Facts About F-14 Tomcat: Top Gun Movie Legend And Iran’s Best Fighter Jet
 |
| Facts About F-14 Tomcat: Top Gun Movie Legend And Iran’s Best Fighter Jet |
One of the most famous and recognizable American fighter jets has got to be the F-14 Tomcat. Featured in the classic movie Top Gun and serving 36 years in the Navy protecting the United States, this powerhouse of a plane is still missed by airpower affections and the pilots and Radar Intercept Officers (RIO) - the flight officers in the aft seat of the jet - who flew it.
As you can already imagine, the Grumman F-14 Tomcat is a daredevil in the world of naval aviation. Let’s check out the history and the reasons why that is so:
What is the F-14 Tomcat?
The F-14 Tomcat is a supersonic, twin-engine, variable-sweep wing, two-place fighter designed to attack and destroy enemy aircraft at night and in all weather conditions. The F-14 can track up to 24 targets simultaneously with its advanced weapons control system and attack six with Phoenix AIM-54A missiles while continuing to scan the airspace. The Tomcat is the only U.S. plane capable of carrying the long-range Phoenix missile, which can fire at targets from distances of about 80 miles. Armament also includes a mix of other air intercept missiles, rockets, and bombs.
Manufactured by Grumman Aircraft Corporation, the F-14 employs variable geometry wings to optimize aircraft performance throughout the flight envelope. The F-14 swing-wing could be manually controlled by the pilot or shifted automatically according to the plane’s speed. It moved forward to allow the plane to land on tiny aircraft carrier decks at relatively low speeds and backward as the plane dashed out to intercept Soviet bombers. The multiple tasks of navigation, target acquisition, electronic countermeasures (ECM), and weapons firing are divided between the pilot and the radar intercept officer (RIO).
History of F-14 Tomcat
The F-14 was developed to replace the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, the fighter in service with the U.S. Navy. This resulted from the experience accumulated by Grumman in developing the naval version of the F-111A of USAF the F-111B which was canceled because it has proved somewhat maneuverable, heavy, and, in general, poorly designed for operations based on an aircraft carrier, Which led to the cancellation of the project 1968.
The only country besides the U.S. to use the F-14 is Iran. When in 1976 began to receive the first aircraft of a total of 80 ordered along with 424 AIM-54A Phoenix - to cope with fast MiG-25 Foxbat of USSR who made frequent incursions into Iranian airspace. Of the 80 ordered, 79 F-14s were delivered with 270 Phoenix, the last delivery was canceled because of the Islamic Revolution in Iran. Therefore caused the disruption of relations between the two countries. Even with great difficulty to keep them able to fly. It is estimated that the Iranian air force has about 30 planes operational. According to some sources the Iranian F-14 played an important role in War Iran - Iraq, Shooting down over 30 enemy aircraft. Other sources were limited (due to the embargo on spare parts and weapons ) to use its powerful radar to illuminate targets for the fighters F-5 Freedom Fighter and F-4 Phamtom II.
F-14 design and features
F-14 aircraft has a length of 19.1m, a height of 4.8m and a wingspan of 19.55m. It can accommodate two crew members.
The maximum take-off weight of the aircraft is 33.7t , while the empty and loaded weights are 19.8t and 27.7t respectively.
The variable-sweep wing and the twin almost upright tail fins of the F-14 Tomcat give the aircraft its distinctive appearance. The variable-sweep wings are set at 20° for take-off, loitering and landing and automatically change to a maximum sweep of 68°, which reduces drag for high subsonic to supersonic speeds. The wings are swept at 75° for aircraft carrier stowage.
F-14 cockpit
 |
| Photo: deviantart |
Catseye night-vision goggles from BAE Systems have been installed in the F-14 since 1996. The F-14D front cockpit is equipped with a head-up display and two multifunction flat-screen displays. The rear cockpit for the radar intercept officer is equipped with a display that presents fused data from the AN/APG-71 radar and from the suite of aircraft sensors.
82 US Navy F-14Bs were upgraded with Flight Visions Sparrow Hawk HUD and FV-3000 modular mission display system, which improve reliability and night-vision capability. The cockpit is equipped with the NACES zero/zero ejection seat supplied by Martin-Baker Aircraft Company.
