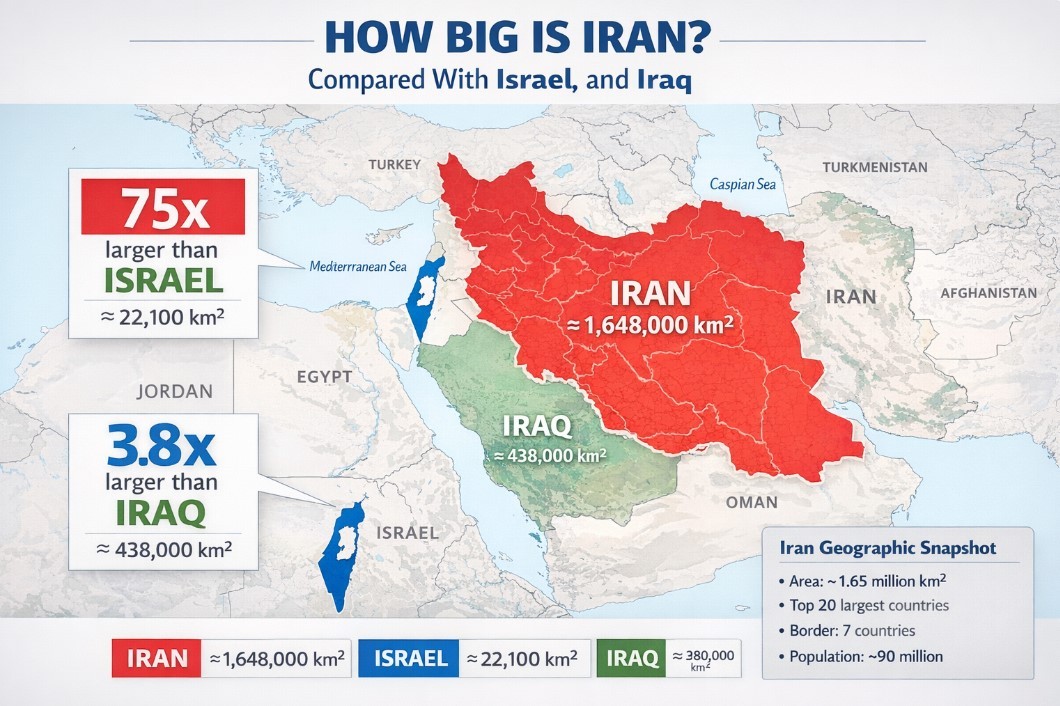
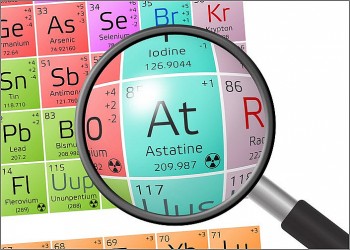
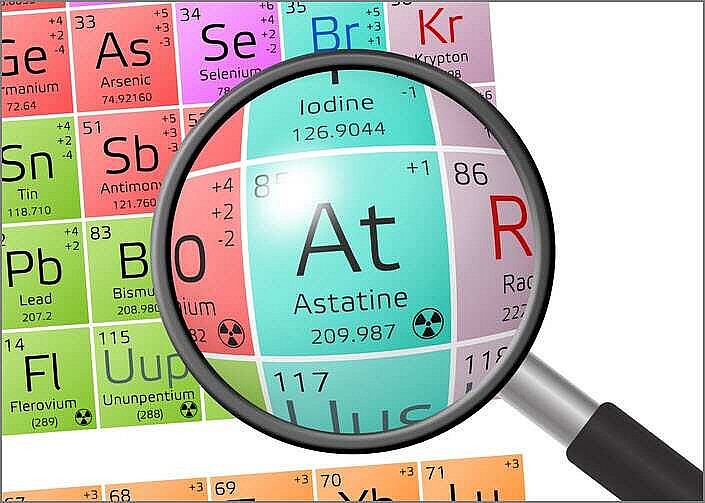
What Is Astatine - the Rarest Natural Element On Earth?
 Top 11 Rarest Elements On Earth Today Top 11 Rarest Elements On Earth Today Do you know all rare elements on earth? What is the rarest type? Read on to explore the interesting facts about the rarest elements on ... |
 |
| Photo earth |
What is Astatine?
