2024 FED/FOMC Meeting Calendar: Full List of Dates, When to Cut Interest Rates
On December 18, the Fed will lower rates by 25 basis points.
90% of economists surveyed by Reuters predict that the U.S. Federal Reserve will lower interest rates by 25 basis points on December 18. The majority of them anticipate a pause in late January due to growing inflation risks.
It is anticipated that President-elect Donald Trump's proposed policies, which include tax cuts and import tariffs, will cause inflation. Shortly after his inauguration on January 20, Trump is anticipated to make rapid progress on his agenda.
Expectations that the Fed can afford to lower interest rates once more before reviewing government policy early next year were reinforced by news on Friday that the U.S. job market was still cooling but remained comparatively resilient.
 |
| 2024 FED Meeting Schedule |
7 FED's Remaining Meetings in 2024 - FOMC Meeting Schedule
The FOMC typically meets eight times a year to discuss monetary policy and make decisions about interest rates. Usually, each date is pencilled in as ‘tentative’, and then confirmed during the preceding meeting.
2022 may be the most memorable year for global investors since the 2008 financial crisis. The three main US stock indexes fell, with the S&P 500 alone losing 19.4%. Bitcoin, the world's largest virtual currency, has experienced significant price declines.
After that, 2023 will be remembered as a lost year for the United States banking industry. In a matter of weeks, three large regional banks, Silicon Valley Bank, Signature Bank, and First Republic Bank, were forced to close.
In general, the events listed above are related to the US Federal Reserve's (Fed) unprecedented monetary tightening campaign over the last 40 years, which aimed to control inflationary pressures.
Because of its enormous power, the Fed is always at the center of the global financial system. Of course, Fed meetings are events that investors worldwide are interested in. The market considers every Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) decision or official comment.
Every year, the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee - the Fed's policymaking agency) will hold eight regular meetings, each about a month and a half apart. Members of the FOMC will make decisions on interest rates and the money supply.
2024 FOMC Meeting Schedule
The FOMC normally convenes eight times a year to decide on interest rate policies and monetary policy. Every date is typically noted as "tentative" and subsequently confirmed at the previous meeting.
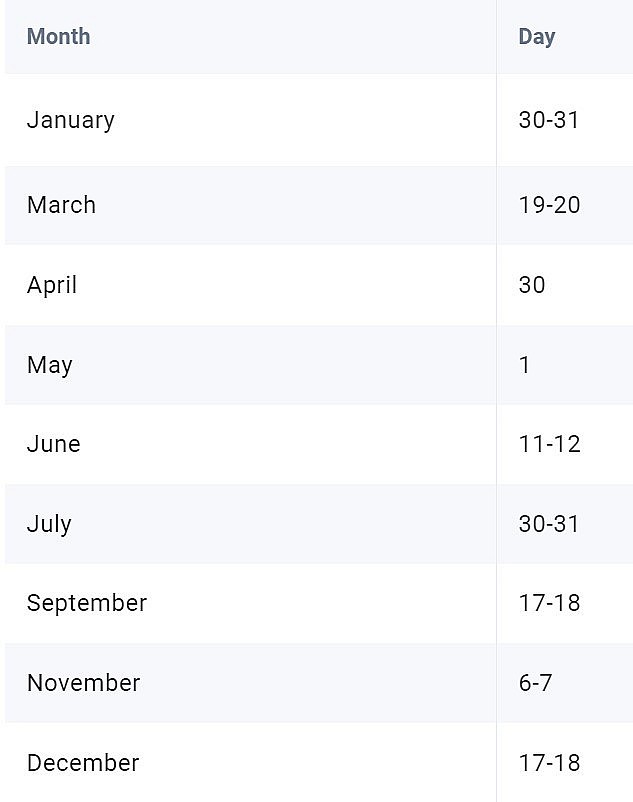 |
| 2024 FOMC Meeting Schedule |
The Fed's first meeting of 2024 was held on January 30-31, and there are seven more meetings scheduled for this year.
The next meeting is scheduled for March 19-20, with the final meeting on December 17-18.
Following the meeting, Fed Chairman - currently Mr. Jerome Powell - will hold a press conference to explain the policy decision and answer questions from the media. About three weeks later, the Fed will release meeting minutes that detail what officials discussed.
During meetings in March, June, September, and December, the Fed announced additional forecasts for economic growth, unemployment, inflation, and so on.
In some cases, the Fed may convene extraordinary meetings. For example, in March and May 2020, the Fed lowered interest rates to near-zero levels to help the economy during the pandemic. This is one of the reasons why inflation will rise in 2021.
When Will the Fed Lower Interest Rates?
 |
| FOMC Meeting |
To contain inflation, the Fed raised interest rates 11 times between March 2022 and July 2023. At the final meeting of 2023, the central bank indicated that interest rates would be cut at least three times in 2024, each by 25 basis points.
At its first meeting in 2024, the Fed kept its benchmark interest rate unchanged at 5.25 - 5.5%. This is the highest level in more than 22 years, as shown in the fourth chart in the article.
Chairman Jerome Powell told the press that the Fed is unlikely to cut interest rates in March because officials need to be confident in the rate at which inflation is cooling.
