20 Incredible Facts About The Human Body
 |
| Top 20 amazing facts about human's body |
| Contents |
Your left and right lungs differ slightly from one another. Whereas the lung on your right side of the body is split into three lobes, the lung on your left side is divided into two lobes. Moreover, your left lung is a little bit smaller, making room for your heart.
Let’s check out top 20 amazing facts about your body, as human’s body is just as complicated as the system of a computer, and is amazing as such.
20. The average person takes 23,000 breaths a day
 |
| Photo: Getty Images |
We breathe between 17,000 and 23,000 times per day on average, yet it's likely that we don't always breathe correctly. Put it down to how we handle stress.
Our fight-or-flight reaction naturally activates when we perceive a threat, according to Dr. Katherine Rosa of the Harvard-affiliated Benson-Henry Center for Mind Body Medicine. Our hearts beat more quickly, our breathing becomes shallower, and we begin to prepare to flee from the danger.
The food you eat gives your body the glucose it needs. The cells react with the glucose when you breathe in oxygen, enabling your body to use it as energy. When your breathing is impaired, sluggishness and exhaustion are frequently present.
It is essential to breathe in oxygen to support the defense of your immune system. Superoxides, which are produced by your body when you breathe in oxygen, aid in the body's defense against viruses and bacteria.
In addition to superoxides, the nasal turbinates are important for purifying the air you breathe. The fleshy parts of the nose called nasal turbinates aid in the conduction, filtration, and humidification of the air you breathe.
19. Beards are the fastest growing hairs on the human body
 |
| Photo: IStock |
The hormone testosterone is mostly responsible for the growth of facial hair. Levels of testosterone might change. The typical range is 264 to 916 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL) for males between the ages of 19 and 38. For testosterone, this roughly corresponds to the third through 98th percentiles.
Low testosterone levels might have a negative impact on beard development. With the guidance of a doctor, taking supplements may promote beard development in men who have clinically low testosterone levels. Using supplements won't likely assist if your testosterone levels are normal.
Even if your testosterone levels are normal, you could still be genetically predisposed to have a sparse beard. Genetic differences, ethnicity, and heredity are the main causes of this.
Remember that both of your parents' genes are passed on to you. The shape of your beard may be predicted by your father's, as well as by your maternal grandfather.
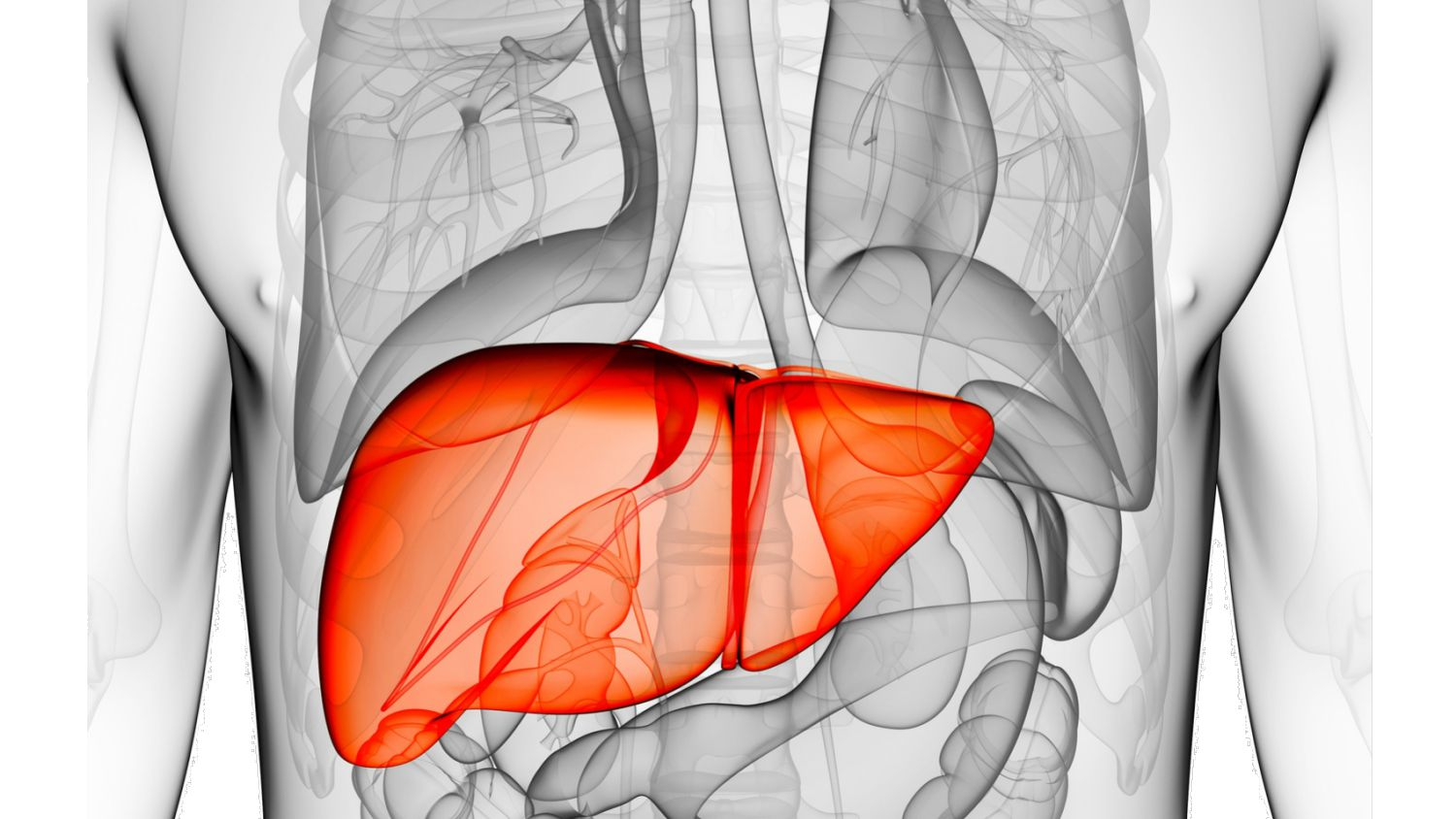
18. The human liver is responsible for more than 500 distinct processes in the body
 |
| Photo: ThoughtCo |
In the human body, the liver is both the largest gland and the largest solid organ. It performs more than 500 necessary activities.
The liver, which is regarded as a component of the digestive system, performs functions like protein synthesis, detoxification, and the generation of substances that aid in food digestion.
The liver is reddish-brown in color and has a rubbery feel. It weighs between 3.17 and 3.66 pounds (lb), or between 1.44 and 1.66 kilograms (kg). It is located behind the lungs and to the left and above the stomach.
The only organ that is heavier and larger than the liver is the skin.
The liver has two lobes: a bigger right lobe and a smaller left lobe, and it is generally triangular in shape. The falciform ligament, a band of tissue that holds it attached to the diaphragm, divides the lobes.
The exterior of the liver is covered by a layer of fibrous tissue known as Glisson's capsule. The peritoneum, a membrane that creates the lining of the abdominal cavity, is used to further cover this capsule.
This shields the liver from harm and aids in keeping it in place.