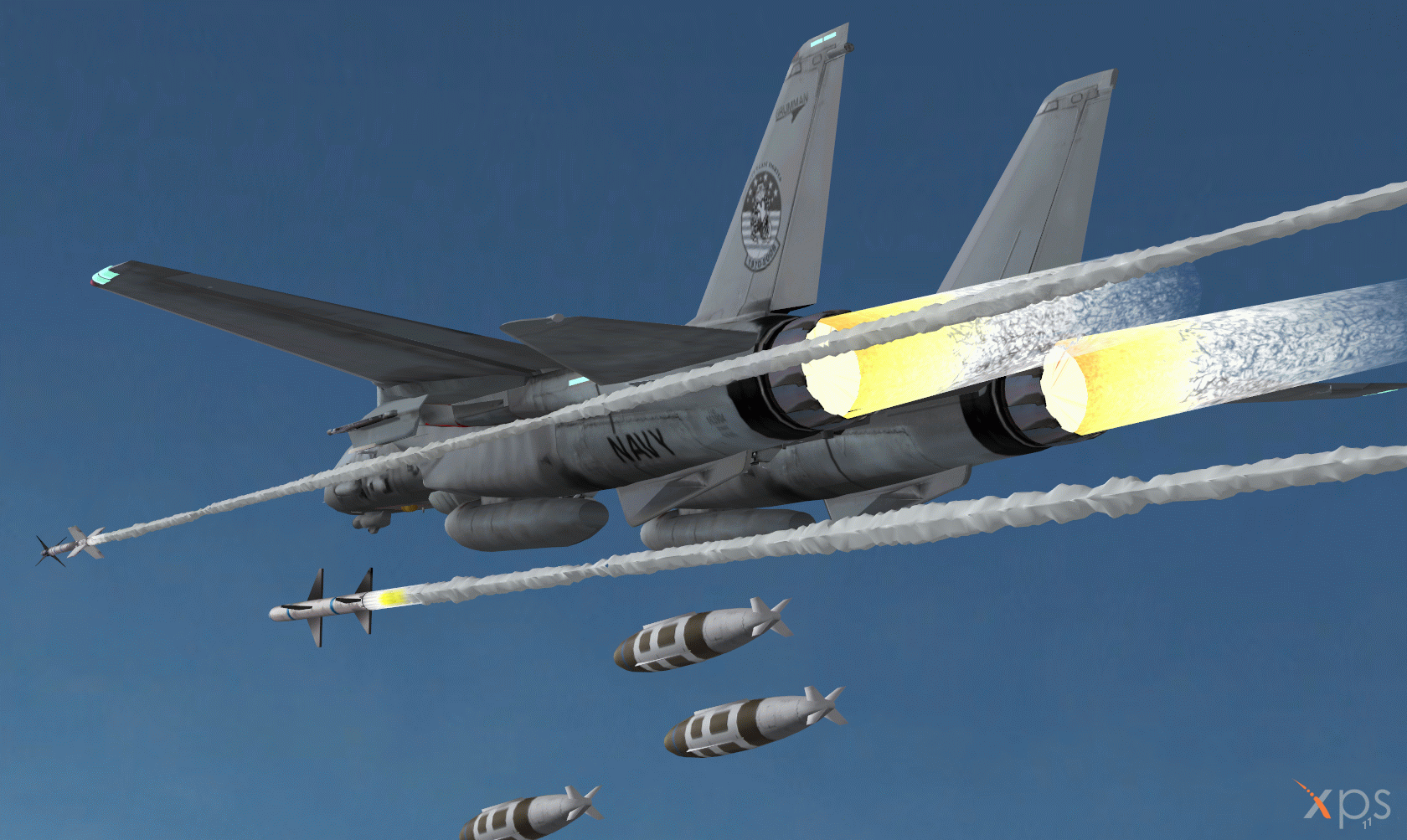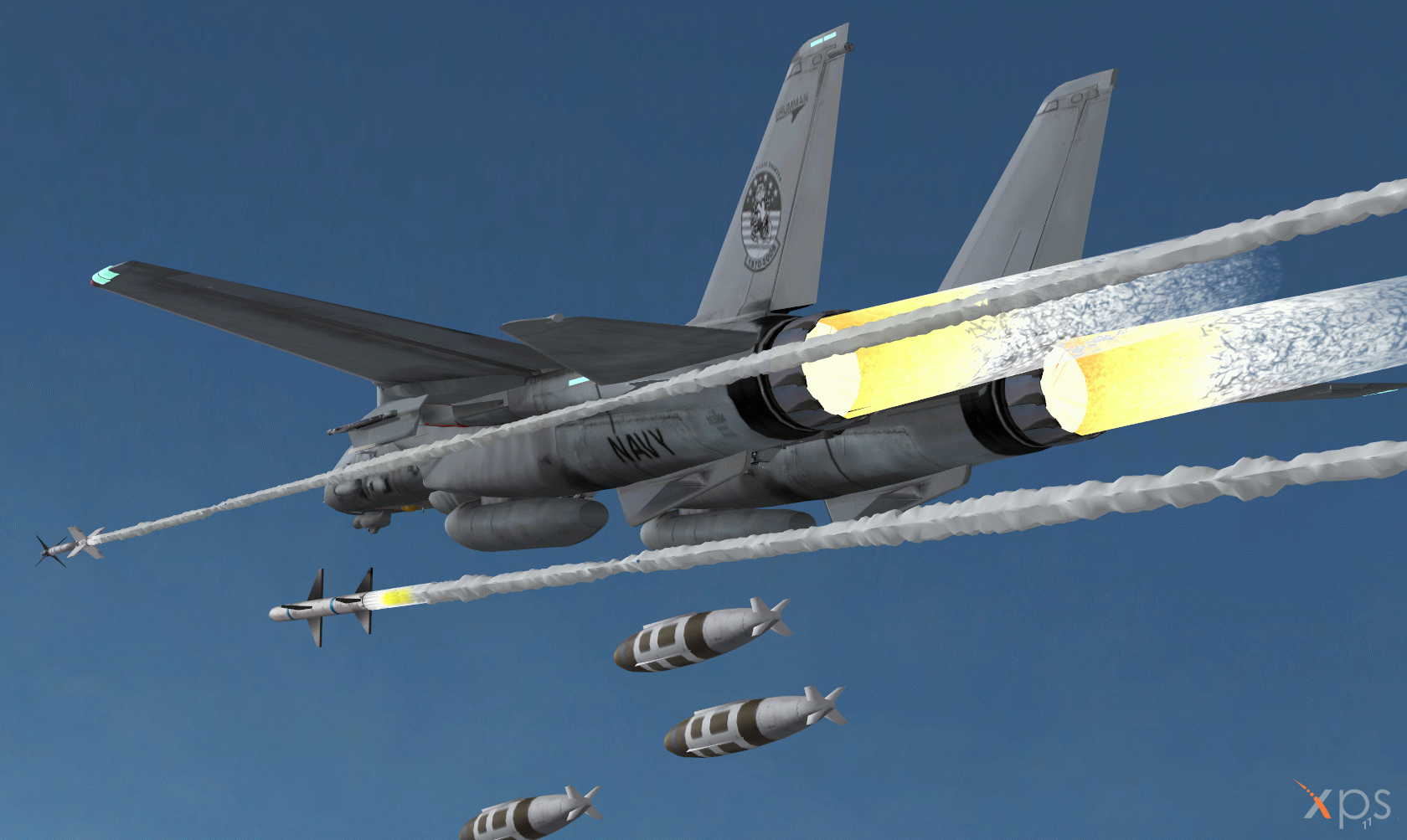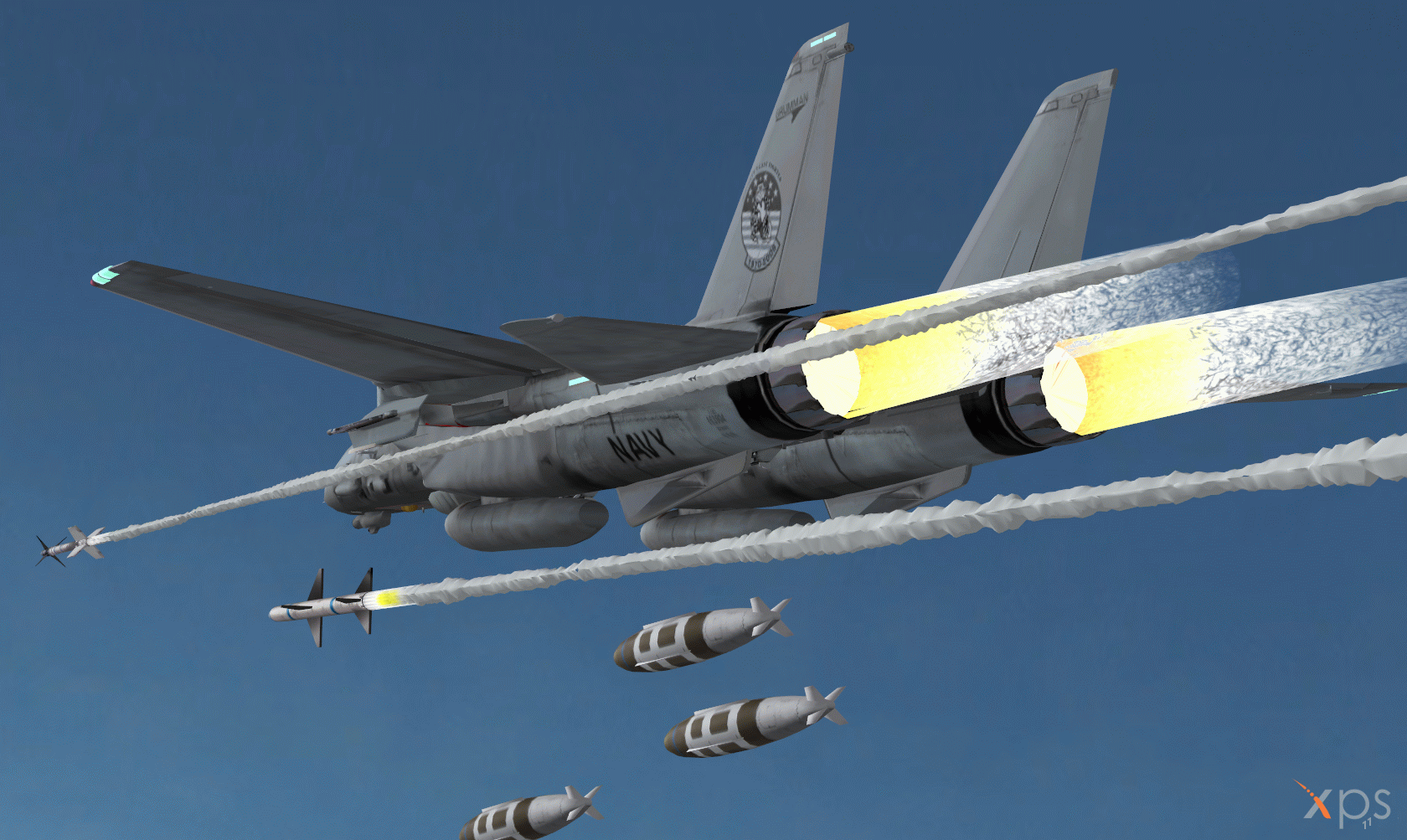
Tomcat weapons
The F-14 is armed with a General Electric Vulcan M61A-1 20mm gun with 675 rounds of ammunition, which is mounted internally in the forward section of the fuselage on the port side.
The aircraft has eight hardpoints for carrying ordnance, four on the fuselage, and two each side under the fixed section of the wings. The aircraft can carry the short, medium and long-range air-to-air missiles AIM-9, AIM-7, and AIM-54, and air-to-ground ordnance including the Rockeye bomb and CBU cluster bombs.
