What Is Cloud Computing And How Does It Work?
 |
| What Is Cloud Computing? |
Cloud computing is estimated to reach $206.2 billion in market worth in 2019. Cloud computing is changing our lives in many ways - from social media to streaming services, shopping, wearables, or storing files. Cloud computing whether we like it or not is here to stay in one form or another. Now, we together explore the information about cloud computing.
What is the history of cloud computing?
Cloud computing as a term has been around since the early 2000s, but the concept of computing-as-a-service has been around for much, much longer -- as far back as the 1960s, when computer bureaus would allow companies to rent time on a mainframe, rather than have to buy one themselves.
These 'time-sharing' services were largely overtaken by the rise of the PC which made owning a computer much more affordable and then in turn by the rise of corporate data centers where companies would store vast amounts of data.
But the concept of renting access to computing power has resurfaced again and again -- in the application service providers, utility computing, and grid computing of the late 1990s and early 2000s. This was followed by cloud computing, which really took hold with the emergence of software as a service and hyper-scale cloud computing providers such as Amazon Web Services.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing can be described as a virtual pool of shared resources offering compute, storage, database, and network services that can be rapidly deployed at scale.
There are two huge factors that have contributed to the success of cloud computing: 1) technological advancements, such as virtualization of compute instances and abundant high-speed internet access, and 2) widespread investment in constantly building and updating infrastructure, which results in economies of scale. Because of these factors, cloud computing can take all the ingredients that make up a traditional data center and makes all these resources available to consumers on an as-needed basis.
But what are the types of cloud computing and why is it becoming the new standard? To understand what makes cloud computing successful, you’ll need to clearly understand the ways in which companies must manage their IT needs and develop products, especially software.
Why is it called cloud computing?
A fundamental concept behind cloud computing is that the location of the service, and many of the details such as the hardware or operating system on which it is running, are largely irrelevant to the user. It's with this in mind that the metaphor of the cloud was borrowed from old telecoms network schematics, in which the public telephone network (and later the internet) was often represented as a cloud to denote that the just didn't matter -- it was just a cloud of stuff.
This is an over-simplification of course; for many customers location of their services and data remains a key issue.
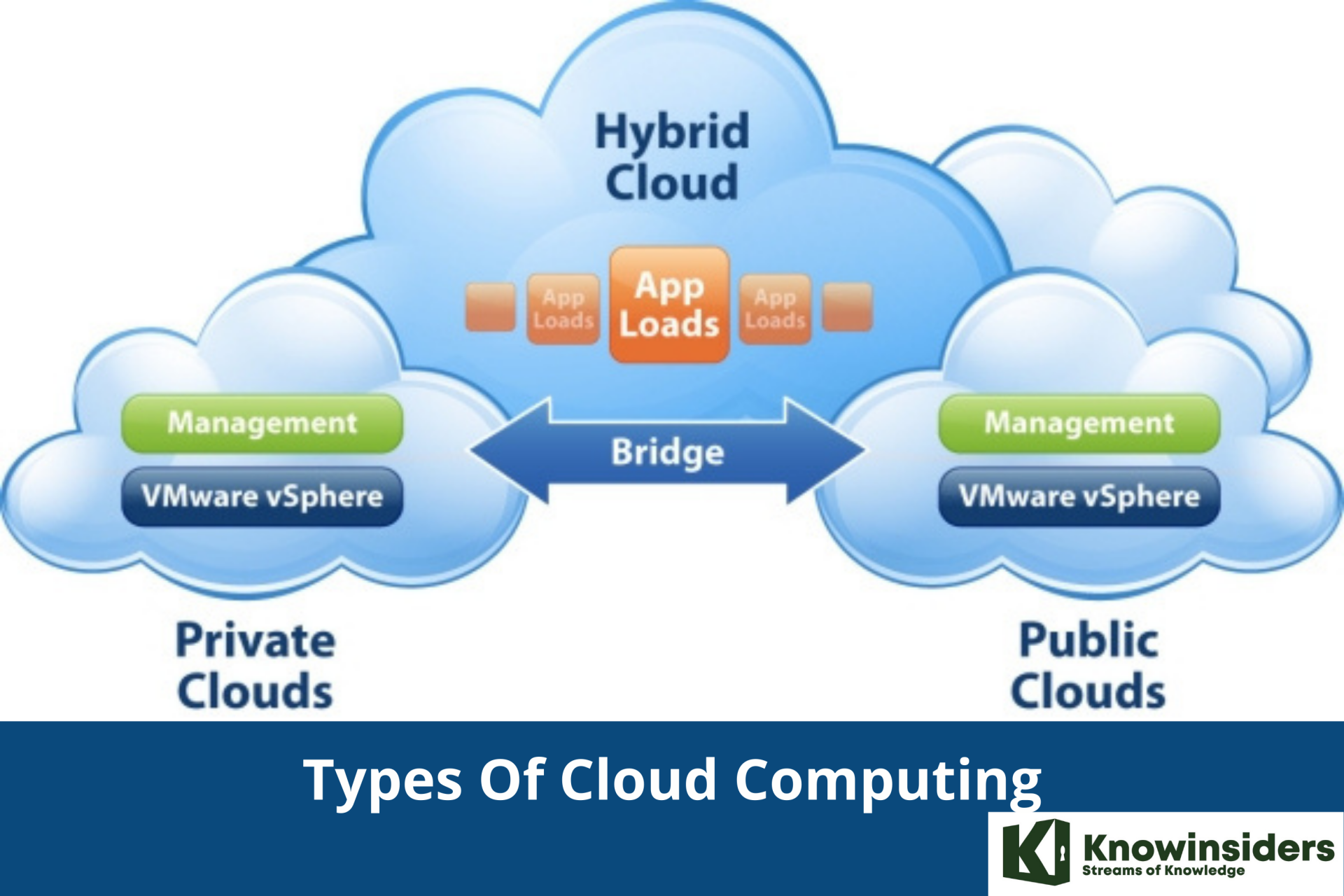
What Are The Different Types Of Cloud Computing?