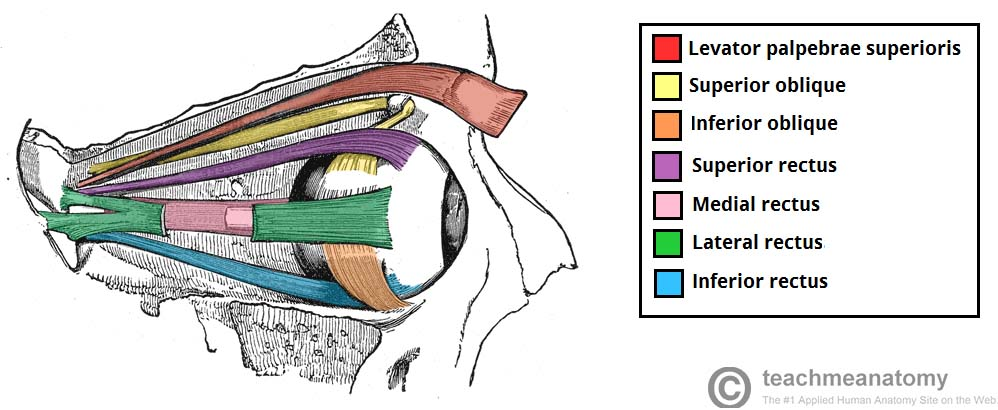
17. Extraocular muscles in the eye are the body’s fastest muscles
 |
| Photo: TeachMeAnatomy |
Extraocular muscles are responsible for moving the eye in different directions. These are the muscles that are considered the fastest, though there are other muscles in the eye.
● Intraocular muscles are those that control the expansion and contraction of the iris to allow more light in the pupil, as well as many other things. These reactions are a bit slower than the extraocular muscles, though they still happen impressively fast.
● The reason the eye is considered the fastest in the body is because many of its movements are involuntary. People can flick their eyes to the side and notice an object without consciously deciding to do so. The muscles in the eye are also about 100 times stronger than they need to be to perform their duties.
16. On a genetic level, all human beings are more than 99 percent identical
 |
| Photo: Nature |
The study of genes and their involvement in inheritance, or the process by which specific traits or conditions are passed down from one generation to the next, is referred to as genetics. Science-based investigations into genes and their consequences are part of genetics. The instructions for creating proteins are included in genes (hereditary units), which control how cells behave and how the body works. Examples of inherited or genetic illnesses include phenylketonuria (PKU), Huntington's disease, and cystic fibrosis (see Learning About Cystic Fibrosis) (Learning About Phenylketonuria).
The study of all of a person's genes (their genome), as well as how those genes interact with one another and with their environment, is known as genomics. This phrase is relatively modern. Because complex diseases like heart disease, asthma, diabetes, and cancer are often brought on by a combination of hereditary and environmental variables rather than by a single gene, genomics involves the scientific study of these conditions. New therapeutic and therapeutic options for some complex diseases are being made possible by genomics, along with novel diagnostic techniques.
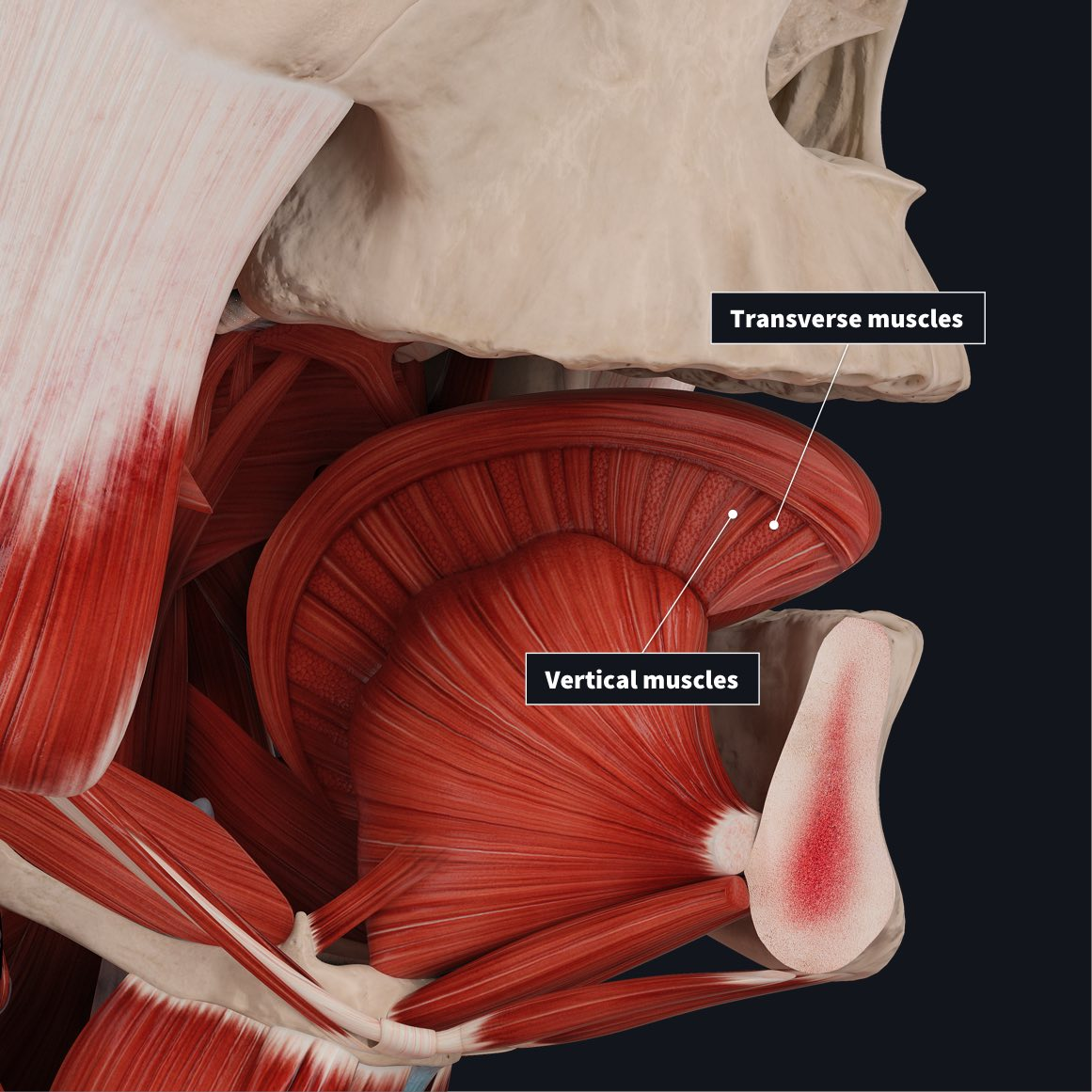
15. Your tongue is made up of eight interwoven muscles
 |
| Photo: Complete Anatomy |
According to the University of Edinburgh, the average human tongue measures about 3.3 inches (8.5 centimeters) for men and 3.1 inches (7.9 cm) for women. According to the Guinness Book of World Records, Nick Stoeberl of Salinas, California, has the tongue that is the longest in the world. It measures 3.97 inches (10.1 cm) from tip to the middle of the closed upper lip. Chanel Tapper of Los Angeles has a tongue that is 3.8 inches (9.75 cm) long, which is the record for a woman.
