of colitis categorized by cause. Infections, poor blood supply, and parasites can all cause an inflamed colon. If you have an inflamed colon, you’ll likely have abdominal pain, cramping, and diarrhoea.
Colon infection causes
There are a few different types of colitis and other conditions that can cause colon inflammation.
Infection
Infectious colitis can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and parasites. A person who has infectious colitis will have diarrhoea and fever, and a stool sample that tests positive for enteropathogens such as:
-salmonella
-campylobacter
-Escherichia coli (E. coli)
Depending on the cause of the infection, infectious colitis may be contracted from contaminated water, foodborne illnesses, or poor hygiene.
Pseudomembranous colitis is another type of infectious colitis. It’s also referred to as antibiotic-associated colitis or C. diff colitis because it results from an overgrowth of the bacteria Clostridium difficile. It’s most often caused by antibiotic use that interferes with the balance of healthy bacteria in the colon.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
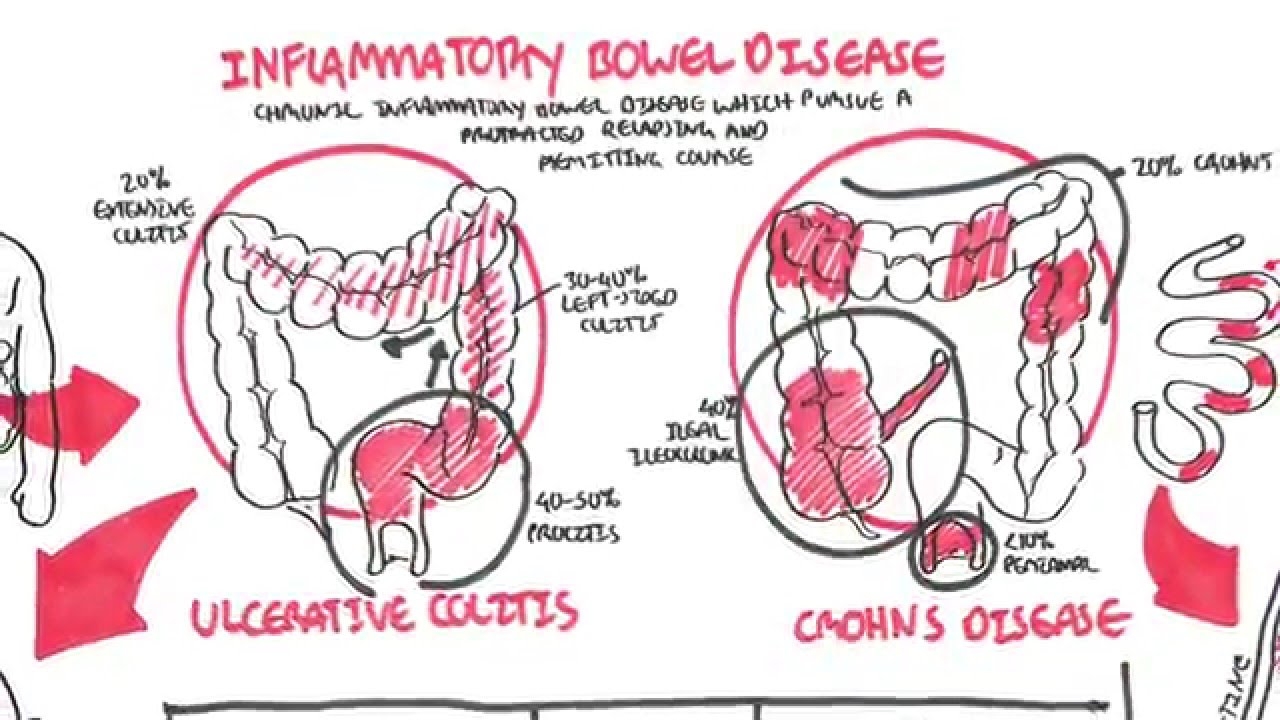 |
| Photo: YTB |
According to the Centers for Disease Control and PreventionTrusted Source, approximately 3 million U.S. adults had IBD as of 2015. IBD is a group of chronic diseases that cause inflammation in the digestive tract. There are many conditions that fall under the IBD umbrella, but the two main types are:
Crohn’s disease. This condition causes inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract. Any part of the digestive tract can be affected, but it most often develops in the ileum, which is the last part of the small intestine.
Ulcerative colitis. This causes chronic inflammation and ulcers in the innermost lining of the colon and rectum. People with ulcerative colitis have an increased risk for colon cancer.
Ischemic colitis
Ischemic colitis occurs when there’s reduced blood flow to a portion of the colon. This stops the cells in your digestive system from getting the oxygen they need.
It’s usually caused by narrowed or blocked arteries. People who are age 60 or older, have high cholesterol, or a clotting disorder have an increased risk for ischemic colitis.
Ischemic colitis can affect any part of your colon but you usually feel pain on the left side of the abdomen. It can occur gradually or suddenly
Symptoms on your right side may indicate blocked arteries to your small intestine that can quickly cause necrosis of intestinal tissue. This is life-threatening and requires urgent surgery to clear the blockage and remove the damaged portion.