Not all clouds are the same and not one type of cloud computing is right for everyone. Several different models, types, and services have evolved to help offer the right solution for your needs.
First, you need to determine the type of cloud deployment, or cloud computing architecture, that your cloud services will be implemented on. There are three different ways to deploy cloud services: on a public cloud, private cloud, or hybrid cloud.
Public cloud
Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers, which deliver their computing resources, like servers and storage, over the Internet. Microsoft Azure is an example of a public cloud. With a public cloud, all hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure is owned and managed by the cloud provider. You access these services and manage your account using a web browser. Learn more about the public cloud.
Private cloud
A private cloud refers to cloud computing resources used exclusively by a single business or organization. A private cloud can be physically located on the company’s on-site data center. Some companies also pay third-party service providers to host their private cloud. A private cloud is one in which the services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network. Learn more about the private cloud.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds, bound together by technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. By allowing data and applications to move between private and public clouds, a hybrid cloud gives your business greater flexibility, more deployment options, and helps optimize your existing infrastructure, security, and compliance. Learn more about the hybrid cloud.
What Are The Different Types of Cloud Services?
 |
| Photo: KnowInsiders |
Most cloud computing services fall into four broad categories: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), serverless, and software as a service (SaaS). These are sometimes called the cloud computing "stack" because they build on top of one another. Knowing what they are and how they’re different makes it easier to accomplish your business goals.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
The most basic category of cloud computing services. With IaaS, you rent IT infrastructure—servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, operating systems—from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
Platform as a service refers to cloud computing services that supply an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. PaaS is designed to make it easier for developers to quickly create web or mobile apps, without worrying about setting up or managing the underlying infrastructure of servers, storage, network, and databases needed for development.
Serverless computing
Overlapping with PaaS, serverless computing focuses on building app functionality without spending time continually managing the servers and infrastructure required to do so. The cloud provider handles the setup, capacity planning, and server management for you. Serverless architectures are highly scalable and event-driven, only using resources when a specific function or trigger occurs.