The tongue is highly flexible since it is made up of eight intertwined, striated muscles that may move in any direction. Muscles contain fat and glands all over them, and a mucous membrane covers the outside. The taste buds and serous glands are located in tiny nodes called papillae that cover the dorsum, often known as the top of the tongue.
While the taste buds taste food through receptors that give data to the brain, the serous glands release some of the salivary fluid. Nerve endings called receptors respond chemically to the food that is consumed. According to Encyclopedia Britannica, each taste bud has between 50 and 150 taste receptor cells. There are various reactors for various flavors.
 Top 20 Most Mythical Creatures From Legends, Folklore and Fairytales Top 20 Most Mythical Creatures From Legends, Folklore and Fairytales Check out the top 20 mythical creatures in legends, folklores and fairytales in the article below. |
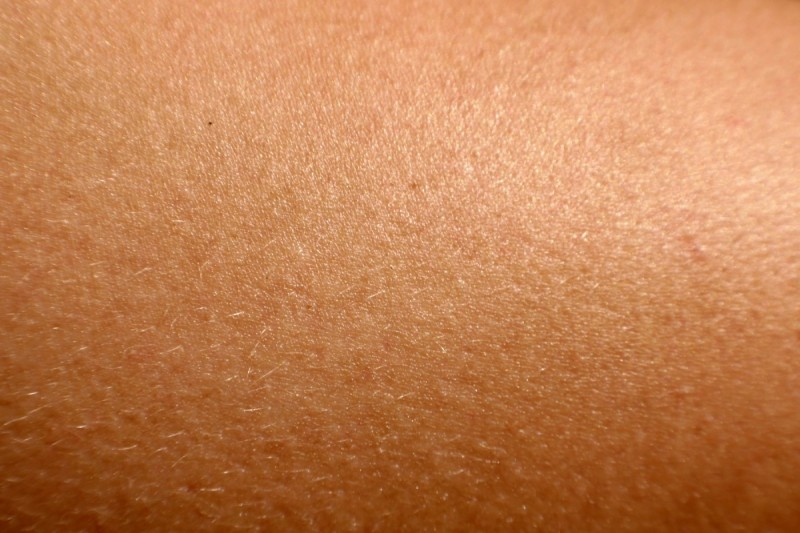
14. Skin is the human body’s largest organ
 |
| Photo: Getty Images |
Our largest organ, the skin, weighs about 8 pounds (3.6 kilograms) and occupies 22 square feet (2 square meters) in an adult. This fleshy covering accomplishes much more than just keeping us looking presentable. In fact, without it, we would essentially vanish.
Skin protects the body from temperature extremes, toxic substances, and the sun's harmful rays by acting as a waterproof, insulating covering. It also produces vitamin D, which is necessary for turning calcium into strong bones, and antimicrobial chemicals that fight illness. In addition, the skin serves as a massive sensor loaded with nerves that keeps the brain connected to the outside environment. In allowing us to move freely, skin demonstrates its incredible versatility.
13. If all the blood vessels in the human body were laid end to end, they would encircle the Earth four times
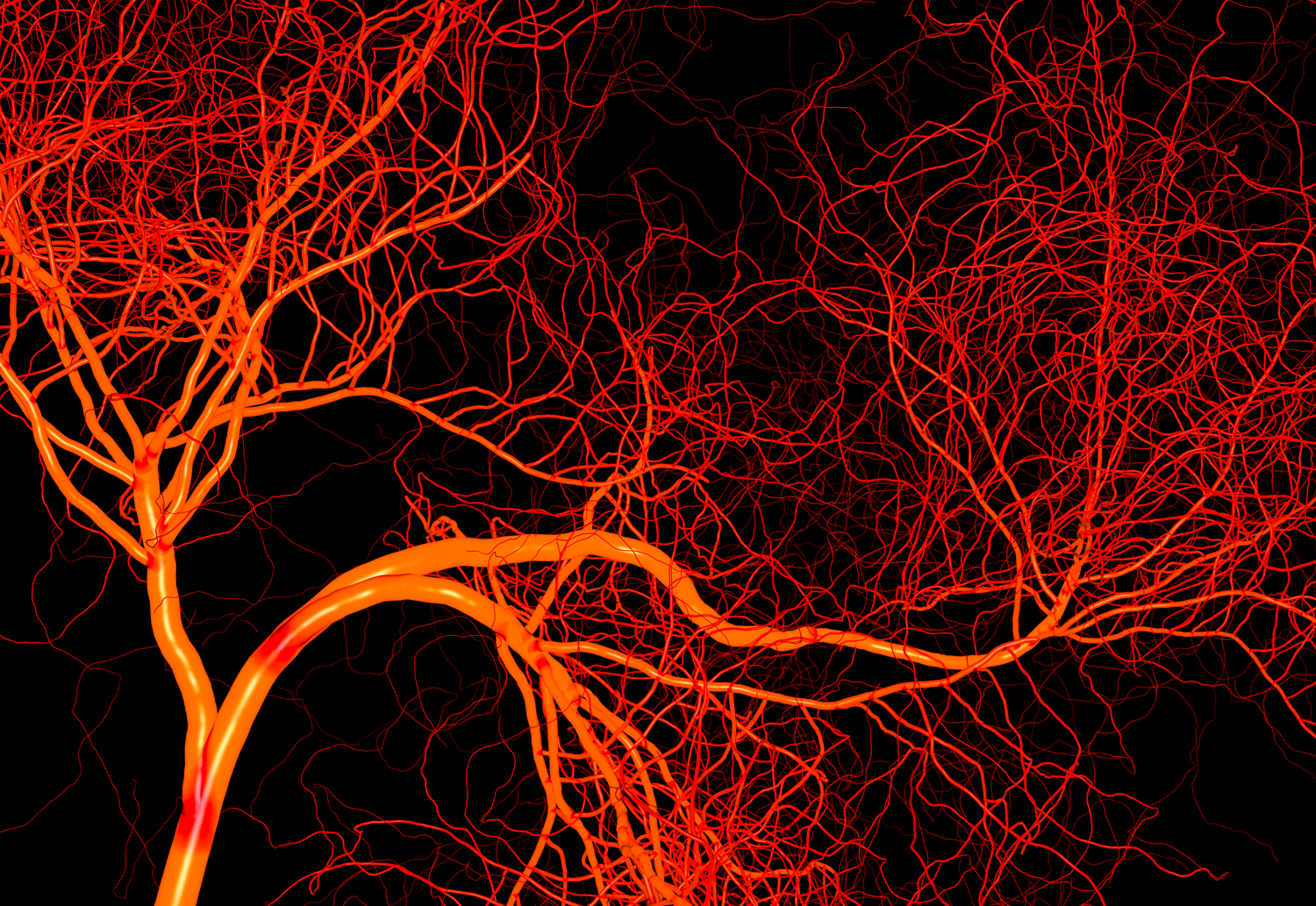 |
| Photo: The Franklin Institute |
The human circulatory system is made up of three different kinds of blood vessels: capillaries, veins, and arteries. All three of these veins deliver nutrients, hormones, oxygen, and blood to organs and cells. While veins return oxygen-depleted blood from tissues back to the heart, arteries transport oxygenated blood from the heart to the body's tissues. Veins accomplish this directional flow in part thanks to unique valves. The arteries and veins are joined by microscopic blood vessels called capillaries, which allow nutrients in the blood to diffuse to the body's tissues.