Many officials have also stated in recent weeks that they will focus on future data and expect to see more evidence that inflation is definitely returning to the 2% target.
The Fed's preferred measure of inflation, the core personal consumption expenditures price index (or core PCEPI), remains above 2%, at 2.8% in January. As a result, Fed officials prefer to proceed gradually and cautiously.
Not to mention that the economy is still growing steadily, with 2.5% expected in 2023, up from 1.9% in 2022. Notably, US GDP growth has exceeded 2% in six consecutive quarters, despite some fears of a recession.
The unemployment rate is approaching its historic low of 3.7%. Between March 2022 and January 2024, US businesses added an average of 297,000 jobs per month, exceeding pre-pandemic levels.
Last week, Boston Fed President Susan Collins and New York Fed President John Williams stated that the first interest rate cut could occur "sometime later in 2024". Meanwhile, Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic is preparing to lower interest rates this summer.
The majority of economists polled by Reuters expect the Fed to lower interest rates in June. The financial market has reached the same conclusion after gradually delaying forecasts from March to March. May has passed and we are now in June.
Who Controls the Decisions of the Fed?
 |
| Fed Chairman Jerome Powell |
2024 FOMC Members
Jerome H. Powell, Board of Governors, Chair
John C. Williams, New York, Vice Chair
Thomas I. Barkin, Richmond
Michael S. Barr, Board of Governors
Raphael W. Bostic, Atlanta
Michelle W. Bowman, Board of Governors
Lisa D. Cook, Board of Governors
Mary C. Daly, San Francisco
Philip N. Jefferson, Board of Governors
Adriana D. Kugler, Board of Governors
Loretta J. Mester, Cleveland
Christopher J. Waller, Board of Governors
Alternate Members
Susan M. Collins, Boston
Austan D. Goolsbee, Chicago
Kathleen O'Neill, First Vice President, St. Louis
Jeffrey R. Schmid, Kansas City
Sushmita Shukla, First Vice President, New York
As previously stated, the FOMC is the agency in charge of the Fed's monetary policy decisions. This committee has 12 members, including 7 members of the Board of Governors, the President of the New York Federal Reserve Branch, and four of the remaining 11 branch presidents.
The remaining four will serve one-year terms on a rotating basis. Four regional banking groups, each with one representative, select the rotating seats: Boston, Philadelphia, and Richmond; Cleveland and Chicago; Atlanta, St. Louis, and Dallas; and Minneapolis, Kansas City, and San Francisco.
Non-FOMC branch Fed presidents cannot vote, but they can attend meetings, participate in discussions, and provide feedback on the economy and policy options.
The New York Fed branch is the sole agency in charge of implementing FOMC-issued monetary policy and serves as the Fed system's representative in the currency market.
The New York Fed branch is also the only bank for the United States Treasury, holding a large amount of Treasury deposits as well as the world's largest gold treasury. Because of the important roles mentioned above, the President of the New York Fed branch is always the FOMC's Vice Chairman.
What is the Federal Funds Rate?The Fed requires commercial banks to hold 10% of their deposits in central bank accounts. Banks will lend to each other to meet the required reserve ratio. The FOMC will determine the interest rate that banks earn when lending money to other banks - this is the federal funds rate that we frequently discuss. Depending on the situation, banks will adjust the interest rates they charge their customers. The federal funds rate serves as the benchmark for interest rates on all other loans, including credit card interest rates, home mortgages, and car loans. When the FOMC raises the target range of interest rates, borrowing costs for US consumers and businesses will increase. For example, credit card interest rates rose from 16.3% in March 2022 to nearly 21% in January 2024. However, the committee's interest rate hike will slow the economy and lower inflation. This is exactly what we have witnessed for nearly two years. On the contrary, when the FOMC lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes easier while also stimulating inflation to rise again. This is one of the reasons Fed officials are so cautious. |
 When Do the NYSE, Dow Jones, and Nasdaq Stock Markets Open and Close in the United States? When Do the NYSE, Dow Jones, and Nasdaq Stock Markets Open and Close in the United States? What is the opening and closing time of the US stock market (NYSE, Dow Jones, Nasdaq, etc.)? View the hours of operation, holidays, break, and ... |
 Can Foreigners Buy or Invest in the US Stock Exchange? Can Foreigners Buy or Invest in the US Stock Exchange? How do non-US residents buy (invest in) stocks in the United States? Continue reading to learn about the guidelines and tips for foreigners investing in ... |
 Top 3 Zodiac Signs Who Are Geniuses in Stock Investment Top 3 Zodiac Signs Who Are Geniuses in Stock Investment The following three zodiac signs have an excellent chance of becoming stock market geniuses because they have a strong desire to become wealthy quickly, a ... |
 Full List of U.S 2024 Stock Market Holidays: Are NYSE and Nasdaq Open or Closed? Full List of U.S 2024 Stock Market Holidays: Are NYSE and Nasdaq Open or Closed? The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq, the two main U.S. stock exchanges, are closed on non-weekend business days known as stock market ... |