The Raytheon AIM-7 Sparrow is a medium-range radar-guided air-to-air missile with range of 45km. Lockheed Martin / Raytheon AIM-9 Sidewinder is a short-range air-to-air missile with range of 8km.
Raytheon AIM-54 Phoenix is a long-range air-to-air missile with range of 150km. The F-14 can carry up to six Phoenix missiles and can fire the missiles almost simultaneously at six different targets.
The F-14D can carry four joint direct attack munitions (JDAM). The first operational deployment of a precision-guided JDAM from an F-14 was in March 2003.
In 1995, the US Navy installed the Lockheed Martin LANTIRN precision strike navigation and targeting pod on the F-14. The LANTIRN targeting pod includes a dual field of view FLIR and a laser designator/rangefinder. The navigation pod also contains a FLIR and terrain-following radar. A Lockheed Martin infrared search and track system is installed in a sensor pod under the nose.
Sensors
The F-14D is equipped with a Raytheon AN/APG-71 digital multimode radar, which provides non-cooperative target identification, and incorporates low sidelobe techniques and enhanced frequency agility.
The F-14 carries a tactical air reconnaissance pod system (TARPS), which carries a recon / optical KS-87B forward or vertical frame camera, a low-altitude panoramic view KA-99 camera together with a Lockheed Martin AN/AAD-5 infrared line scanner. The pod is equipped with a digital imaging system for the transmission of near-real-time imagery to the aircraft carrier command center via a secure UHF radio data link.