It is believed that if a human child's arteries, veins, and capillaries were extended end to end, they would wrap around the Earth around 2.5 times (the equivalent of about 60,000 miles). According to Eidson, the blood vessels in an adult human would travel 100,000 miles, or four times around our planet.
12. The big toe is one of the most important structural parts of the body
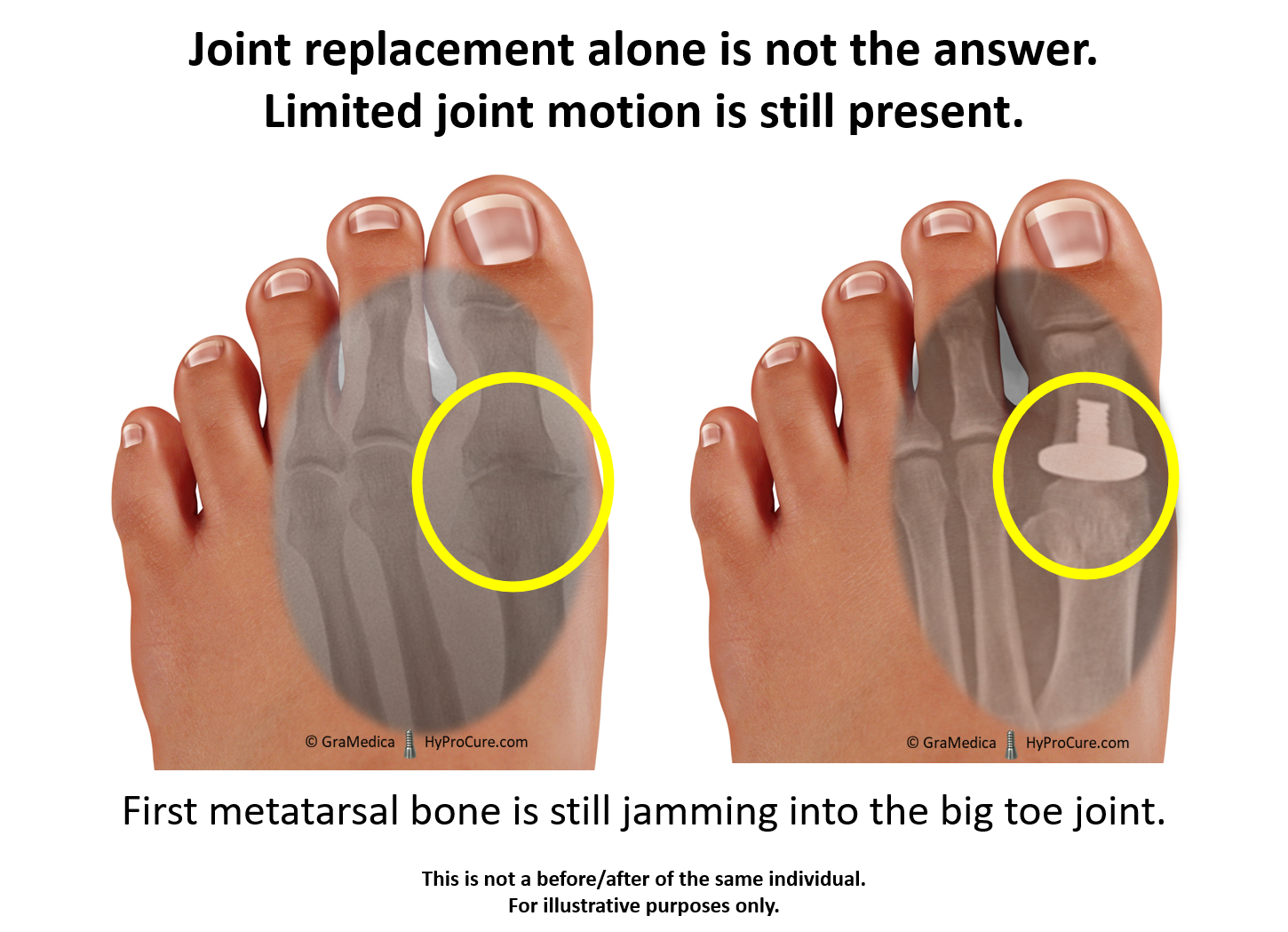 |
| Photo: HyProCure |
Each foot is made up of 26 bones, 30 joints and more than 100 muscles, tendons and ligaments, all of which work together to provide support, balance and mobility.
Joints in the feet are formed wherever two or more of these bones meet. Except for the big toe, each of the toes has three joints, which include:
• Metatarsophalangeal joint (MCP) – the joint at the base of the toe
• Proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) – the joint in the middle of the toe
• Distal phalangeal joint (DP) – the joint closest to the tip of the toe.
Each big toe has two joints:
• Metatarsophalangeal joint
• Interphalangeal joint
The surfaces of the bones where they meet to form joints are covered with a layer of cartilage, which allows them to glide smoothly against one another as they move. The joints are enclosed by a fibrous capsule that is lined with a thin membrane called the synovium, which secretes a fluid to lubricate the joints.
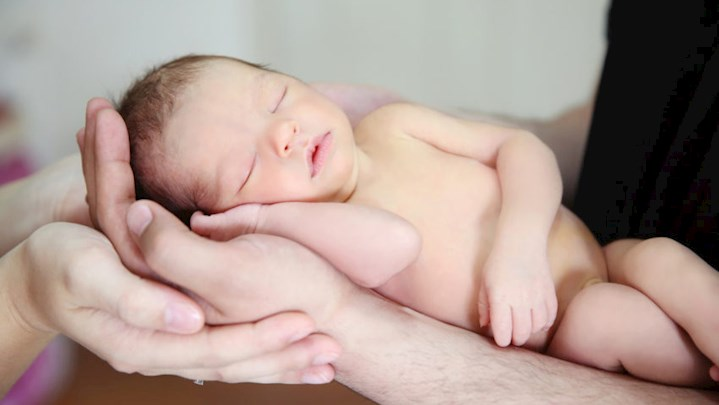
11. During the first month of life, an infant is learning so many new things that the number of connections, called synapses, between brain cells increases from 50 trillion to 1 quadrillion
 |
| Photo: Getty Images |
A baby's brain is born with 100 billion neurons, virtually all of the brain's future neurons, or almost as many nerve cells as stars in the Milky Way. Three weeks after conception, the prenatal process of the brain's development begins. The brain creates trillions more "synapses" (connections between brain cells) and neurons than it need before birth. The brain goes through a number of remarkable changes in the first few years of life.
The neurons and certain connections in the brain are present at birth. More and more synapses are formed as the neurons become older. At birth, there are 2,500 synapses per neuron; by the age of two or three, there are approximately 15,000 synapses per neuron. The brain naturally removes connections that are infrequently or never used as part of brain growth.