Software as a service (SaaS)
Software as a service is a method for delivering software applications over the Internet, on-demand, and typically on a subscription basis. With SaaS, cloud providers host and manage the software application and underlying infrastructure, and handle any maintenance, like software upgrades and security patching. Users connect to the application over the Internet, usually with a web browser on their phone, tablet, or PC.
What cloud computing services are available?Cloud computing services cover a vast range of options now, from the basics of storage, networking, and processing power through to natural language processing and artificial intelligence as well as standard office applications. Pretty much any service that doesn't require you to be physically close to the computer hardware that you are using can now be delivered via the cloud. |
What is cloud security?
 |
| Photo: KnowInsiders |
Traditionally, security concerns have been the primary obstacle for organizations considering cloud services, particularly public cloud services. In response to demand, however, the security offered by cloud service providers is steadily outstripping on-premises security solutions.
According to security software provider McAfee, today, 52% of companies experience better security in the cloud than on-premises (link resides outside IBM). And Gartner has predicted that by this year (2020), infrastructure as a service (IaaS) cloud workloads will experience 60% fewer security incidents than those in traditional data centers (PDF, 2.3 MB) (link resides outside IBM).
Nevertheless, maintaining cloud security demands different procedures and employee skillsets than in legacy IT environments. Some cloud security best practices include the following:
- Shared responsibility for security: Generally, the cloud provider is responsible for securing cloud infrastructure and the customer is responsible for protecting its data within the cloud—but it's also important to clearly define data ownership between private and public third parties.
- Data encryption: Data should be encrypted while at rest, in transit, and in use. Customers need to maintain full control over security keys and hardware security modules.
- User identity and access management: Customer and IT teams need a full understanding of and visibility into network, device, application, and data access.
- Collaborative management: Proper communication and clear, understandable processes between IT, operations, and security teams will ensure seamless cloud integrations that are secure and sustainable.
- Security and compliance monitoring: This begins with understanding all regulatory compliance standards applicable to your industry and setting up active monitoring of all connected systems and cloud-based services to maintain visibility of all data exchanges between public, private, and hybrid cloud environments.
How does cloud computing work?
Assume that you are an executive at a very big corporation. Your particular responsibilities include making sure that all of your employees have the right hardware and software they need to do their jobs. To buy computers for everyone is not enough. You also have to purchase software as well as software licenses and then provide this software to your employees as they require. Whenever you hire a new employee, you need to buy more software or make sure your current software license allows another user. It is so stressful that you have to spend lots of money.
But, there may be an alternative for executives like you. So, instead of installing a suite of software for each computer, you just need to load one application. That application will allow the employees to log in to a Web-based service that hosts all the programs for the user that is required for his/her job. Remote servers are owned by another company and will run everything from e-mail to word processing to complex data analysis programs. It is called cloud computing, and it could change the entire computer industry.
In a cloud computing system, there is a significant workload shift. Local computers have no longer to do all the heavy lifting when it comes to running applications. But cloud computing can handle that much heavy load easily and automatically. Hardware and software demands on the user's side decrease. The only thing the user's computer requires to be able to run is the cloud computing interface software of the system, which can be as simple as a Web browser and the cloud's network takes care of the rest.
