Facts About the Mercury - The First Crewed Spaceflights In The US
 What Is The First Spaceship In The World? What Is The First Spaceship In The World? |
 What is the Oldest Spacecraft of NASA - Voyager 1 What is the Oldest Spacecraft of NASA - Voyager 1 |
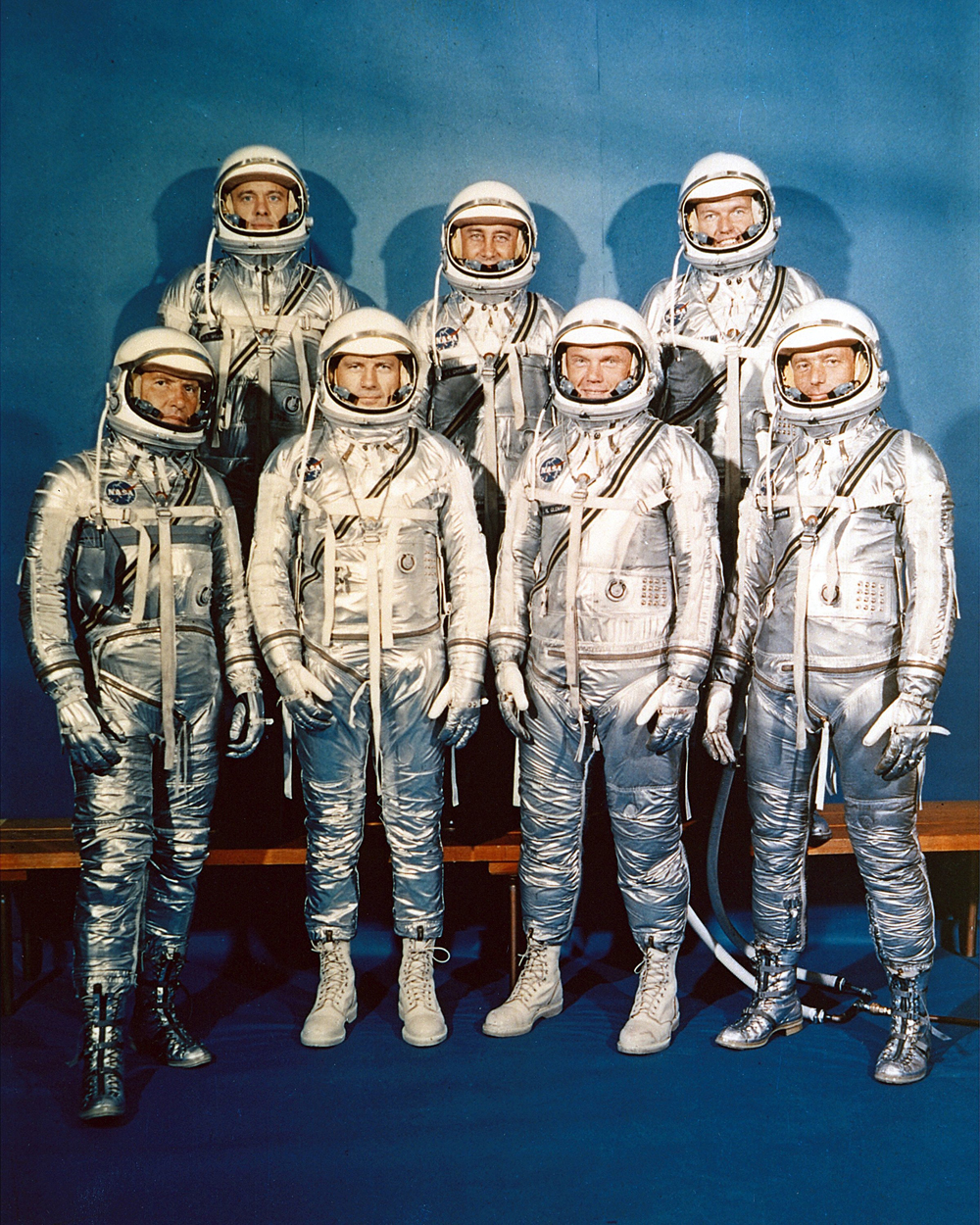 |
| NASA announced the seven Project Mercury Astronauts on April 9, 1959, only six months later. They are: (front, l to r) Walter H. Schirra, Jr., Donald K. Slayton, John H. Glenn, Jr., and Scott Carpenter; (back, l to r) Alan B. Shepard, Jr., Virgil I. Gus Grissom, and L. Gordon Cooper. (Image credit: NASA) |
What was the Mercury Program?
The Cold War, a struggle between the Soviet Union and the United States for dominance and prestige in the world, broke out in the late 1950s, and the two countries soon started battling it out in space. Both countries started initiatives to launch people into space. That initiative was known as Project Mercury in the US.
NASA's first attempt at sending people into space was with Mercury. The program's two objectives were to send a man into space before the Soviet Union and to test whether humans could function effectively in space.
Mercury failed to achieve its second goal, but it did lay the technological groundwork for more difficult missions in the Gemini and Apollo programs. Additionally, it made the original seven astronauts famous.