"Windows of opportunity" are critical junctures in a child's life when certain kinds of learning occur. For instance, researchers have found that between 2 to 4 months of age, vision-related neurons start firing rapidly, reaching a peak at 8 months. Babies start to notice the world during this time, which is not a coincidence.
 Top 10 Most Mysterious People In The World Top 10 Most Mysterious People In The World There are things on earth that we have never found out, as for the list of the 10 most mysterious people in the world right ... |
10. Fingernails and hair are made out of the same substance – keratin
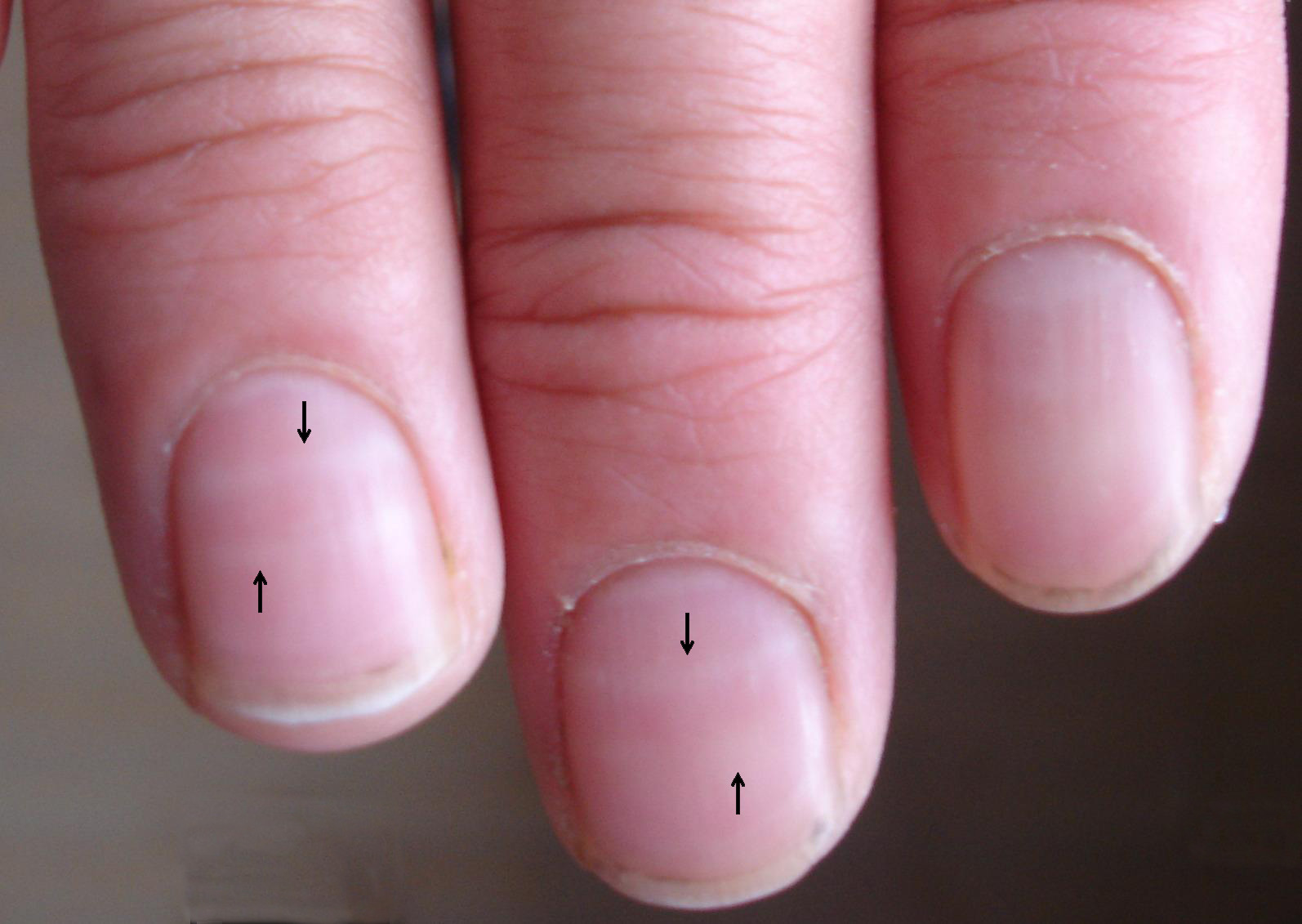 |
| Photo: Wiley Online Library |
Keratin is a strong protein that is used to create fingernails. (Keratin is used by animals for making their hooves, horns, and claws; it is not just used by primates.)
The outer layer of skin and hair are both strengthened by keratin. Because the keratin strands that make up fingernails are more dense, they are harder than hair and skin (packed together). Also water-repellent is keratin. Because of this, when you swim or take a bath, you don't bloat up like a sponge!
9. The satisfying sound of cracking your knuckles comes from gas bubbles bursting in your joints
 |
| Photo: Wikipedia |
Why do you hear your joints snap, crackle, and pop? Dr. Robert Klapper, an orthopaedic surgeon and co-director of the Joint Replacement Program, will explain.
According to Dr. Klapper, the noise of cracking or popping in our joints is actually the result of nitrogen bubbles bursting in our synovial fluid.
According to Dr. Klapper, synovial fluid reduces friction and protects our cartilage by lubricating your joints like the oil in an automobile engine. It typically takes 20 minutes for the nitrogen bubbles in the synovial fluid to reform in your joints before they can crack once more.
The 20-minute pause, during which gas bubbles are re-forming in the synovial fluid, may be a draw of knuckle cracking. During that time, you might feel more relaxed, as if your joints are no longer under pressure.
But the majority of the satisfaction is psychological.
According to Dr. Klapper, "feeling good after cracking your knuckles is a psychological experience."