To supplement TARPS, US Navy F-14s were also fitted with fast tactical imagery (FTI) line-of-sight system for targeting and reconnaissance.
How strong is the F-14 Tomcat?
The Tomcat was considered an air superiority fighter and interceptor In charge of defending the naval groups against aircraft belonging to the Soviet Navy which were armed with cruise missiles. The F-14 was equipped with long-range radar, the Hughes AN/AWG-9 which was originally developed for the F-111B, was able to detect targets the size of the bombs distances beyond the 160 km ( 100 miles ), achieving 24 targets to pursue and attack six simultaneously. Originally, the primary armament of the F -14 missile was the AIM-54 Phoenix, able to focus on a target up to 200 km ( 120 miles ), although this has been withdrawn from service on September 30 of 2004. The F -14 was the only aircraft to carry this weapon, which was designed as an integral part of the weapon system Tomcat. medium-range arms are guaranteed by AIM-7 Sparrow of semi-active radar, supported by guided missiles Infrared AIM-9 Sidewinder and an M-61 Vulcan cannon 20mm to fight savannah. The F -14 was designed with some capacity for air-ground combat, although this aspect has not been explored until the end of his career, The Tomcats are now fitted with the detection system target LANTIRN to take advantage of laser-guided bombs and other precision weapons. Some F-14s are also equipped with the system TARPS(From English Tactical Air Reconnaissance Pod System) And thus constitute the only tactical reconnaissance platform for Marine.
Why Iran Flies the F-14
Even today, the F-14 Tomcat isn’t something you’d want to see your potential adversaries flying – and yet around 40 of the aircraft are in service with the Iranian Air Force.
No, the aircraft wasn’t provided to the Islamic Republic as part of the Reagan-era Iran-Contra deal but were actually provided to Iran prior to the outbreak of the Iranian Islamic Revolution that broke out in 1978. Until that point, Iran had been a steadfast ally of the United States – and was even the second Muslim-majority country after Turkey to recognize the State of Israel.
Throughout the 1970s, the Iranian military was armed with U.S.-made equipment from M16 rifles to M60 Patton tanks, while the Imperial Iranian Air Force (IIAF), which was established in 1920, became the only military force other than the United States Navy to be equipped with the F-14 Tomcat and the AIM-54A Phoenix air-to-air missiles. Interestingly enough, the IIAF had also placed an order for more than 150 F-16 Fighting Falcon fighter aircraft in 1976. However, those deliveries were not made and instead were subsequently sold to the Israeli Air Force.
Keeping Them Flying
 |
| Photo: militarymachine |
Since the revolution, Iran has been barred from purchasing weapons, but also the components and spare parts, to maintain the aircraft. As a result the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force (IRIAF), which essentially inherited the equipment and structure of the former IIAF, had to get creative. This was complicated by the fact that the IRIAF lost many of its command officers, many of whom were considered as loyal to the Shah or pro-U.S. while other personnel was caught up in post-revolution purges.
The IRIAF was seen as ill-prepared for the Iran-Iraq War, but dozens of the F-14s were used within days of the first clashes. An Iraqi Mil Mi-25 Hind helicopter – an export version of the Soviet Mi-24 attack helicopter – was reported to have been the first “kill” by an F-14. The IRIAF aircraft performed better than expected in the war, reportedly shooting down as many as 160 Iraqi aircraft, but it took a toll on Iran.
While only 12 to 16 Tomcats were reported to have been lost in the war with Iraq, the lack of parts has been an issue. Of the 79 Grumman F-14 Tomcats originally delivered in the 1970s, only around 40 to 43 of the upgraded F-14AM are believed to be in the current inventory – and of those only 20 are believed to be fully mission capable.
When the U.S. Navy retired the F-14 in 2007, the Pentagon even made the decision to destroy all the remaining spare parts to ensure that those wouldn’t find a way to Tehran. That wasn’t entirely successful and in 2007, a Long Island man was arrested for exporting F-14 and F-5 parts to Malaysia which were destined for Tehran.
It is also worth noting that in 2010, Iran even requested the 80th F-14 that it had purchased in 1974 that was never delivered to the Islamic Revolution. Not surprisingly it wasn’t provided. Yet, it is still impressive that after more than 40 years Iran has kept the F-14s flying by cannibalizing remaining airframes and fabricating parts – proving to a few of the IRIAF’s Tomcats haven’t used up all of their nine lives.