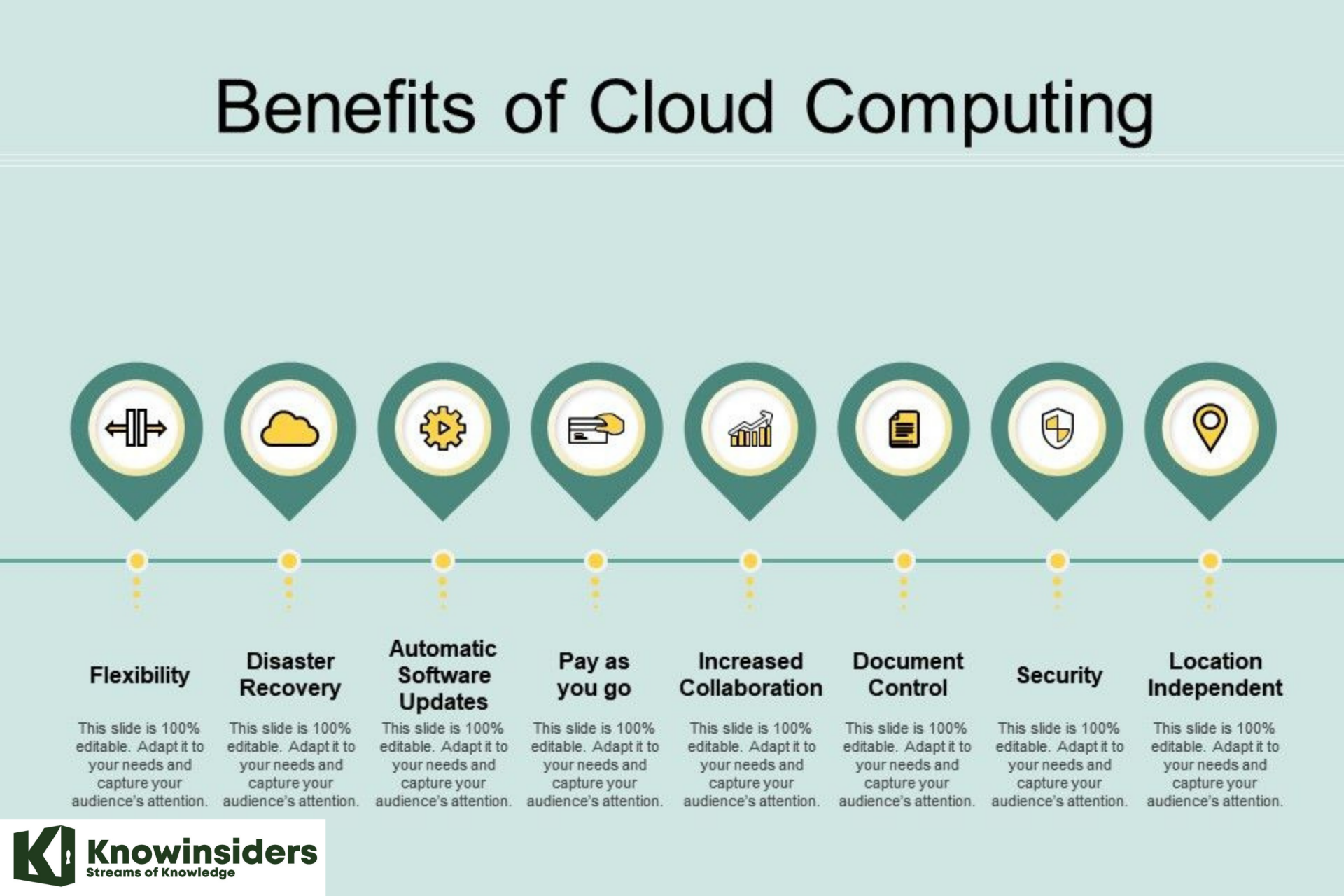
What are the benefits of cloud computing?
 |
| Photo: KnowInsiders |
Cloud computing is a big shift from the traditional way businesses think about IT resources. Here are seven common reasons organizations are turning to cloud computing services:
Cost
Cloud computing eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software and setting up and running on-site datacenters—the racks of servers, the round-the-clock electricity for power and cooling, and the IT experts for managing the infrastructure. It adds up fast.
Speed
Most cloud computing services are provided self-service and on-demand, so even vast amounts of computing resources can be provisioned in minutes, typically with just a few mouse clicks, giving businesses a lot of flexibility and taking the pressure off capacity planning.
Global scale
The benefits of cloud computing services include the ability to scale elastically. In cloud speak, that means delivering the right amount of IT resources—for example, more or less computing power, storage, bandwidth—right when they’re needed, and from the right geographic location.