8. The human nose can detect about 1 trillion smells
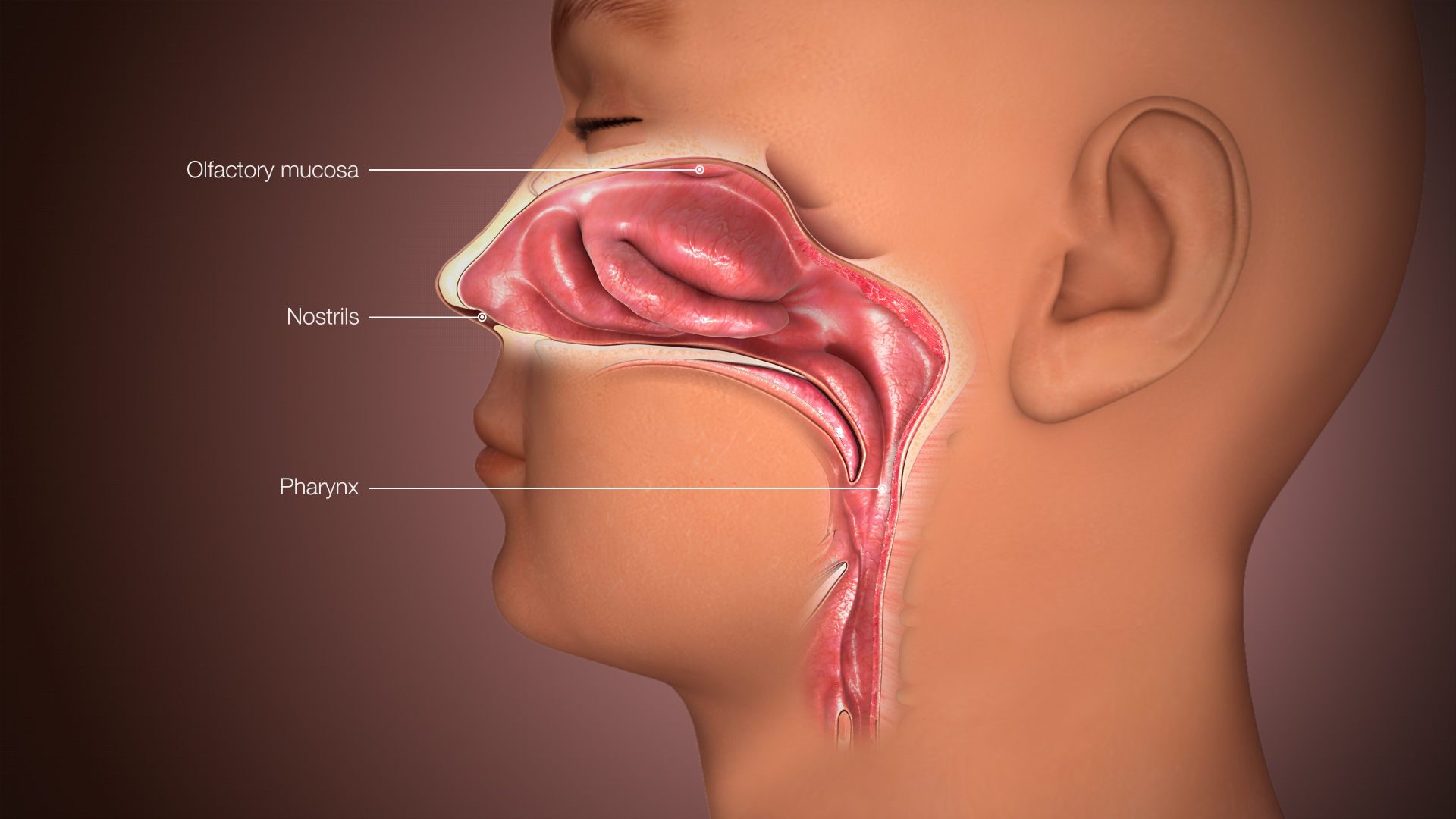 |
| Photo: Wikiwand |
Measurements of sight and hearing are simple. For instance, the wavelength of light affects color, whereas certain noise frequencies determine sound.
However, smell is affected by millions of different chemicals, each of which activates nose receptors in a different way. Smell is not just about being able to detect energy. For instance, 275 different chemicals combine to create the distinctive scent of a rose.
The Rockefeller University's Smell Study researcher Andreas Keller and his team chose 128 compounds in an effort to determine the lower limit of the human olfactory system because they knew it would be impossible to measure every known odor-producing chemical.
More than the 128 we used, there are undoubtedly millions or billions of different odorous molecules. How they combine is unknown and a subject of ongoing research, according to Keller.
7. You have two kidneys, but only one is necessary to live
 |
| Photo: iStock |
Your kidneys filter out waste and extra fluid from your blood so it can be excreted from your body in your urine.
One kidney can filter enough blood to keep your body functioning normally. This is why you can survive and be healthy with only one kidney.
The recommendations for healthy living if you have only one kidney are basically the same for people with two kidneys. They include:
• eating a healthy diet
• exercising regularly
• maintaining a healthy weight
• staying hydrated
• maintaining a normal blood pressure and blood sugar (managing high blood pressure or diabetes if they develop)
• seeing your doctor regularly for checkups
In addition, if you have a solitary kidney, you should be extra careful about keeping it functioning well. This includes:
• protecting it from injury
• avoiding medications that can be harmful, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
Reasons for having one kidney
There are a number of reasons you may have just one kidney. These include the following:
You were born with only one kidney.
One of your kidneys was removed (nephrectomy) to treat a medical condition or injury.
You’ve had a kidney transplant.
You donated a kidney to someone who needed a transplant.
You can also have two kidneys but only one that functions, which is the same as having a single kidney.
One big difference in outcomes of having one kidney relates to whether you were born with just one kidney versus having lost or donated one.
For those born with one kidney, the solitary kidney does the job of both kidneys from day one, often growing into a larger and better functioning kidney.
When one kidney is removed or donated, the other kidney does not compensate, and therefore the overall kidney function is decreased by half.
 Top 20 Most Amazing Stories Of Survival In The World Top 20 Most Amazing Stories Of Survival In The World If you’re a fan of outlandish survival-themed movies and novels, then you already know how entertaining these fictitious adventures can be. Check out top 20 ... |
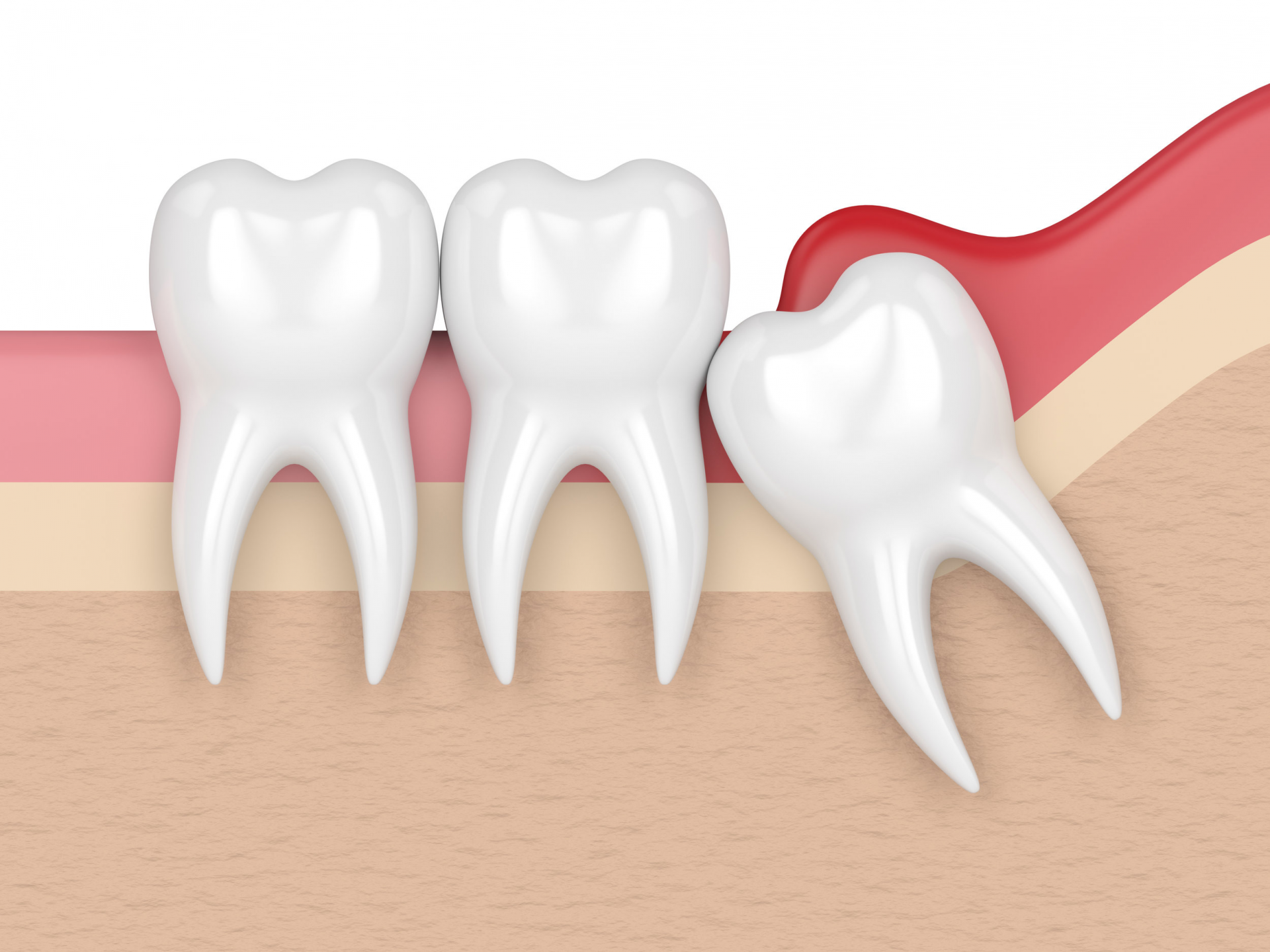
6. Wisdom teeth serve no purpose
 |
| Photo: Adobestock |
Humans no longer require wisdom teeth, according to anthropologists, so some people may never develop them. It's possible that wisdom teeth will become completely unnecessary, just like the appendix did. Some researchers wouldn't be shocked if people stopped having wisdom teeth in the future.