F-14 vs. F-15: What is the Difference?
The F-14 Tomcat is a (now retired) supersonic, twin-engine, two-seat fighter aircraft, developed for use by the United States Navy. The F-15 Eagle is a twin-engine, all-weather tactical fighter used by the U.S. Air Force. The F-15 was developed as an air superiority fighter. The F-14 is used as an interceptor, for air superiority, and as a multi-role combat aircraft. It was retired by the U.S. Navy in 2006 but is currently used by the Iranian air force.
Design
The F-14 is 62 feet 9 inches long, with a spread wingspan of 64 feet and a swept wingspan of 38 feet. Its loaded weight is 61,000 pounds.
The F-15 is 63 feet 9 inches long, with a wingspan of 42 feet 10 inches. Its loaded weight is 20,200 pounds.
Cockpit
An F-15D from Tyndall Air Force Base, Florida releasing flares
The F-14 has a bubble canopy that contains two seats and allows for all-around visibility.
The cockpit of the F-15 is mounted high in the forward fuselage. It has a one-piece windshield and large canopy.
Engines
The F-14 initially used two Pratt & Whitney TF30 turbofan engines. However, as 28% of accidents were attributed to the use of these engines, they were eventually replaced by two General Electric F110 engines.
The F-15 uses two Pratt & Whitney F100 axial-flow turbofan engines with afterburners mounted side-by-side in the fuselage.
Armament
The F-14 can carry over 6,700 kg of stores under the fuselage and wings. It was fitted with an internal 20 mm M61 Vulcan Gatling-type cannon. It can also carry AIM-54 Phoenix, AIM-7 Sparrow, and AIM-9 Sidewinder missiles, and both laser-guided and unguided bombs.
The F-15 can be armed with AIM-7F/M Sparrow missiles, AIM-120 AMRAAM advanced medium-range air-to-air missiles, AIM-9L/M Sidewinder missiles, and an M61A1 20 mm Gatling gun.
Operators
F-14s are currently only used by the Iranian Air Force after the U.S. retired them from use in February 2006.
F-15s are used by the US Air Force, Israel, Japan, South Korea, Saudi Arabia, and Singapore.
Facts About The F-14 Tomcat1) The F-14 made its first flight nearly 45 years ago, on December 21, 1970 2) The F-14 was the largest and heaviest US fighter to fly from an aircraft carrier. 3) Depending on wing sweep, the fuselage provides between 40-60% of the total lift for the F-14. 4) The F-14 was the only launch platform for the AIMG-54 Phoenix missile, and it could carry up to 6 of the 1,000-pound missiles at a time. 5) The F-14 had one of the most powerful radars available at the time - it was able to track up to 24 targets at once. 6) The F-14 had incredible flexibility - it served as the Navy's maritime air superiority fighter, fleet defense interceptor, and aerial reconnaissance platform. That's three very different roles for one jet. 7) The only country currently operating the F-14 is...Iran. 8) The F-14s were exported to Iran in 1976, when the US had positive diplomatic relations with the country. 9) The F-14s wings can be 'overswept' to 75 degrees to save space on aircraft carriers. 10) During testing, an F-14 was landed on an aircraft carrier with an asymmetrical wing sweep. 11) The F-14 doesn't have ailerons. Instead, it uses wing spoilers at low speeds, and differential 'tailerons' at high speed. 12) The last F-14 combat mission was flown in 2006, but the 'Tomcat' is still one of the most unique, impressive, and fastest military aircraft ever built. |
 What is Dostarlimab: Drug of 100% Cure for Cancer What is Dostarlimab: Drug of 100% Cure for Cancer For the first time in history, a small clinical trial in the United States showed 100% eradication of the cancer disease in patients by Dostarlimab. ... |
 What is the Legal Age to Buy a Gun in America: 18 or 21? What is the Legal Age to Buy a Gun in America: 18 or 21? Possessing a gun may provide a sense of security, but to avoid any violation, law enforcement has set a minimum age limit as to who ... |
 What is Tesla ‘Optimus’ Robot: Feature, Appearance, Price and More What is Tesla ‘Optimus’ Robot: Feature, Appearance, Price and More Tesla CEO Elon Musk says the company’s robot, named Optimus, will be worth more than the car business and running within months. What is it ... |