History of Project Mercury
 |
| Photo: NASA |
In order to capitalize on the high-altitude flights that test pilots were already performing, there were some calls to establish a military astronaut space program.
At first, President Dwight Eisenhower concurred, but after consulting with some advisers, he decided to support the idea of a civilian space agency called NASA that would launch the first astronauts into space. The former National Advisory Committee on Astronautics (NACA) and a number of other organizations came together to form NASA in 1958.
After reviewing 500 records, NASA determined that the first 110 men were qualified. Three groups of these men were arbitrarily and equally divided, and each group was given a private briefing informing them of the chance to travel into space. The third group of military personnel, however, was never needed because so many men from the first two groups agreed to take part in the astronaut program if chosen.
The semi-finalists were then subjected to rigorous psychological and physical testing in order to narrow the field. On April 9, 1959, the seven astronaut candidates were revealed to the world. They overnight rose to international fame, along with their families.
A $500,000 (or roughly $4.3 million today) exclusive contract with Life magazine added to their notoriety. The astronauts were portrayed in the media as American heroes battling communism in space.
What Spacecraft Was Used for Project Mercury?
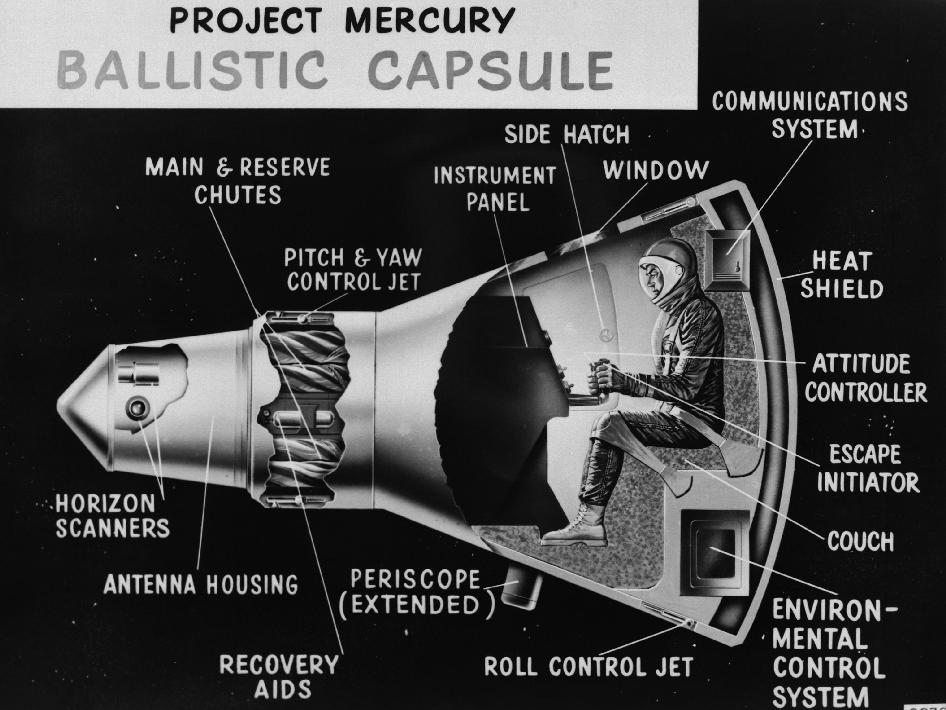
This project inspired the design of the Mercury spacecraft. One astronaut could fit inside the constrained capsule. Throughout the flight, the astronaut remained in his seat.
For Project Mercury, two different kinds of rockets were employed. Redstone rockets were used on the first two of the six flights that included an astronaut. An Atlas rocket was used for the four manned missions that orbited the Earth. Both of these rockets were initially intended to be military-grade missiles for the US.
The project was given the name Mercury in honor of a swift Roman deity. Each astronaut gave their craft a name. The name of Alan Shepard's Mercury capsule contains a 7. This was as a result of it being the seventh one produced. There was also a 7 among the other astronauts. The seven astronauts who were selected for the project were honored by this.
Who is Alan Shepard - the first American in Space
Navy Commander Alan Bartlett Shepard Jr., the first American astronaut to venture into space, is sent into orbit on May 5, 1961 aboard the Freedom 7 spacecraft. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) achieved a significant win with the suborbital flight, which lasted 15 minutes and rose 116 miles into the atmosphere.
In order to keep U.S. space efforts current with recent Soviet accomplishments, like the 1957 launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, NASA was founded in 1958. The two superpowers competed to be the first nation to launch a man into space and bring him back to Earth in the late 1950s and early 1960s. When cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin was launched into space, placed in orbit around the planet, and safely returned to Earth on April 12, 1961, the Soviet space program emerged victorious. Shepard's suborbital flight a month later restored confidence in the American space program.
Up until the late 1960s and the success of the Apollo lunar program, NASA remained in close pursuit of the Soviet Union. With Apollo 11, a three-stage spacecraft that carried American astronauts to the moon's surface and brought them back to Earth in July 1969, the Americans made a significant advancement. As part of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, Alan Shepard, the first American in space, became the fifth astronaut to walk on the moon on February 5, 1971.