However, most adults do get their wisdom teeth due to genetics. According to one studyTrusted Source, at least 53% of people had at least one wisdom tooth erupt. They were more common in men than in women.
Your wisdom teeth may not all be visible, but that doesn't mean they aren't. Sometimes wisdom teeth never fully develop and never show. If you have wisdom teeth buried under your gums, an X-ray can confirm this.
Whether or not they are visible, wisdom teeth can harm one's oral health. Impaction refers to wisdom teeth that have not yet broken through the gums. This can occasionally lead to even worse issues than obvious wisdom teeth.
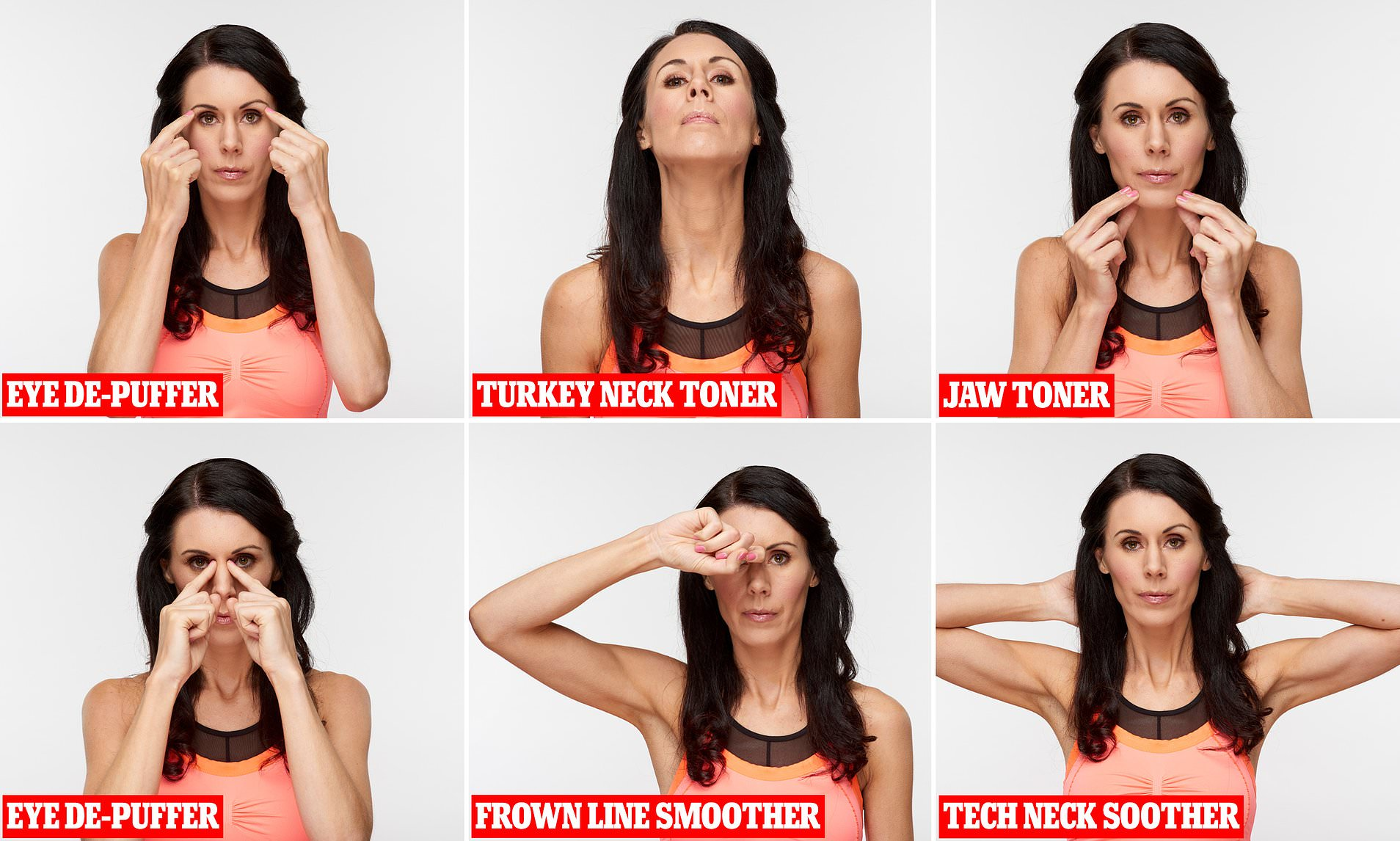
5. You use an average of 43 muscles in your face when you frown
 |
| Photo: Daily Mail |
When we make facial expressions, we're essentially sending out a packet of data that other people can pick up on, decode, and interpret. We can convey thousands of different messages by contracting or expanding our facial muscles in various combinations and degrees, which give clues to our general emotional state, our short-term feelings about our immediate environment, our mental health, our personality and mood, our physical health, our creditworthiness, and whether or not we think others are creditable.
Whether intentionally or unintentionally, the smile is perceived as a friendly gesture in all cultures, especially when it is used to greet someone. The general consensus is that frowns also convey sadness or disapproval.
The majority of the face's 43 muscles are managed by the seventh cranial nerve (also known as the facial nerve). Just in front of the ears, a nerve leaves the cerebral cortex and emerges from the skull. Then, it divides into the temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, and cervical branches. These branches energize muscles that enable the face to contort and twist into a variety of expressions and reach various parts of the face.