Astatine is a chemical element that is radioactive. Astatine has the symbol At and the atomic number 85. The heaviest halogen discovered is at. It was created in 1940 by Dale R. Corson, Kenneth Ross Mackenzie, and Emilio Segrè. Although At is produced in nature by radioactive decay, it is typically found in minute amounts due to its short half-life (the time it takes for one half of the atoms of a given radioactive substance to decay or disintegrate). Natural minerals contain trace amounts as well.
Astatine - Key Facts• 85 is the atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus). • On the periodic table of elements, the atomic symbol is: At • Atomic weight (average atomic mass): 210 • Density: about 4 ounces per cubic inch (approximately 7 grams per cubic cm) • At room temperature, the phase is solid. • 576 degrees Fahrenheit is the melting point (302 degrees Celsius) • The boiling point is unknown. • There are at least 30 radioactive isotopes (atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons). • The most common isotopes are: At-210 (zero percent natural abundance), Am-211 (negligible percent of natural abundance) |
How Rare is Astatine?
Astatine is currently the rarest element on Earth (only one ounce is found in the entire planet's crust).
History of Astatine
 |
According to Peter van der Krogt, Dmitri Mendeleyev, a Russian chemist who organized the elements into a periodic table that is still in use today, predicted the features of an unknown element that would fill a gap in the periodic table for element No. 85. A historian from the Netherlands. Because of its direct subdivision of iodine into a group of halogen elements, Mendeleyev named this element eka-iodine.
| Most of what we know about this element comes from theoretical research rather than practical experiments. For example, researchers think that astatine looks like a black solid because it is located in the halogen column of the periodic table. The heavier the elements in the halogen column, the darker the color. Colorless fluorine, yellow-green chlorine, red-brown bromine, dark gray-violet iodine. Therefore, logically, the next element, astatine, should be darker. |
What is Astatine’s application?
 |
In spite of being extremely rare, astatine may have some important practical applications.
When the element decays, it emits alpha particles, radioactive particles that form from the combination of two protons and two neutrons. For several reasons, alpha particles target cancer cells very effectively.
According to Mehran Makvandi, a radiologist at the University of Pennsylvania's medical school, astatine emits fewer alpha particles than other isotopes like actinium-225. The element also emits only alpha particles, which are the least toxic type of radiation.
| If scientists can attach astatine isotope to a molecule that looks for cancer cells, they could create a cancer therapy that doesn't harm surrounding tissue. Since astatine is so rare and unstable, it's not an easy task. |
Interesting Facts about Astatine
1.It is the heaviest known halogen with properties similar to other halogen elements. They lack metal properties, have low boiling and melting points, are diatomaceous earth, are poor electrical and heat conductors, and are brittle in solid form.
2.Astatine is highly radioactive, but because it is rare and short-lived, it poses no threat to the environment or human health.
3. Where Can I Find Astatine?
The element's total amount in the earth's crust is estimated to be less than 30 grams, formed by the decay of uranium and thorium mineral deposits.
4. To date, only 0.05 micrograms of At have been produced.
The health consequences of astatineAt any given time, the total amount of astatine in the earth's crust is less than 30 grams, and only a few micrograms have ever been artificially produced. Because of this, as well as its short lifetime, there is no reason to consider the effects of astatine on human health. Astatine is studied in a few nuclear research laboratories because of its high radioactivity, which necessitates special handling techniques and precautions. Astatine is a halogen that, like iodine, may accumulate in the thyroid. From a chemical standpoint, one can speculate that its toxicity would be similar to that of iodine. |
| The effects of astatine on the environment Astatine is not found in significant quantities in the biosphere and thus does not pose a risk. |
 Top 11 Rarest Elements On Earth Today Top 11 Rarest Elements On Earth Today Do you know all rare elements on earth? What is the rarest type? Read on to explore the interesting facts about the rarest elements on ... |
 10 Rarest Flowers In The World 10 Rarest Flowers In The World There are thousands of flowers in the world, yet some flowers are so rare, bloom in specific seasons, or even after decades. Check out right ... |
 Top 20 Weirdest and Rarest Animals In The World - In Danger of Extinction Top 20 Weirdest and Rarest Animals In The World - In Danger of Extinction World of animals have lots of weird things. You might have never heard of animals in the list below as they are weirdest and rarest ... |