 Where Are the Apollo 14' 'Moon Trees' on Earth Today? Where Are the Apollo 14' 'Moon Trees' on Earth Today? |
Reaching Orbit
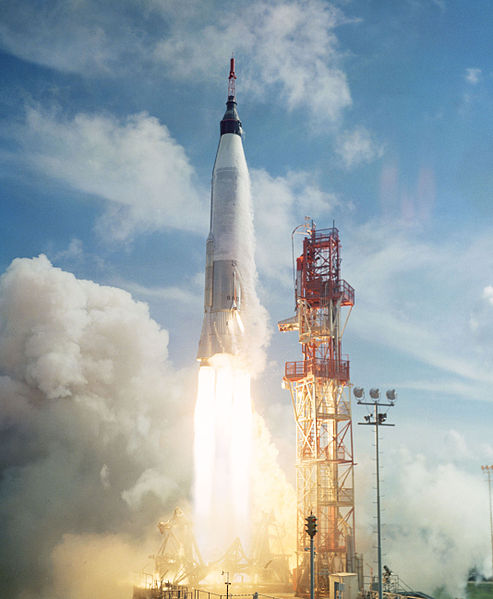 |
| Photo: White Eagle Aerospace |
Despite being technological achievements for NASA and its contractors, the Mercury missions were only able to travel between Florida and the Atlantic Ocean in arcs of 15 minutes. While this was going on, the Soviet Union had already completed orbital missions that made multiple Earth orbits, including Gagarin's historic first human spaceflight. Along with other mission modifications, a more potent rocket would be needed to send the Americans into orbit.
As a result, John Glenn's Friendship 7 spacecraft orbited the Earth three times using a more potent Mercury-Atlas rocket combination. Glenn's mission on February 20, 1962, was an additional test of the spacecraft and a human's response to several hours in space. He also noticed strange "fireflies" that seemed to follow his spacecraft during the course of his five-hour mission; this phenomenon was later attributed to ice crystals erupting from the hull.
Controllers on the ground noticed a sign that his landing bag had been deployed too soon. They held off on telling Glenn before telling him to keep his retrorocket package fastened to his spacecraft as a safety precaution close to re-entry. Glenn was disappointed that he had not been informed as soon as the issue arose because it turned out that the indication was false. After his flight, Glenn became a household name. He wanted to go back into space, but according to the New York Times, John F. Kennedy and others thought he was too valuable to risk. Glenn (who later rose to become the senator for Ohio) made his first space flight back in 1998 at the age of 77 on board STS-95.
On May 24, 1962, the Aurora 7 Mercury mission encountered splashdown issues once more. After about five hours in space, pilot Scott Carpenter made a 250 miles (400 km) off-course landing. Some representatives of the space program, notably flight director Chris Kraft, attributed the issue to Carpenter's lack of focus during the mission.
Carpenter explained it was a combination of technical issues (some sensors were acting up), excessive fuel use, and Glenn's firefly mystery in two oral interviews with NASA.
How Did NASA Make Sure Mercury Was Safe?NASA carried out several test flights before Project Mercury's astronauts took to the skies. There were no passengers on board these launches. Test flights assisted NASA in identifying and resolving issues. A Mercury capsule that was being launched on the first Atlas rocket exploded. Only about four inches were lifted off the ground during the first Mercury-Redstone launch. NASA gained knowledge for repairing and securing the rockets from these flights. Three more "astronauts" contributed to making Mercury a safer planet. Sam, a rhesus monkey, and Ham and Enos, two chimpanzees, flew in Mercury capsules. Sam and Ham flew in the lower atmosphere. On a "Little Joe" rocket, Sam flew. Ham was launched by a Redstone rocket. An Atlas rocket carried Enos into space. He completed two orbits of the planet. NASA knew it was safe for astronauts because all three primates returned home without incident. Why Was Project Mercury Important?Project Mercury taught NASA a lot. The agency gained knowledge on how to launch astronauts into Earth orbit. It gained knowledge about how people could function in space. It gained knowledge of how to pilot an orbiting spacecraft. These were very significant lessons. In subsequent space programs, NASA used them. Mercury was followed by the Gemini program. There was space on the Gemini spacecraft for two astronauts. With Gemini, NASA learned even more. Mercury and Gemini worked together to get NASA ready for the Apollo program. NASA first set foot on the moon during the Apollo mission. |
 What Are Spaceships That Have Carried People Into Orbit? What Are Spaceships That Have Carried People Into Orbit? Since 1961, there have been some different spaceships that have carried humans into Earth orbit and beyond. Here's a look back at the history of ... |
 How NASA's Perseverance rover makes history land on Mars - Video How NASA's Perseverance rover makes history land on Mars - Video NASA's Perseverance rover has confirmed to touch down on Mars to conduct its ambitious mission of finding whether life has been existed on the red ... |
 Can Planets Collide In Space? Can Planets Collide In Space? People on Earth often ask: Can planets collide with one another? Short answer: Yes, but very rarely! |