Nobody has, however, really figured out exactly how many muscles are required to smile or frown; one person's smile is another person's smirk. Additionally, not everyone has the same number of facial muscles; some people actually have 40% fewer facial muscles than others, allowing for a wider range of expression.
4. In one hour, your heart produces enough energy to raise a ton of steel 3 feet off the ground
 |
| Photo: Pixabay |
Your heart generates enough energy in an hour to lift a ton of steel three feet off the ground.
When you frown, your face uses 43 muscles on average. To smile, only 17 muscles are required.
Red blood cells travel extensively. The cells travel through the body approximately 250,000 times after being formed inside the bones, covering a distance of 60,000 miles each time, before dying 120 days later in the bone marrow.
There are 206 bones in the adult human body, and the hands and feet account for more than half of them.
In a typical person's lifetime, the heart beats 3 billion times on average.
3. Goose bumps evolved to make our ancestors’ hair stand up, making them appear more threatening to predators
 |
| Photo: Getty Images |
Goosebumps are a physiological condition that we inherited from our animal ancestors; while it was helpful for them, it is not very helpful for us. The term "goosebumps" refers to small skin growths that resemble the skin of a bird after the feathers have been removed. (Thus, we could just as easily refer to them as "turkeybumps" or "duckbumps.") These lumps are the result of tiny muscles that are affixed to each hair contracting. Each time a muscle contracts, the skin's surface depresses slightly, causing the surrounding area to protrude.
Anytime the body feels cold, the contraction also causes the hair to stand up. This rising of hair expands the insulating layer of air in animals with thick coats of hair. More heat is retained the thicker the hair layer. People cannot experience this reaction because we lack a hair coat, but goosebumps still happen.
2. It’s possible to brush your teeth too aggressively
 |
| Photo: Getty Images |
Too much tooth brushing refers to both "how much" and "how well" you brush your teeth. You run the risk of developing dental abrasion, tooth sensitivity, and gum recession in your mouth if you brush excessively or compulsively.
According to the USC Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry, dental abrasion describes the mechanical forces from a foreign object that cause tooth structure to be lost. In this instance, vigorous brushing wears down the tooth enamel and eventually the softer cementum and dentin structures. Abrasion can be recognized by looking for worn, shiny, and frequently yellow or brown spots on the tooth close to the gum line. Another indication of abrasion is notching, which is a wedge- or V-shaped indentation of the tooth along the gumline.
The nerve endings in the dentin layer either become exposed or are brought close enough to the surface to cause tooth sensitivity when toothbrush abrasion wears away the tooth enamel. When your teeth are exposed to hot, cold, sweet, or sour stimuli or when you brush your teeth, this sensitivity could make you feel uncomfortable or in pain.
Your gums may also start to recede if you keep brushing too vigorously and incorrectly. The softer cementum of the root is exposed and vulnerable when this occurs. In addition to being more susceptible to decay, exposed cementum is also easily worn away and notched, creating sensitivity and pain.
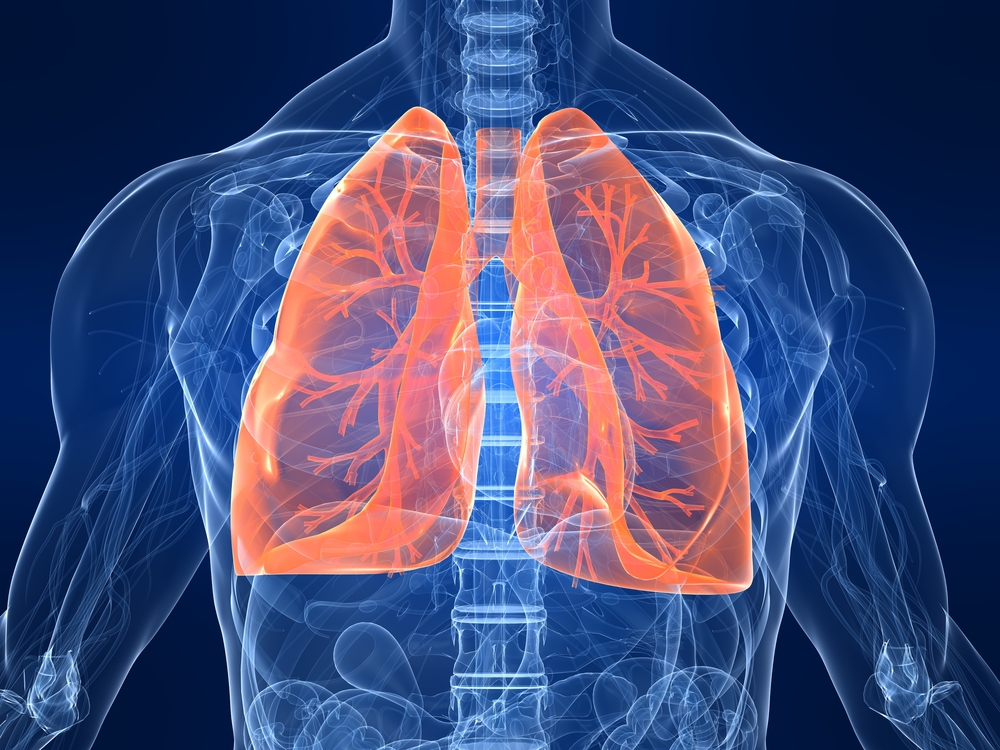
1. Adult lungs have a surface area of around 70 square metres
 |
| Photo: Live Science |
The tiniest airways in the respiratory system are called alveoli, which are tiny balloon-shaped structures. Because the alveoli are so thin, oxygen and carbon dioxide (CO2) can move between them and blood vessels known as capillaries fairly easily.
The number of alveoli per cubic millimeter of lung tissue is approximately 170. In the human lungs, which have a surface area of about 70 square meters, there are literally millions of cells, though the exact number varies from person to person.
The respiratory system, which begins when we inhale air through our mouth or nose, ends at the alveoli. The oxygen-rich air passes through the trachea and enters either the right or left bronchus before entering one of the two lungs. Following the alveolar duct, the air is then directed through progressively smaller bronchioles before entering a single alveolus.
The fluid layer known as a surfactant that lines alveoli helps to keep the air sac's surface tension and shape. More surface area is available for oxygen and CO2 molecules to pass through when surface tension is kept constant.
 Top 20 Most Mythical Creatures From Legends, Folklore and Fairytales Top 20 Most Mythical Creatures From Legends, Folklore and Fairytales Check out the top 20 mythical creatures in legends, folklores and fairytales in the article below. |
 Top 20 Tiny Tattoos for Women/Girls First Time Top 20 Tiny Tattoos for Women/Girls First Time Want to have a tiny tattoo but this is your first time? This list will be a suggestion for women and girls who want to ... |
 Top 20 Weird Things Humans Do Every Day Top 20 Weird Things Humans Do Every Day The human species is pretty strange, and we have a ton of day-to-day activities that are super weird when you really think about them. |
 Top 20 Most Amazing Stories Of Survival In The World Top 20 Most Amazing Stories Of Survival In The World If you’re a fan of outlandish survival-themed movies and novels, then you already know how entertaining these fictitious adventures can be. Check out top 20 ... |