Productivity
On-site datacenters typically require a lot of “racking and stacking”—hardware setup, software patching, and other time-consuming IT management chores. Cloud computing removes the need for many of these tasks, so IT teams can spend time on achieving more important business goals.
Performance
The biggest cloud computing services run on a worldwide network of secure data centers, which are regularly upgraded to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing hardware. This offers several benefits over a single corporate data center, including reduced network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
Reliability
Cloud computing makes data backup, disaster recovery, and business continuity easier and less expensive because data can be mirrored at multiple redundant sites on the cloud provider’s network.
Security
Many cloud providers offer a broad set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen your security posture overall, helping protect your data, apps, and infrastructure from potential threats.
What are the advantages and disadvantages?
Cloud computing is not necessarily cheaper than other forms of computing, just as renting is not always cheaper than buying in the long term. If an application has a regular and predictable requirement for computing services it may be more economical to provide that service in-house.
Some companies may be reluctant to host sensitive data in a service that is also used by rivals. Moving to a SaaS application may also mean you are using the same applications as a rival, which may make it hard to create any competitive advantage if that application is core to your business.
While it may be easy to start using a new cloud application, migrating existing data or apps to the cloud may be much more complicated and expensive. And it seems there is now something of a shortage in cloud skills with staff with DevOps and multi-cloud monitoring and management knowledge in, particularly short supply.
In one recent report, a significant proportion of experienced cloud users said that they thought upfront migration costs ultimately outweigh the long-term savings created by IaaS.
And of course, you can only access your applications if you have an internet connection.
What is the future of cloud computing?
Cloud computing is still at a relatively early stage of adoption, despite its long history. Many companies are still considering which apps to move and when. However, usage is only likely to climb as organizations get more comfortable with the idea of their data being somewhere other than a server in the basement. We're still relatively early into cloud adoption -- some estimates suggest that only 10% of the workloads that could be moved have actually been transferred across. Those are the easy ones where the economics are hard for CIOs to argue with.
For the rest of the enterprise computing portfolio, the economics of moving to the cloud may be less clear-cut. As a result cloud computing vendors are increasingly pushing cloud computing as an agent of digital transformation instead of focusing simply on cost. Moving to the cloud can help companies rethink business processes and accelerate business change, goes the argument, by helping to break down data and organizational silos. Some companies that need to boost momentum around their digital transformation programs may find this argument appealing; others may find enthusiasm for the cloud waning as the costs of making the switch add up.
What is Computer Science?Computer Science is the study of computers and computational systems. Unlike electrical and computer engineers, computer scientists deal mostly with software and software systems; this includes their theory, design, development, and application. Principal areas of study within Computer Science include artificial intelligence, computer systems, and networks, security, database systems, human-computer interaction, vision and graphics, numerical analysis, programming languages, software engineering, bioinformatics, and theory of computing. Although knowing how to program is essential to the study of computer science, it is only one element of the field. Computer scientists design and analyze algorithms to solve programs and study the performance of computer hardware and software. The problems that computer scientists encounter range from the abstract-- determining what problems can be solved with computers and the complexity of the algorithms that solve them – to the tangible – designing applications that perform well on handheld devices, that are easy to use, and that uphold security measures. Graduates of the University of Maryland’s Computer Science Department are lifetime learners; they are able to adapt quickly to this challenging field. |
 What Is A Chemical Pregnancy - Symptoms, Causes And More What Is A Chemical Pregnancy - Symptoms, Causes And More What is a chemical pregnancy and what causes a chemical pregnancy? Here's what you need to know about a chemical pregnancy, a very early pregnancy ... |
 What is Business Insurance: Definition, Types and Cost What is Business Insurance: Definition, Types and Cost Business Insurance is one of the most important parts if you want to start a business, which will help protect your businesses against losses. |
 What Is A Money Market Account? What Is A Money Market Account? When it comes to money and savings, it is important to understand how things work, if you choose to open a Money Market Account. |