Allergic colitis
Allergic colitis is more common in babies than adults, affecting between 2 and 3 per cent of infants. The inflammation is an allergic reaction to the proteins found in cow’s milk. A baby with an inflamed colon may be irritable, gassy, and have blood or mucus in their stools. Anaemia and malnutrition are also possible.
Eosinophilic colitis is similar to allergic colitis. When it occurs in an infant, it usually resolves by early childhood. In adolescents and adults, the condition is often chronic. The exact cause of eosinophilic colitis isn’t always known, though proteins in cow’s milk often makes symptoms worse. People with a personal or family history of allergies and asthma appear to have a higher risk.
Microscopic colitis
Microscopic colitis can only be seen through a microscope. It’s characterized by an increase in lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell, in the lining of the colon.
There are two types of microscopic colitis and though both show an increase in lymphocytes, each type affects the tissue of your colon in a different way.
Lymphocytic colitis has a higher number of lymphocytes, and the tissues and lining of the colon are of normal thickness.
In collagenous colitis, the layer of collagen under the lining of the colon is thicker than normal.
The cause of microscopic colitis is not known, but researchers believe it may be linked to:
autoimmune diseases
certain medications
infections
genetics
The symptoms of this type of colitis often come and go, sometimes disappearing without treatment.
Drug-induced colitis
Certain medications, mainly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have been linked to the inflamed colon in some people. Elderly people and people with a history of long-term use of NSAIDs appear to be at highest risk for developing this type of colitis.
Colon infection: Visible symptoms
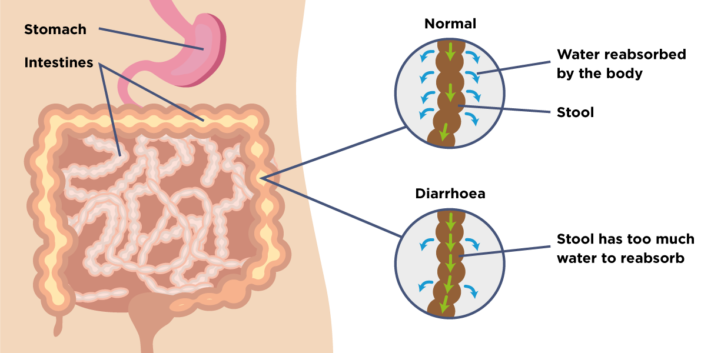 |
| Photo: Guts UK |
Even though there are different types of colitis with different causes, most of the symptoms are the same. Here is a list of some visible symptoms you may suffer from, which is collected from the India express.
- diarrhoea with or without blood
- abdominal pain and cramping
- fever
- the urgency to have a bowel movement
- nausea
- bloating
- weight loss
- fatigue
Colon infection: Possible treatment
As per NCBI, “The presentation of disease in the colon is generally in the form of distinct syndromes, and it is important for physicians to recognise the causative organisms because specific treatment is highly effective.”
The treatment depends on what is causing colitis. Many cases require a little more than symptomatic care, including clear fluids to rest the bowel and medications to control pain. Patients who have been acutely ill often need intravenous fluids among other interventions.
While colon infection caused by diarrhoea and colitis may potentially require antibiotics, depending on the cause, viral infections require fluids and time. Some bacterial infections, such as salmonella, do not need antibiotic therapy as the body is able to get rid of the infection on its own. Other bacterial infections, such as Clostridium difficile, require antibiotic treatment.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Medications are often used to control IBD. Anti-inflammatory medications may be used initially and medications that suppress the immune system can be added, if necessary. Surgery may be an option in severe cases, including removal of the colon and small intestine.
Ischemic colitis
Intravenous fluids are given to rest the bowel and prevent dehydration. If sufficient blood supply is not restored, surgery may be needed to remove parts of the bowel that lost blood supply.
Diarrhoea and abdominal pain
Initial treatment at home may include a clear fluid diet for 24 hours and rest. If symptoms resolve quickly, no further care is needed.
Don't forget the prevention
It can also occur spontaneously in some patients with decreased immunity. It can be prevented by ensuring consumption of hygienic food and clean water. Patients with decreased immunity should be in regular touch with their physicians, advised Dr Vij.
 What Is A Chemical Pregnancy - Symptoms, Causes And More What Is A Chemical Pregnancy - Symptoms, Causes And More What is a chemical pregnancy and what causes a chemical pregnancy? Here's what you need to know about a chemical pregnancy, a very early pregnancy ... |
 Canavan Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Canavan Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Canavan disease is a hereditary condition that prevents the brain’s nerve cells (neurons) from properly sending and receiving information. What Is Canavan Disease and How ... |
 What are Influenza A and B Causes, Symptoms and Prevention What are Influenza A and B Causes, Symptoms and Prevention Flu is a contagious respiratory illness that can infect the nose, throat, and sometimes the lungs. Its symptoms can be mild or severe. The "flu" ... |